The origins of Agile software development
The values and principles of Agile came out of the software development community, specifically from a group of software engineers who worked with so-called lightweight development practices. Their overarching goal was to eliminate the negative aspects of the traditional software development model.
The traditional model was project-based, plan-driven, and followed a linear-sequential software development life cycle (SDLC) approach. A graphical depiction of the traditional model displays a stepwise approach to development through a linear-sequential process, as a single development cycle, thus leading to the name "Waterfall approach."
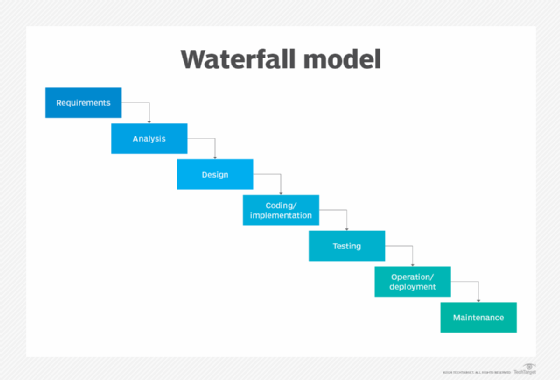
There are multiple problems with the Waterfall model. For example, the linear-sequential process needlessly extended the length of the overall development and project delivery cycles. The project-based nature of the traditional model is predicated on an idea that customers know upfront what their needs and priorities are for the entire project period, which is seldom the case.
Given its plan-driven nature, which drives product delivery schedules and budgets, project teams are reluctant to change the original plans and schedules even when customer priorities and needs change. Moreover, the late-stage testing approach makes it a complicated, time-consuming and costly process to find and fix bugs, or address performance issues.
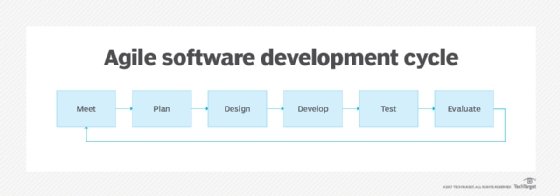
Lightweight but powerful in contrast, the lightweight software development methodologies delivered updates in a continuous and customer-centric manner, adding incremental value rapidly through frequent releases. The iterative development approach enables more frequent testing on smaller sections of code, minimizing the impacts of bugs and defects while improving overall development throughput and efficiencies.
The lightweight approaches generally install small, autonomous and fully self-contained teams that minimize communications, work integration, and dependency issues associated with managing larger teams or organizations. Instead of excessive documentation and reports, the lightweight methodologies provided visibility on priorities and progress through publicly displayed charts and lists, such as product backlogs, burndown and burnup charts, velocity charts and Kanban boards.
All of this works well in relatively small product development activities. Among the lightweight methodologies, Scrum emerged as the leader in Agile-based software development at the small team level. It retains its leadership position in that area to this day. But it wasn't long before organizations attempted to employ the values and principles of Agile on more extensive product development requirements, and across both value creation (i.e., development) and value delivery (i.e., customer-facing and support) activities.
The empiricism and small team models within the Scrum Framework are scalable, as teams of teams. But large organizations represent complex systems that required additional ways of thinking to deal with network density issues that make communications, integrations and dependencies much more challenging to manage. The question then becomes, how to do it?
Scaled Scrum and Lean-Agile strategies
As it turns out, several strategies evolved to enable agility across large product organizations and also to support enterprise-wide business agility initiatives. Some scaling strategies deal more strictly with large software development projects. Others incorporate systems thinking and lean development practices to implement business agility across all value creation and value delivery activities on an enterprise scale.
A shortlist of leading scaled Scrum and Lean-Agile practices include the following:
- Scrum-of-Scrums: The original Scrum scaling strategy as a team of teams.
- Scrum-At-Scale: An extension to the Scrum Guide that scales the basic Scrum-of-Scrums concepts enterprise-wide and across business domains with minimum viable bureaucracy (MVB) via scale-free architectures.
- The Nexus Framework: The software developer's extension to the Scrum Guide that implements Network Integration Teams (NIT) to manage cross-team dependency, integration and synchronization issues on multiteam product development efforts.
- Large Scale Scrum (LeSS): Another scaled-Scrum approach that helps coordinate the activities of multiple teams around features (LeSS Framework) and requirements areas (LeSS Huge Framework), working in collaboration to develop large and complex software-enabled products.
- Disciplined Agile (DA): A Lean-Agile approach to development that provides six product development lifecycles, numerous process guides, and hundreds of potentially useful techniques that allow teams to choose their preferred way of working based on their unique business and organizational needs and situations.
- Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe): With four configurations, a Lean-Agile approach for large organizations working on large-scale product development efforts that can leverage their economies of scale as strengths to provide greater efficiencies and yet incorporate Lean-Agile practices to enable business agility on an enterprise scale.
At the time of this writing, the Scaled-Agile Approach (SAFe) is the leader among the scaled-Agile approaches. But business agility is a relatively new field, and time will tell which practices stay at the top of the leaderboard.
Scaling to achieve business agility
Our modern digital economy drives today's competitive landscape, and organizations need to be agile at all levels of their businesses to compete effectively. Therefore, despite its early origins within the software industry, the values and principles of agile must apply to all value stream activities across an enterprise. In short, this means all aspects of a business must have the ability to respond quickly with frequent improvements that deliver customer-centric value at the lowest possible cost.
At one level, this shouldn't be a surprise. Software and computing systems add useful functionality to products while also making it easier and quicker to add new features. Those two capabilities alone change the competitive landscape dramatically. However, if we only apply agile practices to software development activities, the rest of the organization will lag and fail to deliver the new capabilities to their markets in a timely and cost-efficient manner. So, we must expand our thinking about applying Agile's values and principles on a larger scale to enable enterprise-wide business agility.
Business agility is the ability of an organization to rapidly evaluate alternatives and competitively respond to changes driving both a business and its industry, and do so from a customer-centric and value-added perspective. Installing business agility practices across an organization helps it respond appropriately to competitive drivers while simultaneously keeping a customer-centric approach across the enterprise. In short, business entities must evolve all their value creation and delivery strategies, taking a systems-level view, to stay competitive in our fast-paced and digital-enabled world.
Organizations that make ad hoc or opportunistic changes, without looking at the systemic impacts, fall into a trap called local optimizations. The organization can expend much time, effort and money and not achieve any significant gains. Instead, the enterprise must take a holistic view to optimize and streamline all its value streams. Systems thinking is the essence behind lean development, which is an essential component of any serious attempt at becoming agile on an enterprise scale.
Modern Scrum and Lean-Agile practices aim to achieve enterprise-wide agility by allowing synchronization and coordination between all the value stream activities across an enterprise to produce high-quality and profitable products. The same concepts equally apply to nonprofits and government agencies that seek to deliver high-quality and customer-centric services at the lowest possible costs.
No one should think it's an easy task to obtain business agility on an enterprise scale. It takes executive-level commitments, strategy, structural changes, a lot of trial and error, and leadership. Ultimately, success breeds success, and organizational culture evolves incrementally to support the most effective business strategies.
Editor's note: Readers who want to dive deeper can read Cecil Rupp's book, Scaling Scrum Across Modern Enterprises: Implement Scrum and Lean-Agile techniques across complex products, portfolios, and programs in large organizations. The book is available via Amazon through Packt Publishing and you can read a chapter here.