
Getty Images
Cryptocurrency ETFs explained
Cryptocurrency evolved from a fiat alternative to speculative investment after the SEC's approval of spot Bitcoin ETFs. Discover ETF types, pros, cons and investor alternatives.
Cryptocurrency has long been positioned as an alternative to traditional fiat currency, providing individuals and organizations with an alternative form of money.
While the original promise of cryptocurrency was as a replacement or alternative to fiat currency -- such as the U.S. dollar -- the reality is that it has seen the most promise and activity as a speculative form of investment. The rise in value of different cryptocurrencies, most notably Bitcoin has led to growing investor interest in the digital currency.
The value of Bitcoin is extremely fluid, with pricing changing dramatically over time. In July 2021, Bitcoin was valued at approximately $29,796. In contrast, Bitcoin topped $120,000 on July 14, 2025.
Investors have had numerous ways they could acquire and invest in cryptocurrency, including buying cryptocurrency directly. One of the easiest ways, however, didn't emerge until Jan. 10, 2024, with the regulatory approval from the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) in the U.S. for spot Bitcoin exchange-traded funds (ETFs), providing an accessible and simplified approach for investors of all levels to get into the cryptocurrency market.
What are cryptocurrency exchange-traded funds (ETFs)?
At the most basic level, a cryptocurrency ETF is a broad term that refers to any ETF that provides exposure to cryptocurrencies or related cryptocurrency assets. Cryptocurrency ETFs can include various types of assets, such as actual cryptocurrencies, futures contracts on cryptocurrencies, or stocks of companies involved in the cryptocurrency industry.
Cryptocurrency ETFs can offer exposure to a single cryptocurrency, such as Bitcoin, or a basket of different cryptocurrencies such as Ethereum. The related concepts of spot ETFs and futures ETFs are also commonly included under the overall cryptocurrency ETF category.
Spot ETFs invest in actual cryptocurrencies and track their value. With spot cryptocurrency ETF, investors can participate in the rise or decline in value of a cryptocurrency, without buying and holding the actual cryptocurrency via an exchange.
Unlike a spot cryptocurrency ETF, which tracks the actual current value, a futures ETF tracks the prospective value of a cryptocurrency with a futures contract. A futures contract is a financial instrument that provides an option to the contract holder to buy or sell an asset for a certain price, by a specific date. A futures contract does not convey ownership of the asset itself.
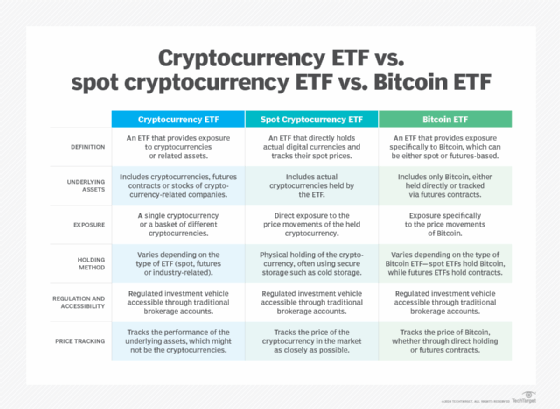
Cryptocurrency ETF vs. spot cryptocurrency ETF vs. Bitcoin ETF
Understanding the difference between the various subcategories and types of cryptocurrency ETFs can be confusing. The chart below provides a simplified explanation of each type of cryptocurrency ETF.
How do ETFs work?
An ETF is a form of equity investment listed on a public stock exchange such as the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) or Nasdaq.
An ETF trades on a public exchange similar to an individual stock. However, instead of simply being a financial vehicle to track the performance of a single company, an ETF generally holds a group of different assets or individual stocks. Some ETFs track specific industries, such as banking or healthcare, as well as ETFs that track a stock market index, such as the S&P 500.
ETFs generally have some financial overhead, which is integrated into the cost of the ETF as the management expense ratio.
An ETF is similar to a mutual fund, which also holds a group of stocks or equities. However, a mutual fund is not traded on a public stock exchange, whereas an ETF is traded on stock exchanges, making it more accessible to acquire and trade.
Cryptocurrency stock ETFs
A cryptocurrency stock ETF can hold and invest in any number of different cryptocurrencies and related assets such as financial activities on a blockchain.
There is a growing number of cryptocurrency ETFs in the market, following are five popular examples, based on assets under management (AUM), which provide a measure for the financial size of a given ETF.
- Amplify Transformational Data Sharing ETF (NYSE:BLOK). Invests in companies involved in blockchain technology and cryptocurrency-related businesses.
- Bitwise Crypto Industry Innovators ETF (NYSE:BITQ). Provides exposure to cryptocurrency mining, exchanges and other cryptocurrency-related services.
- First Trust SkyBridge Crypto Industry and Digital Economy ETF (NYSE:CRPT). Invests in companies involved in the cryptocurrency industry and digital economy.
- Global X Blockchain ETF (NASDAQ:BKCH). Invests in companies that are developing or utilizing blockchain technology.
- VanEck Digital Transformation ETF (NASDAQ:DAPP). Invests in companies involved in digital assets, blockchain technology and digital infrastructure.
Bitcoin ETFs
Bitcoin ETFs are ETFs that invest only in Bitcoin.
Bitcoin ETFs can refer to any exchange-traded fund that provides exposure to Bitcoin and is often interchangeably used with the term Bitcoin futures ETFs. Before January 2024, this class of ETFs did not hold Bitcoin directly and was largely about investing in Bitcoin futures contracts. After January 2024 when the SEC allowed spot cryptocurrency ETFs, the category can also include ETFs invested directly in Bitcoin. This list specifically focuses on those who hold and invest in Bitcoin futures.
Among the largest Bitcoin ETFs based on AUM:
- Bitwise Bitcoin Strategy Optimum Roll ETF (NYSE:BITC).
- Hashdex Bitcoin Futures ETF (NYSE: DEFI).
- ProShares Bitcoin Strategy ETF (NYSE:BITO).
- Simplify Bitcoin Strategy PLUS Income ETF (NASDAQ:MAXI)
- Valkyrie Bitcoin Strategy ETF (NASDAQ:BTF).
Spot cryptocurrency ETFs
Spot cryptocurrency ETFs are the newest category, having only been granted approval in January 2024 by the SEC. A spot cryptocurrency ETF invests directly in cryptocurrency, and as of March 2024 the only cryptocurrency that is allowed is Bitcoin, though it is likely that Ethereum will be added in the future.
Spot ETFs aim to track the real-time, or "spot," price of Bitcoin, which provides a more direct exposure to a cryptocurrency's market movements. Spot ETFs are seen as purer form of Bitcoin investment because they reflect the current market price of Bitcoin without the potential discrepancies that can occur with futures contracts.
When the SEC first allowed spot cryptocurrency ETFs on Jan. 10, 2024, it approved the following 11 ETFs:
- ARK 21Shares Bitcoin ETF (NYSE:ARKB).
- Bitwise Bitcoin ETF (NYSE: BITB).
- Fidelity Wise Origin Bitcoin Fund (NYSE: FBTC).
- Franklin Bitcoin ETF (NYSE: EZBC).
- Grayscale Bitcoin Trust (NYSE:GBTC).
- Hashdex Bitcoin Futures ETF (NASDAQ:DEFI).
- Invesco Galaxy Bitcoin ETF (NYSE: BTCO).
- iShares Bitcoin Trust (NYSE: IBIT).
- Valkyrie Bitcoin Fund (NASDAQ: BRRR).
- VanEck Bitcoin Trust (CBOE: HODL).
- WisdomTree Bitcoin Fund (CBOE: BTCW).
Advantages of cryptocurrency ETFs
Cryptocurrency ETFs offer several advantages for investors looking to gain exposure to the cryptocurrency market. Among the advantages are the following:
- Exposure without direct ownership. Investors in cryptocurrency ETFs can gain exposure to cryptocurrencies without the need to directly own, manage or secure the digital assets themselves.
- Simplified investment process. As opposed to buying cryptocurrency directly through an exchange, cryptocurrency ETFs can be bought and sold through traditional brokerage accounts improving the accessibility for average investors.
- Liquidity benefits. ETFs are traded on public stock exchanges and can typically offer more liquidity than directly holding cryptocurrency, allowing for easier buying and selling.
- Accessibility in retirement accounts. Cryptocurrency ETFs can potentially be included in traditional retirement accounts such as 401(k)s and IRAs, which might not otherwise be possible with direct cryptocurrency holdings.
- Regulated investment vehicle. Cryptocurrency ETFs traded on public stock exchanges are regulated financial products, which can offer a sense of legitimacy and security for investors.
Disadvantages of cryptocurrency ETFs
Cryptocurrency ETFs, while offering a bridge for traditional investors into the digital currency space, come with their own set of disadvantages.
- Lack of direct ownership. Investors in cryptocurrency ETFs do not own the underlying digital assets directly. This is particularly true for cryptocurrency futures ETFs.
- Restricted trading hours. The major public stock exchanges are not open 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, which trade the ETFs. In contrast, the various cryptocurrency exchanges are open 24/7.
- Market volatility. While the public stock markets always carry risk, cryptocurrency ETFs are also subject to the high volatility of the cryptocurrency markets.
Remember to be on the lookout for cryptocurrency scams. Check out some of the most popular types of cryptocurrency scams.
Alternatives to cryptocurrency ETFs
For investors seeking alternatives to cryptocurrency ETFs, there are multiple options available that offer exposure to the cryptocurrency and blockchain space including:
- Direct cryptocurrency investments. It's still an option to buy various cryptocurrencies directly through cryptocurrency exchanges, which provides an investor with full control over the digital assets.
- Public cryptocurrency companies. Another option is to directly buy the individual stocks of companies active in the cryptocurrency market.
- Cryptocurrency mutual funds. This type of mutual fund invests in a portfolio of companies involved in the cryptocurrency and blockchain industry. Instead of trading on a public exchange where pricing fluctuates daily, a mutual fund is more tightly held with pricing determined at the end of a trading day.
- Cryptocurrency mining. It is still possible to go through the mining process and "mine" cryptocurrency directly with the right hardware. However, bitcoin mining is a computationally intense process and might not be the best approach for the average investor.
Sean Michael Kerner is an IT consultant, technology enthusiast and tinkerer. He has pulled Token Ring, configured NetWare and has been known to compile his own Linux kernel. He consults with industry and media organizations on technology issues.




