NFTs vs. cryptocurrency: Key differences and how they work
With the surge in popularity of non-fungible tokens and cryptocurrency, it's important to know the similarities between the two assets and how they vary in uniqueness and use.
Cryptocurrency and non-fungible tokens are the two most popular applications that run on blockchain. While there is considerable overlap in how the two work, there are significant differences between them. The uses for cryptocurrency and NFTs also vary widely.
Cryptocurrency is an encrypted form of digital currency that relies on blockchain technology and doesn't depend on financial institutions to verify transactions. NFTs are one-of-a-kind digital assets that are stored on a blockchain and cannot be duplicated or cloned. Let's take a closer look at NFTs and cryptocurrency and examine their similarities and differences.
What are NFTs?
NFTs are unique digital assets that do not necessarily have a physical manifestation. They represent photos, music, videos, trading cards and other items. Nearly any digital asset, such as a collectible digital character, virtual real estate or original social media post, can be created and purchased as an NFT.
Among the somewhat esoteric NFTs is one created by Jack Dorsey -- the original founder of Twitter -- of the first message ever sent on Twitter.
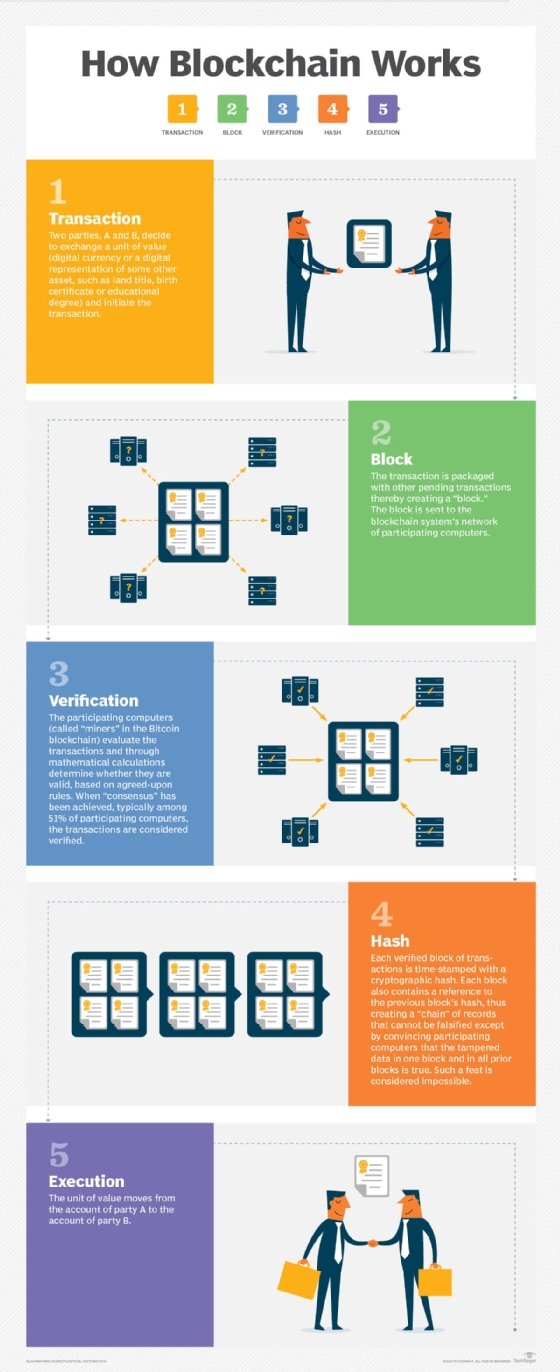
NFTs are stored on distributed ledger technology, of which blockchain is a common type. The digital ledger lets NFTs be managed, bought and sold online. Every transaction on a blockchain is written to this digital ledger, which publicly records each NFT transaction to substantiate who owns the item. NFTs commonly have a value attached to them, which can be set by the creator, that can increase or decrease based on market demand. Blockchain technology makes the ledger essentially immutable, which means it usually can't be tampered with.
The NFT creator keeps the copyright for the item and the right to copy it as many times as they want. Although the creator might create numerous copies of the original, if the buyer of the NFT wants to make copies, they must first get permission from the creator, and each copy is considered a unique NFT.
NFTs are sold in collaboration with auction houses or in NFT marketplaces, such as the following:
- NBA Top Shot, an online marketplace that runs on the Flow blockchain where users can bid on, purchase and sell digital highlights of NBA players. An NBA Top Shot video featuring LeBron James honoring Kobe Bryant sold for close to $400,000.
- OpenSea, a peer-to-peer (P2P) marketplace implemented on the Ethereum blockchain for NFTs, virtual collectibles and rare digital items.
- Rarible, an open marketplace secured with the Ethereum blockchain that lets artists and creators issue and sell NFTs.
- SuperRare, a digital art marketplace powered by the Ethereum blockchain where people can buy and sell NFTs from top artists.
- KnownOrigin, an artist-driven platform that also runs on Ethereum where digital creators can authenticate, show and sell their collectibles and artwork.
- Decentraland Marketplace, a decentralized virtual reality platform running on Ethereum where users can create, experience and make money on what they build and own.
- Venly, formerly known as Arkane Network, is a digital collectibles marketplace for general collectors and gamers -- Venly is based on the Binance cryptocurrency exchange and Ethereum and Polygon blockchains.
What is cryptocurrency?
Cryptocurrency is an encrypted form of digital currency. Unlike traditional currency issued by governments, cryptocurrency doesn't rely on a government or financial institution for its creation or use.
Cryptocurrency is typically stored in a crypto wallet and lets anyone send and receive payments. When an individual transfers cryptocurrency, the transactions are recorded in the immutable distributed ledger.
Several organizations have issued their own cryptocurrencies -- often referred to as tokens -- which let people trade specifically for the product or service a company provides. An individual must exchange real currency for the cryptocurrency required to purchase the product or service.
Examples of popular cryptocurrencies are the following:
- Bitcoin, a cryptocurrency created in 2009. People can buy and sell bitcoin using different currencies in marketplaces called bitcoin exchanges.
- Ether from Ethereum, a blockchain-based software platform that lets developers create smart contracts and distributed applications.
- Litecoin, an open source P2P cryptocurrency.
- Tether, a stablecoin whose price is directly tied to the value of the government-issued or fiat currency it represents, such as the U.S. dollar, euro or yen. Its price is generally more stable than that of bitcoin and Ether, which fluctuate considerably.
How are NFTs and cryptocurrency similar?
There are several ways NFTs and cryptocurrency are similar:
- Digital assets. Both are a form of digital asset that can be owned, bought and sold.
- Web 3.0 technology. NFTs and cryptocurrency are both part of Web 3.0, which proponents call the next generation of the internet.
- Blockchain-based. NFTs and cryptocurrencies share a foundation in blockchain technology, which establishes a decentralized and transparent system to validate and document transactions and also guarantees security and authenticity.
- Decentralized. Cryptocurrencies and NFTs are managed in a decentralized manner with regulations set by their respective communities.
- Tokenization. At the core of how both cryptocurrency and NFTs are used is a form of tokenization. Cryptocurrency is functionally a token that is created on a blockchain to signify a unit of value, while an NFT is a token on blockchain enabling ownership of a unique digital asset.
- Ownership and transferability. Individuals can own, buy and sell both NFTs and cryptocurrencies on blockchain.
The two technologies also work together. An individual can choose to buy or sell an NFT for an agreed-upon amount of cryptocurrency.
What are the differences between NFTs and cryptocurrency?
There are several differences between the two, including the following:
- Uniqueness. The main difference is that every NFT is unique, which sets it apart from fungible tokens, such as cryptocurrency, that can be traded or exchanged for one another with no loss of value.
- Target use. NFTs are fundamentally a type of digital collectable item, much like art or wine. Cryptocurrency can also be collected, though the purpose is not as a collectible, but rather as a form of payment.







