What is a word in computing architecture?
In computing architecture, a word is a fixed unit of data containing a specific number of bits that can be addressed and moved between storage and the computer processor. It is not unlike a word in English, which is the basic building block of linguistic communication or the exchange of information.
In the computer science world, the defined bit length of a word is equivalent to the width of the computer's data bus so that a word can be moved in a single operation from storage to a processor register. For any computer with an 8-bit architecture, every 8 bits equals 1 byte, and any multiples of that 8-bit byte make up a word -- i.e., the word size is some multiple of 8 bits. In Intel's PC processor architecture, a word is 16 bits, or two contiguous 8-bit bytes. For IBM's Z family of mainframe computers, a word is 64 bits, or eight contiguous 8-bit bytes.
Processors and embedded systems with word sizes up to 64 bits, or 8 bytes, can support advanced instruction sets and faster system clock and bus speeds. The compilers for these computers use algorithms designed to convert information to the specific word length for which each computer is architected. Generally, the longer the architected word length, the more the computer system processor can do in a single operation.
Word sizes in computer architectures
Common computer processor architectures support from one to eight contiguous words. But there are also computer architectures that use a half word, which is half the number of bits in a word, and a double word, or dword, which is two contiguous words. Intel's processor architecture also supports a quad word, or two contiguous double words, and a double quad word, or two contiguous quad words. The following image depicts examples of an 8-bit byte, 8-bit word and 16-bit double word.
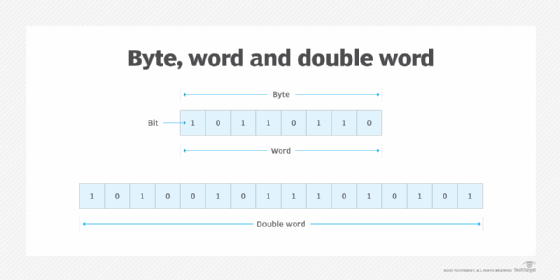
Functions of a computer word
A computer word can contain various data types and data structures. It might contain a computer instruction, a storage address, certain application data that is manipulated, or even processing-related data and instructions such as digital signal processing. In some architectures, a double word or larger unit is required to contain an instruction, an address or application data. An instruction is typically a word in length, but some architectures support half-word and double-word instructions.
A computer's word size is typically a function of its design and how it moves data bits within the various system elements. For example, registers are important holders for various system functions, such as addressing, and the word size is likely the size the computer accepts.
The following systems use words:
- Fixed-point numbers. These numerical values typically include a standard word with different bit counts for various activities.
- Floating-point numbers. These numerical values have a minimum size of one word and can also have multiple word sizes using the basic word.
- Addresses. These are used for memory. Addresses can be a single word, or multiples or fractions of that word.
- Registers. These hold data in preparation for processing and can support data sizes ranging from standard words to fixed- and floating-point numbers and other combinations.
- Memory-processor transfer. The movement of data from memory to central processing unit (CPU) typically uses registers that support the word size used by memory -- usually a single word. However, variable word sizes might also be used, depending on the system.
- Instructions. Computing functions are executed using a variety of instructions that are typically formatted in the same size as the word used in the computer's architecture.
- Unit of processing. These instructions are routed directly to the CPU to run operating systems and applications.
Importance of word size
The word size is an important decision made during the design phase of a computing system. It becomes the foundation on which the computer's capabilities are based. Once the word size has been decided, the architecture can be designed to accommodate multiple word sizes, such as double words, as part of the overall processing environment.
For example, Microsoft Windows uses a 16-bit word as its foundation. Multiples of the 16-bit word size can be accommodated based on the Intel processor type used. An Intel x86 processor can support 32-bit or 64-bit words, which are then used to support Microsoft -- and other vendor -- applications, including word processing software, various programming languages and application programming interfaces.
How word length affects computer processor performance
The word length that a computer can process is another way to express the amount of data that the processor can handle simultaneously. More data can be transferred to the processor in a single pass if the word length that the processor can handle on a single pass is longer. This increases processor performance.
Learn what space-based architecture is and how it influences performance for data-intensive systems.