Trusted Platform Module (TPM)
What is a Trusted Platform Module (TPM) and why is it important?
A Trusted Platform Module (TPM) is a specialized chip on a laptop or desktop computer that is designed to secure hardware with integrated cryptographic keys. A TPM helps prove a user's identity and authenticates their device. A TPM also helps provide security against threats like firmware and ransomware attacks.
A TPM is used for digital rights management (DRM) to protect Windows-based systems and to enforce software licenses. It can also store passwords, certificates or encryption keys. TPM chips can be used with any major operating system and work best in conjunction with other security technologies, such as firewalls, antivirus software, smart cards and biometric verification.
A TPM chip is located on a computer's motherboard as a dedicated processor. Cryptographic keys store Rivest-Shamir-Adleman (RSA) encryption keys specific to the host system for hardware authentication.
Each TPM chip contains an RSA key pair called the Endorsement Key (EK). The pair is maintained inside the chip and cannot be accessed by software. The Storage Root Key is created when a user or administrator takes ownership of the system. This key pair is generated by the TPM based on the EK and an owner-specified password.
A second key, called an Attestation Identity Key (AIK), protects the device against unauthorized firmware and software modification by hashing critical sections of firmware and software before they are executed. When the system attempts to connect to the network, the hashes are sent to a server that verifies they match expected values. If any of the hashed components have been modified, the match fails, and the system cannot gain entry to the network.
The term TPM is sometimes used in reference to the set of specifications applicable to TPM chips. The nonprofit Trusted Computing Group (TCG) publishes and maintains TPM specifications.
TPM uses and benefits
TPMs provide the following benefits:
- Generate, store and limit the use of cryptographic keys.
- Ensure platform integrity by using metrics that can detect changes to past configurations.
- Provide platform device authentication with TPM's RSA key.
- Mitigate firmware, ransomware, dictionary and phishing attacks.
- Protect digital media rights using DRM technology.
- Ensure software licenses are protected.
How does Windows use TPMs and why are they required?
Windows 7, 8, 10 and 11 all support Trusted Platform Modules. Microsoft combines the security features found in Windows with the benefits of TPMs to offer more practical security benefits. For example, Windows uses TPMs to provide the following security features:
- Windows Hello is a biometric identity and access control feature that supports fingerprint scanners, iris scanners and facial recognition technology that use TPMs. It uses both an EK and an AIK.
- Dictionary attack protection helps protect against a brute-force attack that breaks into a password-protected computer network by systematically entering every word in a dictionary as a password.
- BitLocker Drive Encryption encrypts logical volumes. It differs from Microsoft's Encrypting File System in that BitLocker can encrypt an entire drive, whereas EFS only encrypts individual files and folders. If the computer or hard disk is lost or stolen, when powered off, the data on the volume is kept private. BitLocker may still be susceptible to cold boot attacks, so two-factor authentication is also typically used.
- Virtual smart cards are based on TPMs and are similar to physical smart cards. They are used for authentication to external resources.
- Measured boot helps detect malware during boot sequences and ensures TPM measurements reflect the starting state of Windows and Windows configuration settings.
- Health attestation makes AIK certificates for TPMs, as well as parses measured boot data to evaluate device health.
- Credential guard uses virtualization-based security to isolate credentials. TPMs are used here to protect keys.
TPM 2.0 explained
TPM 2.0 was created by TCG to better improve Trusted Platform Modules with new features. For example, the new algorithm interchangeability feature enables TPMs to use different algorithms in case one does not work against specific threats. Prior to this, TPM 1.2 was limited to using Secure Hash Algorithm 1. Basic verification signatures were also improved with the added support of personal identification numbers and biometric and Global Positioning System data. Improved key management enables keys to now be handled for limited and conditional use.
The new and updated features of TPM 2.0 offer more flexibility, enabling the chip to be used in more resource-constrained devices. TPM 2.0 can run on new PCs on any version of Windows 10 for desktop and on Windows 11 devices that support TPMs.
Different types of TPM implementations
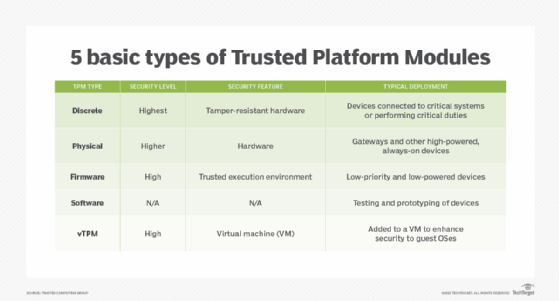
The following Trusted Platform Modules differ by how they are implemented:
- Discrete TPMs are specific and dedicated chips. This is potentially the most secure type of TPM, as they typically are less likely to have bugs and must also implement tamper resistance.
- Physical-based TPMs are integrated into the main central processing unit (CPU) and include security mechanisms that make it tamper-resistant.
- Firmware-based TPMs run in a CPU's trusted execution environment. These TPMs are almost as secure as physical TPM chips.
- Software-based TPMs do not provide additional security and run the risk of having bugs or being externally attacked.
- Virtual TPMs are provided by a hypervisor, which independently retrieves security codes from a virtual machine.
History of TPM
TCG developed TPMs and have updated them over time. One notable update was version 1.2, which became standardized as International Organization for Standardization/International Electrotechnical Commission 11889 in 2009. TCG continues to work on the standard, integrating new additions and features. Its most recent update, version 2.0, was released in 2019. This version adds new features to increase the security of TPM. Version 2.0 works for Windows 10 and only some versions of Windows 11.
Learn more about TPMs and how they augment protection in internet of things systems.
