disruptive technology (disruptive innovation)
What is disruptive technology (disruptive innovation)?
Disruptive technology, often referred to as disruptive innovation, is when a new business model attracts an underserviced market or revenue stream and grows until it supplants incumbent competitors. Technologies are not in themselves disruptive, but their application in a new business model can be.
The term disruptive technology was originally coined by Harvard Business School professor Clayton Christensen in 1995 and further expounded in his book The Innovator's Dilemma in 1997. In the follow-up work, The Innovator's Solution, he replaced the term with disruptive innovation.
The term disruptive innovation is often misapplied to any new technology that is better or replaces an existing technology.
What are the characteristics of a disruptive innovation?
In The Innovator's Dilemma, Christensen separates new technology into two categories: sustaining and disruptive. Sustaining technology relies on incremental improvements to an already established technology and supports existing players in the market.
Disruptive technology is a development that allows a new player to service a lower market segment that incumbent players do not cover due to lower profitability. As the disruptive technology advances, the quality improves so that it supplants the incumbent in the more profitable high-end market.
In The Innovator's Solution, Christensen instead uses the term disruptive innovation. He recognized that a technological advancement is not in and of itself either sustaining or disruptive. Instead, it is how the technology is applied to a new market or in a new business plan that it becomes disruptive to the market.
Key to understanding this is the fact that most incumbent players in a market have large research and development departments and follow technological advancements themselves. So, they will quickly adopt any obviously superior technology. Disruptive companies instead use the innovation to open a new market segment at a lower price point. It is the lack of market flexibility of the incumbent players that allows companies to eventually disrupt the market, not pure technological superiority.
Example of disruptive innovation
A recent example of a disruptive innovation was the introduction of the resale of customer data in the television industry.

While technological innovations such as cheaper glass and panel manufacturing have contributed to the reduction in cost of consumer television sets, that alone does not explain the rise of new television brands and massive reduction in the cost of high-definition TV sets in recent years. Instead, monetizing the collection and selling of user data as an alternative revenue stream disrupted the television industry.
New entrants in the market exploited this to greatly reduce the price of TV sets and create a new lower market segment for big-screen TVs. Now, almost all television manufacturers need to participate in this revenue stream or they won't be competitive in the market.
False disruptive innovation vs. real disruptive change
The terms disruptive technology and disruptive innovation are often misunderstood and misapplied. This happens so frequently that these terms have become almost meaningless buzzwords in many industries. Nevertheless, an understanding of what is and isn't truly disruptive to a market can benefit all players, large and small.
Real disruptive innovations are not single technological advancements at one point in time. Instead, they can only be recognized over a period of time as the market changes.
The trajectory of a disruptive innovation usually follows this path:
- A technological development or market plan allows a new player in a market to enter at a lower quality and price than existing players.
- The new player captures consumers who are not covered by existing products. These consumers can be entirely new or existing consumers who are less demanding. These lower-priced products are less profitable to the new company than the higher-priced products for incumbent players.
- The innovative technology or strategy continues to improve to the point that the quality of the product matches or exceeds existing products. The new player can now enjoy the greater profitability of the high-end or mainstream market.
The automobile is often incorrectly considered a disruptive technology. Early automobiles were expensive and only available to wealthy people. They didn't disrupt the transportation market, which was still well served by other modes of transport such as locomotive, boat, and horse and buggy.
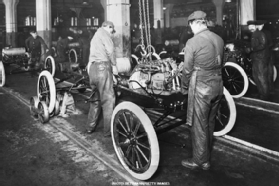
Instead, the disruptive innovation was assembly line manufacturing, introduced by Ford. This allowed Ford to enter the underserviced middle-class transportation market and eventually supplant other modes of transport.
Electric cars and Tesla Inc. are often thought of as disruptive, but generally for incorrect reasons. Early Tesla cars entered the market at the high end. Also, the overall market for electric cars is more sustaining to the automotive industry as a whole, rather than disrupting incumbent players from the bottom up. Instead, the more disruptive aspects of Tesla's approach are its fast development cycle, end-to-end supply chain control, and using in-house dealerships and repair shops instead of third-party ones.
The disruptive nature of smartphones is also easily misunderstood. Early smartphones, including the first iPhone, were expensive high-margin items. They were a sustaining technology for the cellphone market. Instead, their disruptive nature was in other areas.

The introduction of app stores offered low-cost alternatives to existing software packages. Smartphones also were a low-cost alternative method for internet access compared with a traditional desktop computer and fixed internet line. This led to smartphones disrupting the market for PCs.
