timeline
What is a timeline?
A timeline is a visual representation of a chronological sequence of events along a drawn line that helps a viewer understand time relationships. The term can be used to refer to things in the past or future, or that are purely conceptual. Increasingly, timelines combine text and graphic as infographics.
Timelines are useful for documenting any type of development, providing a clear history and assisting viewers in understanding past and current trends. The tools can also help with management tasks. In project management, for example, a timeline depicts milestones, deadlines and other significant dates and events throughout the project's lifecycle, clearly tying goals to specific dates. Annotations to the timeline can be used to track progress.
Types of timelines
Three types of timelines include chronological, roadmaps and Gantt charts:
- Chronological timelines put events into the order that it occurred. They usually deal with past events that can be tied to a specific time. Depending on the scale it can be done by year, day, or even down to the second.
- Roadmaps are a timeline of expected releases or decommissions. These are often publicly available to inform customers of upcoming releases or changes.
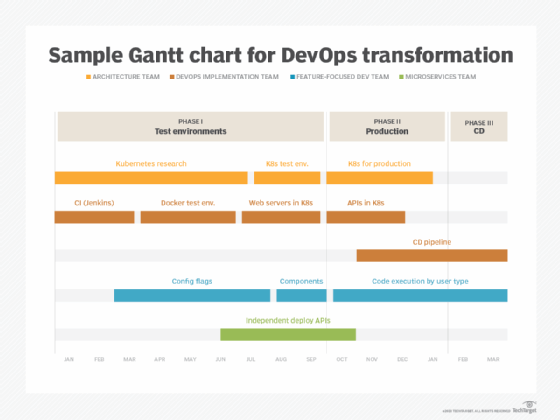
- Gantt charts are a project management timeline that uses bars to signify the phases of a project. These bars can be of various lengths to show how long a phase will take and may overlap.
Example timeline: Notable events on the Internet
Here is a timeline with images and video depicting important events in Internet history:
1950s and early 1960s: Early mainframe computers are developed. The need for a system to interconnect them to share data quickly becomes evident. Researchers begin theoretical work on switched networks.
1965 through 1969: The National Physical Laboratory in the United Kingdom and Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency in the United States begin developing early protocols for network communication.
Oct. 29, 1969: The first message is sent over ARPANET (Advanced Research Projects Agency Network) consisting of the letters L and O of the word LOGIN, at which point the computer crashes. In the following months a small four node network is established.
1971: The first network email messages are sent over ARPANET establishing the @ symbol as the standard to separate the user from the network. The first computer virus, called Creeper, is detected on ARPANET.
1975: ARPANET is declared operational, and additional universities are added.
1977: The TCP/IP protocol is first used for routed packet traffic on ARPANET.
January 1, 1983: ARPANET switches over completely to the TCP/IP protocol allowing for it to work with many other networks around the world.
1983: ARPANET is divided between civilian and military use. The term Internet is first used to describe the combination, or interconnection, of these two networks.
1986: The National Science Foundation Network begins operations. Several network connections are made for NSFNET, which eventually become some of the core backbone of the early Internet.
1990: ARPANET is decommissioned. This can be considered the watershed moment when early research networks became the Internet as we understand it today.
1991: HTML is first publicly released forming the basis of the World Wide Web.
May 1991: NFSNET is opened for commercial traffic by ISPs.
1992: The first consumer dial-up internet access is offered.
1993: The first widely used web browser, Mosaic is released.
1994: The BGP protocol is first used on the internet to automatically manage routing between networks.
1995: The first item is sold on AuctionWeb, later renamed eBay. Amazon opens on July 16, initially only selling books.
1997: The first social network, SixDegrees.com, is launched.
1998: Google is founded. It quickly becomes the most popular web search engine.
May 5, 2000: The ILOVEYOU worm is released by Onel de Guzman. It spreads itself by sending emails to infected user's contact lists. It is estimated that upwards of 10% of the world's computers are eventually infected by it.
2001: Wikipedia launches and becomes the leader in collective web content generation.
July 2002: Amazon Web Services is created, becoming the first widely available cloud computing platform.
2004: Term Web 2.0 coined, representing a new wave websites and applications that make use of user-generated content for end users.
2004: The Facebook (later just Facebook) launches to provide an online book of faces for university students to connect and share information. Founded by Harvard University students, it goes on to become the leading social networking platform in the world.
April 23, 2005: The first video is uploaded to YouTube.

Juyl 2006: Twitter microblogging site launches under the name twittr with its first message "just setting up my twttr."
2007: Hulu video streaming service launches by major television networks to put their content online
June 9, 2008: The iPhone 3G is introduced. It leads the way for high-speed mobile internet access and begins the smartphone and mobile device revolution.
January 3, 2009: The first bitcoin block is mined.
May and June 2013: Edward Snowden releases classified US Government files relating to clandestine government tracking of internet data for security intelligence purposes.
2014: Web 3.0 term coined by Gavin Wood. While Web 3.0 is still evolving and isn't a canonical, universally accepted definition yet, its general principles revolve around the advent of a genuinely decentralized, more democratic version of the internet.
Additional timeline examples
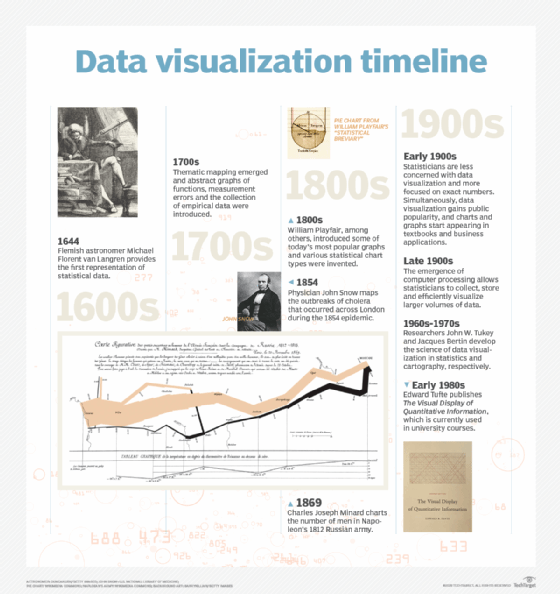
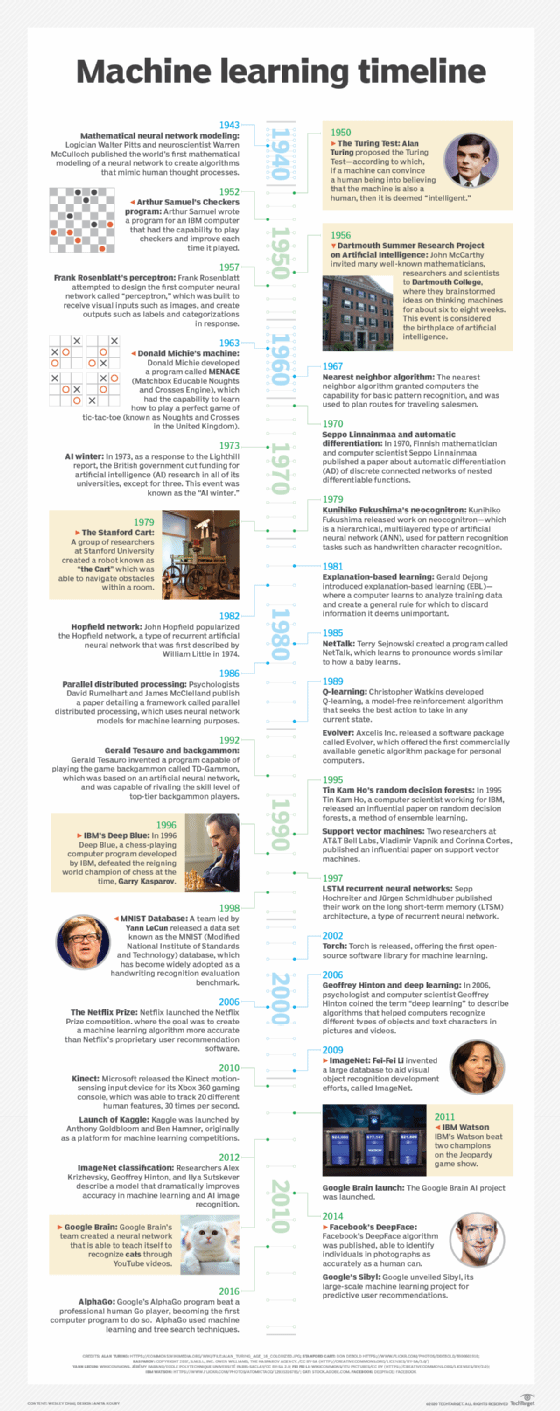
History of machine learning timeline
Here is an example of a timeline that addresses the history of machine learning in infographic form.
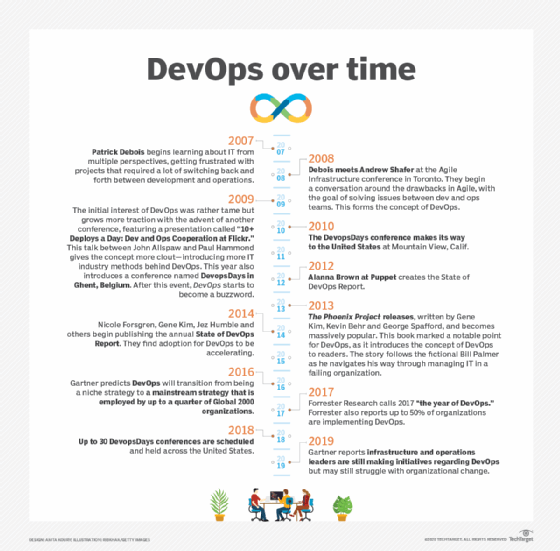
History of DevOps timeline
This timeline addresses the history of DevOps -- a shared philosophy in which development and operations teams work together.
History of virtualization timeline
This timeline overs the history of server virtualization and its impact on data center management.

History of Metaverse timeline
This timeline presents a history of the concept of the metaverse, which is a version of the internet that enables people to socialize, play, shop and work in a 3D immersive virtual environment.

