What is a 3-tier application architecture?
A three-tier application architecture is a modular client-server architecture that consists of a presentation tier, an application tier and a data tier. The data tier stores information, the application tier handles logic and the presentation tier is a graphical user interface that communicates with the other two tiers. The three tiers are logical, not physical and might or might not run on the same physical server.
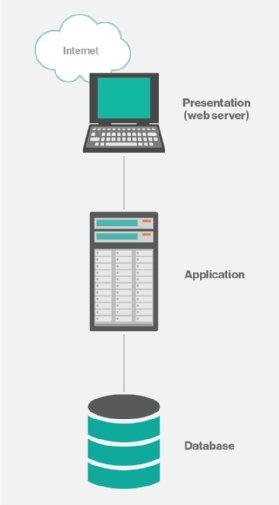
The logical tiers of a 3-tier application architecture
Presentation tier. This tier, which is built with HTML5, cascading style sheets and JavaScript, is deployed to a computing device through a web browser or a web-based application. The presentation tier communicates with the other tiers through application programming interface calls.
Application tier. The application tier, which may also be referred to as the logic tier, is written in a programming language such as Java and contains the business logic that supports the application's core functions. The underlying application tier can either be hosted on distributed servers in the cloud or on a dedicated in-house server, depending on how much processing power the application requires.
Data tier. The data tier consists of a database and a program for managing read and write access to a database. This tier may also be referred to as the storage tier and can be hosted on-premises or in the cloud. Popular database systems for managing read/write access include MySQL, PostgreSQL, Microsoft SQL Server and MongoDB.
Benefits of a 3-tier app architecture
The benefits of using a three-tier application architecture include improved horizontal scalability, performance and availability. With three tiers, each part can be developed concurrently by a different team of programmers coding in different languages from the other tier developers. Because the programming for a tier can be changed or relocated without affecting the other tiers, the three-tier model makes it easier for an enterprise or software packager to continually evolve an application as new needs and opportunities arise. Existing applications or critical parts can be permanently or temporarily retained and encapsulated within the new tier of which it becomes a component.
Three-tier application programs might also be referred to as n-tier programs. In this context, the letter n stands for "a number of tiers."







