What is governance, risk and compliance (GRC)?
Governance, risk and compliance (GRC) refers to an organization's strategy, or framework, for handling the interdependencies of the following three components:
- Corporate governance policies.
- Enterprise risk management programs.
- Regulatory and company compliance.
The term GRC was coined in 2007 by OCEG -- formerly the Open Compliance and Ethics Group -- a nonprofit think tank. GRC emerged as a discipline in the early 21st century when companies recognized that coordinating the people, processes and technologies they used to manage governance, risk and compliance could benefit them in two ways. A synthesized approach would help ensure their organizations acted ethically. It would also help them achieve their business goals by reducing the inefficiencies, miscommunication and other perils of a siloed approach to governance, risk management and compliance.
Any size organization can use GRC. Developing a GRC discipline is especially important for large organizations that have extensive governance, risk and compliance requirements and where programs that meet these requirements often overlap.
Why is GRC important today?
As businesses grow increasingly complex, they need a way to effectively identify and manage key activities within the organization. They also need the ability to integrate traditionally distinct management activities into a cohesive discipline that increases the effectiveness of people, business processes, decision-making, technology, facilities and other important business elements.
GRC achieves this by breaking down the traditional barriers between business units, requiring them to work collaboratively to achieve the company's strategic goals. It aids organizations in adhering to required regulatory standards while also expanding the coverage of an increasingly large risk and threat landscape. GRC has become one of the mainstay components of today's well-managed organizations.
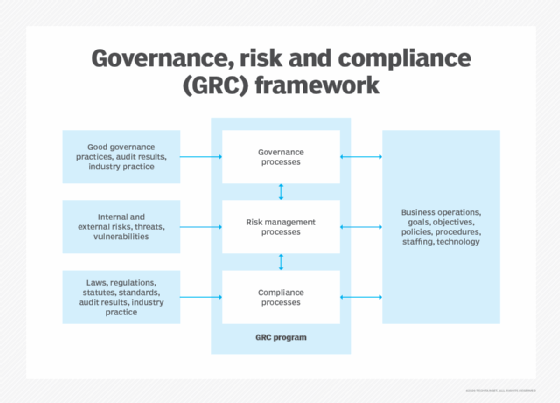
How does GRC work?
The three components of GRC are defined as follows:
- Governance. Governance refers to the ethical management of an organization by its leaders in accordance with approved business plans and strategies. This includes the facilitation of clear policies, guidelines, resources and other oversight methods.
- Risk. Risk management refers to an organization's process for identifying, categorizing, assessing and enacting strategies to minimize risks that would hinder its operations. This also relates to the concept of positive risks, which are opportunities that could increase business value or damage an organization if action is not taken. Risk management also includes having defined processes in place for responding to potential threats. There is always some level of risk within an organization, making it an important core component of GRC.
- Compliance. Compliance refers to the level of adherence an organization has to any mandated standards, laws, regulations and best practices. These might be required by the business itself, by relevant industrial groups or by governing bodies. This component also includes monitoring for changes in laws or required frameworks, enabling the organization to adapt to new business practices as needed.
These three activities traditionally functioned separately. In a GRC approach, each of the three components continues to interact with and support existing business functions, but the intersection of the three is where the benefits become apparent.
GRC strengths and limitations
If properly implemented, GRC policies, practices and software can offer the following benefits:
- Reduced costs. By eliminating redundant and disconnected processes, resources and tools, GRC simplifies business operations, efficiently decreasing time and money waste.
- Security. GRC provides increased visibility into risks, threats and vulnerabilities, enabling businesses to secure their infrastructure from cybersecurity and other threat vectors.
- Compliance. GRC helps organizations achieve ongoing compliance with required standards and regulations.
- Protection from penalties. By helping them achieve compliance, GRC protects businesses against unfavorable internal audits, financial penalties and litigation.
- Reduced risks. Companies using GRC can see a reduction in risk across the entire organization, including business risks, financial risks, operational risks and security risks.
- Operational efficiency. GRC enables organizations to gather information quickly and accurately. It reduces duplication of efforts and automates routine tasks and workflows, which enhances operational efficiency.
- Transparency and accountability. GRC encourages businesses to be transparent about their practices, which builds trust with stakeholders.
However, if GRC isn't properly implemented or if senior management support for GRC is minimal, potential issues can emerge. Problems include high costs related to reduced risk visibility, reduced performance due to weak risk visibility and fragmentation across the organization's departments and workforce. The implementation of GRC might be complex for some inexperienced organizations, and, without proper planning, tools and processes might be poorly integrated.
How to effectively implement a GRC strategy
GRC software implementation typically involves complex installations that include vendor negotiation and data coordination between the vendor's technical team and multiple departments in the organization, including business, IT, security, compliance and auditing.
Major challenges include integrating data and other relevant information from internal departments and external organizations into useful GRC information and providing all GRC system users with proper training to obtain maximum benefit from the software.
Changes in the corporate culture might be needed to accommodate the new GRC system's collaborative nature. Periodic testing of GRC software is essential to make sure internal departments are using it properly. Like other critical systems, GRC software must be added to technology disaster recovery (DR) plans to ensure it remains operational in a disruptive event.
The following tips can help organizations deploy GRC:
- Set clear goals. Organizations must establish specific business objectives and try to pinpoint what they hope to achieve with the GRC efforts.
- Identify operational gaps. After acquiring relevant data on existing GRC practices, businesses should review data quality, analyze the maturity of each process and identify any operational gaps by conducting a gap analysis.
- Get the team on board. To cultivate acceptance of the GRC program, businesses should align themselves with the GRC plan and budget, thereby establishing a top-down focus for the program.
- Test the GRC framework. Before organization-wide adoption, the organization should conduct small-scale testing on a particular business unit or process. This makes it easier to determine whether the selected GRC framework is in line with the objectives and, if not, to make the necessary adjustments.
- Define clear roles and responsibilities. In the realm of GRC, success hinges on a collaborative team approach. Senior executives set important policies, but legal, financial and IT teams also share responsibility for the success of GRC. Individual duties should be clearly defined to promote accountability and speed up the reporting and resolution of GRC issues.
GRC software tools and considerations
GRC software combines applications that manage GRC's core functions into a single integrated package. These tools enable an organization to pursue a systematic, organized approach to managing and implementing a GRC strategy. Instead of using siloed applications, administrators can use a single framework to monitor and enforce rules and procedures. Successful installations help with risk mitigation, reduce costs incurred by multiple installations and minimize complexity for managers.
GRC software products are available from numerous vendors. Products typically accommodate virtually any type or size of organization, including those with multiple lines of business.
Per market intelligence firm IDC and other independent resources, vendors of GRC products include the following:
- Archer.
- AuditBoard.
- DigitalXForce.
- Diligent.
- IBM.
- LogicGate.
- MetricStream.
- OneTrust.
- ServiceNow.
- Vanta.
Software considerations
GRC software can be confusing for businesses because the market is replete with many types of products, including the following:
- Integrated GRC products that aim to provide an enterprise-wide approach to GRC, as noted above.
- GRC products that target only certain areas, such as finance, IT or risk.
- Point products that target one component of GRC but not all three.
Effective GRC software should include risk examination and risk assessment tools that identify links to business processes, internal controls and operations. GRC software identifies the processes and tools that control those risks and integrates the single, multipoint and enterprise-wide software the business currently uses.
GRC software should also provide a structured approach for compliance with legal and regulatory requirements, such as those specified in the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, General Data Protection Regulation, or occupational health and safety regulations.
Other features commonly offered in GRC platforms include operational risk management, IT risk management, policy, audit management, third-party risk management, issue tracking and document management. GRC tools are increasingly cloud-based, but on-site systems and freeware options are available. GRC vendors are incorporating automation and AI technologies, including machine learning and natural language processing, to help organizations keep abreast of new and evolving risks and to make GRC tools more user-friendly.
Who can benefit from GRC software?
Once in place, GRC dashboards and data analytics tools can help administrators identify an organization's risk exposure, measure progress toward quarterly goals or quickly pull together an information audit.
GRC software can, therefore, satisfy the needs of multiple stakeholders, such as the following:
- Business executives who need to identify and manage risks.
- Finance managers assigned to meet regulatory compliance requirements.
- Legal counsel grappling with discovery and records retention.
- IT directors managing software installations related to GRC projects across an organization.
- Human resource managers involved in handling sensitive employee information.
GRC maturity model
When embarking on a GRC program, it's beneficial to establish a benchmark from which to plan and execute the program. A maturity model is one possible approach, as it defines the stages an organization can progress through to achieve a suitable level of GRC excellence.
The basic GRC maturity model below can be expanded and modified into greater detail as needed and serve as part of the GRC program planning process.
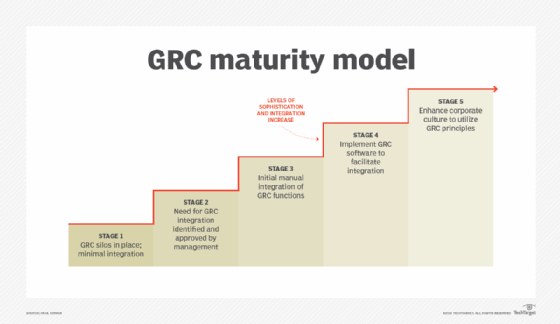
Stage 1 describes an organization with minimal integration of GRC: The three disciplines of GRC coexist but don't collaborate on governance, risk and compliance. As the stages progress, senior management recognizes the importance of GRC integration. Manual processes commence, and the software takes them to a higher level of cross-organization integration and automation. And, finally, by Stage 5, the organization's culture -- and, by extension, its way of doing business -- has adopted a fully integrated GRC approach.
The dos and don'ts of GRC practices
Managing governance, risk and compliance is one of an organization's most important and complex activities. As the organization establishes a GRC program, keep the following dos and don'ts in mind.
Dos
- Be prepared to justify the integration of GRC activities using a business case approach.
- Secure senior management support and funding for a GRC program.
- Carefully examine the possible approaches to a GRC program and develop a project plan.
- If software is part of the plan, perform due diligence when selecting a software product.
- Prepare and deliver awareness and training activities to sell employees and management on the value of integrated GRC activities.
- Recognize that not all employees will embrace a GRC program; make sure those who stand to benefit the most are on board.
- Partner with IT to develop an effective system rollout plan.
- Provide opportunities for employees to test the system before it's put into production.
- Note employee comments during the test period and share them with the technology vendor.
- Provide regular briefings to senior management and employees on the program status.
- Implement the rollout; check for issues and resolve them quickly.
- Establish a system maintenance and updating process.
- Make sure the new system is included in DR plans.
- Track program performance and share results with employees and management.
Don'ts
- Don't assume an integrated GRC program will benefit the company; it might not.
- Don't assume senior management will quickly embrace a GRC program.
- Don't assume employees will embrace a GRC program, especially if it means changing the way they've performed their work over the years.
- Don't forget to examine the different approaches to a GRC program; consider a maturity model.
- When determining whether an integrated GRC approach will work, don't conduct a minimalist examination and analysis of business processes; understand the business as much as possible.
- Don't hesitate to contact other organizations to see if their GRC approach worked; this is especially important if GRC software is being considered.
- Don't fail to collaborate with IT throughout the project.
- Don't assume employees and management will attend awareness and training sessions; this is where management support can help.
- Don't ignore the importance of having a project plan for the GRC system implementation.
- Don't get upset if management decides to defer or cancel the program.
In today's landscape, organizations must fulfill diverse regulatory compliance needs. Learn about open source GRC tools that can help compliance professionals.







