stack overflow
What is stack overflow?
A stack overflow is a type of buffer overflow error that occurs when a computer program tries to use more memory space in the call stack than has been allocated to that stack. The call stack, also referred to as the stack segment, is a fixed-sized buffer that stores local function variables and return address data during program execution.
The call stack adheres to a last-in, first-out (LIFO) memory architecture. Each function gets its own stack frame for storing variable and address data. When a function is called, the function's stack frame is added to the top of the call stack. The stack frame will remain in memory until the function is finished executing. The stack frame is then dropped from the stack, freeing up memory for other stack frames.
The size of a call stack is usually defined at the start of a program. Its size depends on multiple factors, such as the architecture of the host computer, the programming language being used and the amount of available memory in the system. If a program demands more memory than is available in the call stack, a stack overflow occurs, which can cause the program -- or even the entire computer -- to crash.
What causes stack overflow?
One of the most common causes of a stack overflow is the recursive function, a type of function that repeatedly calls itself in an attempt to carry out specific logic. Each time the function calls itself, it uses up more of the stack memory. If the function runs too many times, it can eat up all the available memory, resulting in a stack overflow.
Stack overflow errors can also occur if too much data is assigned to the variables in the stack frame. Array variables are particularly susceptible to stack overflow errors, especially if no logic has been implemented to prevent excess data from being written to the array.
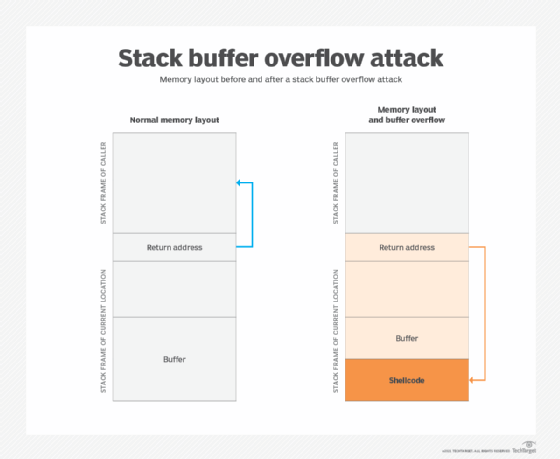
What happens during a stack overflow?
When a stack overflow occurs, the excess data can corrupt other variables and address data, effectively changing variable values and overwriting return addresses. In some cases, this will cause the program to crash. At other times, the program will continue to run, making it more difficult to troubleshoot the problem once the error is discovered. The longer the program runs, the harder this becomes.
A program susceptible to stack overflows can expose security vulnerabilities that hackers can exploit. By overwriting the call stack, they can insert their own executable code, which could have a significant impact on how the program works or how it is accessed. For example, a hacker might be able to use a stack overflow vulnerability to alter a password or delete a configuration file.
What is a heap overflow?
Another type of buffer overflow error is the heap overflow. Unlike the call stack, the heap (or heap segment) is a memory space that's allocated dynamically and that stores global variables. The heap is just as susceptible to buffer overflow errors as the call stack, even if the memory is allocated dynamically. With heaps, program developers are responsible for deallocating memory. If they fail to do this properly, heap overflow can occur, resulting in critical data being overwritten. Heap overflow can also occur when the stored variables contain more data than the amount of allocated memory.
See also: memory allocation, memory management, swap file
