instant messaging
What is instant messaging?
Instant messaging, often shortened to IM or IM'ing, is the exchange of near-real-time messages through a standalone application or embedded software. Unlike chatrooms with many users engaging in multiple and overlapping conversations, IM sessions usually take place between two users in a private, back-and-forth style of communication.
A core feature of many instant messenger clients is the ability to see whether a friend or co-worker is online and connected through the selected service -- a capability known as presence. As the technology has evolved, many IM clients have added support for features such as file transfer and image sharing within an IM session.
Instant messaging differs from email in the immediacy of the message exchange. IM also tends to be session-based, having a start and an end. Because IM is intended to mimic in-person conversations, individual messages are often brief. Email, on the other hand, usually reflects a longer-form, letter writing style.

How does instant messaging work?
Generally, IM users must know each other's username or screen name to initiate a session. Contact or buddy lists of frequent contacts can be created. Once the intended recipient has been identified and selected, the sender opens an IM window to begin the session.
For IM'ing to work as intended, users must be online at the same time, although nearly all instant messaging platforms enable asynchronous interactions between online and offline users. If offline messaging is not supported, attempting to IM an unavailable user results in a notification that the transmission cannot be completed. In addition, the intended recipient must be willing to accept instant messages. Most IM clients can be configured to reject certain users.
When a message is received, the instant messaging application alerts the recipient with a window -- often a pop-up window -- containing the incoming message. Or, depending on the user's settings, a window could indicate an IM has arrived along with a prompt to accept or reject it. Many IM clients notify the user with a distinctive sound, such as a chime or chirp. The user can also receive a visual notification, such as flashing the IM window or its taskbar icon when a message arrives.
In the past, IM clients were often based on proprietary protocols, requiring that users use the same communication software. However, the use of open standards is more common today, enabling multiplatform instant messaging systems, such as Pidgin and Trillian.
Another important shift in IM is the way in which it's accessed and delivered. These apps were long deployed as desktop clients that had to be downloaded and installed. Now, instant messaging is more often found as a feature within another web- or cloud-based service, such as Facebook, Gmail and Skype, or as a mobile app, such as WhatsApp Messenger.
Why is instant messaging used?
Instant messaging is used for real-time communication among users on the internet. Enterprise and consumer users find it an immediate, convenient and flexible alternative to email. IM'ing is faster than email and more direct than other asynchronous forms of communication. Users can IM from a range of devices, not just their phone.
Enterprise instant messaging systems let users indicate their availability, chat with each other, exchange documents and hold group meetings. Instant messaging is a key form of communication to keep remote workers connected and coordinate workflows. Applications that were primarily for other uses are expanding into IM. For instance, Zoom, which is primarily known for video conferencing, contains IM chat features, and the company is planning to expand its chat capabilities.
In a consumer context, instant messaging is a useful alternative to text and Short Message Service (SMS) messages because a cellular network is not required for IM'ing. Many social media platforms incorporate IM features.
Chatbots are a variation on IM'ing. They mimic the user experience in an IM exchange, but instead of speaking with another person, the user is speaking to an automated program. Chatbots are used for automating simple customer service requests.
Applications like Pidgin and Trillian offer encrypted messaging, which can be used for off-the-record chats and sensitive data, like personal health information.
Instant messaging features
Text-based communication has been the chief function of instant messaging for a long time, but it is now one of many features. Other capabilities include the following:
- Availability. Presence technology enables users to see the availability of their contacts. Many apps show if contacts are online or offline and if they have set their status to free or busy. Some clients let users set an away message and provide detail about their availability. In an active session, many apps indicate in real time when a user is typing.
- Images. Many clients let users insert images and emojis into messages.
- File transfer. Sending and sharing files is also a standard part of many IM apps. Facebook Messenger even lets users send money via IM.
- Switching to other communication modes. Numerous instant messaging apps let IM users move to other modes of communication -- such as group chat, voice calls and video conferencing -- within the app.
What are the types of instant messaging?
IM applications are often standalone applications, such as WhatsApp. They can also be embedded applications with multiple purposes.
Instant messaging programs can differ based on the platform they are embedded in. For example, an instant messaging tool can be embedded into the following:
- Social media. For example, Facebook Messenger has a list of Facebook friends that users can open a chat with in a pop-up window. On a mobile device, Facebook Messenger is a separate app that imports contacts from Facebook and displays them as a list.
- Video conferencing. Zoom has a small chat window in the side of the video that can be used to chat with the whole group or an individual.
- Gaming and streaming. Twitch is a streaming platform where users can stream live video and gameplay, alongside a chat window where they can interact with other users.
When they are standalone applications, they often incorporate cross-platform features, such as the following:
- voice over IP
- SMS
- video chat
- file sharing
Some embedded programs have these cross-platform features as well. For example, Facebook Messenger has video chat.
Popular instant messaging software and platforms
While some instant messaging tools are specifically consumer services and other are for enterprises, crossovers do exist. The following is a list of popular consumer and enterprise instant messaging services:
- Cisco Jabber, based on Jabber
- Discord
- Facebook Messenger
- Google Chat
- HCL Sametime
- iMessage
- Line
- Microsoft Teams
- Pidgin
- Slack
- Snapchat
- Trillian
- Viber
- WhatsApp Messenger
AOL Instant Messenger, or AIM, was once one of the most popular tools in the instant messaging market in North America. It was discontinued on Dec. 15, 2017.
What is the difference between instant messaging and texting?
Both instant messaging and texting involve exchanging digital messages in real time. The two methods of communication are different, however.
Texting
Texting uses a cellular network to exchange messages. Two cellphone users can communicate via text using any cellular carrier -- the carriers do not need to be the same. The users do not need an internet connection, just cell carrier plans and cellphones. Cellular companies control the cost and message limits of communicating via text message.
Instant messaging
By contrast, instant messaging requires that both parties have internet connections to exchange messages. The communicating devices do not have to be phones -- they can be computers, tablets, smartphones or any other internet-connected device. IM apps often require users to communicate using the same application. A user cannot send a message on Facebook Messenger to a contact using Microsoft Teams. There may be a delay in message transmission without a proper internet connection.
Instant messaging is also frequently included as a feature of unified communication (UC) tools, like Zoom. Text messaging is less commonly included in these applications.
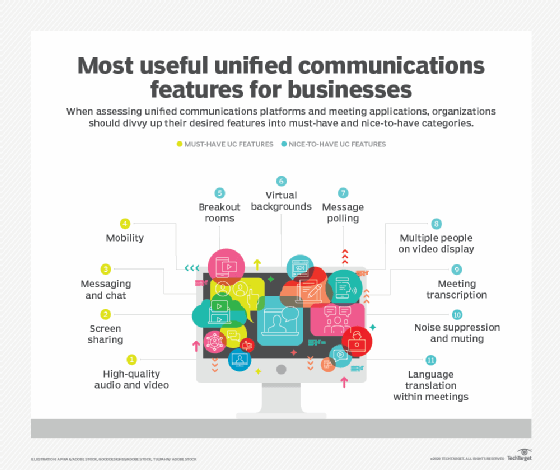
IM and chat tools are important pieces of a UC strategy. Learn how to implement, evaluate and manage UC in the enterprise.






