web crawler
What is a web crawler?
A web crawler, crawler or web spider, is a computer program that's used to search and automatically index website content and other information over the internet. These programs, or bots, are most commonly used to create entries for a search engine index.
Web crawlers systematically browse webpages to learn what each page on the website is about, so this information can be indexed, updated and retrieved when a user makes a search query. Other websites use web crawling bots while updating their own web content.
Search engines like Google or Bing apply a search algorithm to the data collected by web crawlers to display relevant information and websites in response to user searches.
If an organization or website owner wants its website to rank in a search engine, it must first be indexed. If webpages aren't crawled and indexed, the search engine can't find them organically.
Web crawlers begin crawling a specific set of known pages, then follow hyperlinks from those pages to new pages. Websites that don't wish to be crawled or found by search engines can use tools like the robots.txt file to request bots not index a website or only index portions of it.
Performing site audits with a crawling tool can help website owners identify broken links, duplicate content and duplicate, missing or too long or short titles.
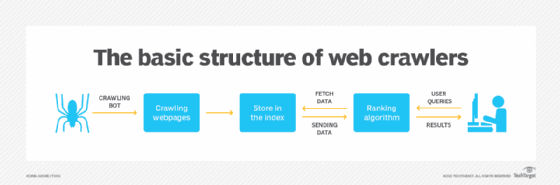
How do web crawlers work?
Web crawlers work by starting at a seed, or list of known URLs, reviewing and then categorizing the webpages. Before each page is reviewed, the web crawler looks at the webpage's robots.txt file, which specifies the rules for bots that access the website. These rules define which pages can be crawled and the links that can be followed.
To get to the next webpage, the crawler finds and follows hyperlinks that appear. Which hyperlink the crawler follows depends on defined policies that make it more selective about what order the crawler should follow. For example, defined policies may include the following:
- how many pages link to that page;
- the number of page views; and
- brand authority.
These factors signify a page may have more important information for indexing.
While on a webpage, the crawler stores the copy and descriptive data called meta tags, and then indexes it for the search engine to scan for keywords. This process then decides if the page will show up in search results for a query, and if so, returns a list of indexed webpages in order of importance.
In the event a website owner doesn't submit its site map for search engines to crawl the site, a web crawler can still find the website by following links from indexed sites that are linked to it.
Examples of web crawlers
Most popular search engines have their own web crawlers that use a specific algorithm to gather information about webpages. Web crawler tools can be desktop- or cloud-based. Some examples of web crawlers used for search engine indexing include the following:
- Amazonbot is the Amazon web crawler.
- Bingbot is Microsoft's search engine crawler for Bing.
- DuckDuckBot is the crawler for the search engine DuckDuckGo.
- Googlebot is the crawler for Google's search engine.
- Yahoo Slurp is the crawler for Yahoo's search engine.
- Yandex Bot is the crawler for the Yandex search engine.
Why web crawlers are important for SEO
Search engine optimization (SEO) is the process of improving a website to increase its visibility when people search for products or services. If a website has errors that make it difficult to crawl, or it can't be crawled, its search engine results page (SERP) rankings will be lower or it won't show up in organic search results. This is why it's important to ensure webpages don't have broken links or other errors and to allow web crawler bots to access websites and not block them.
Likewise, pages that aren't crawled regularly won't reflect any updated changes that may otherwise increase SEO. Regular crawling and ensuring that pages are updated can help improve SEO, especially for time-sensitive content.

Web crawling vs. web scraping
Web crawling and web scraping are two similar concepts that can be easily confused. The main difference between the two is that while web crawling is about finding and indexing webpages, web scraping is about extracting the data found on one or more webpages.
Web scraping involves creating a bot that can automatically collect data from various webpages without permission. While web crawlers follow links continuously based on hyperlinks, web scraping is usually a much more targeted process -- and may only be after specific pages.
While web crawlers follow the robots.txt file, limiting requests to avoid overtaxing web servers, web scrapers disregard any strain they may cause.
Web scraping may be used for analytics purposes -- collecting data, storing then analyzing it -- in order to create more targeted data sets.
Simple bots can be used in web scraping, but more sophisticated bots use artificial intelligence to find the appropriate data on a page and copy it to the correct data field to be processed by an analytics application. AI web scraping-based use cases include e-commerce, labor research, supply chain analytics, enterprise data capture and market research.
Commercial applications use web scraping to do sentiment analysis on new product launches, curate structured data sets about companies and products, simplify business process integration and predictively gather data.
Learn more about four other SEO strategies including creating better topic clusters and backlink strategies.
