How do CPU, GPU and DPU differ from one another?
Data centers use three varieties of processing units: CPU, GPU and DPU. Learn the unique uses for each and how to use them in conjunction to speed up data center workloads.
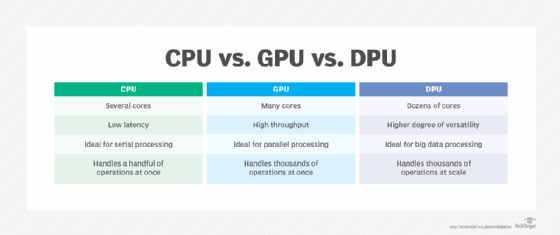
In computing, processor often refers to the central processing unit. The CPU is the most ubiquitous processor, but it is not the sole processing unit available to data centers. GPUs and DPUs can manage increasingly complex processing loads and computing tasks.
All three processing units support complex computing, but each is suited for different tasks or workloads. By using multiple types of processing units in your data center, you can have all the units support each other and further speed up large or complex tasks.
What is a CPU?
The CPU is often described as the computer's brain and the main processor. The CPU uses logic circuitry to interpret, process and execute instructions and commands sent to it from the OS, programs or various computer components.
The CPU is integral to system operations. It performs everything from basic arithmetic and logic to I/O operations. It also handles sending instructions and feeding data to specialized hardware, such as graphics cards.
In the early days of computer history, a CPU often had a single processing core. Today, CPUs can contain multiple cores to perform many instructions at once. This increases overall system performance and speed throughout the data center.
What is a GPU?
Graphics processing units (GPUs) were initially designed to complement the CPU. The units have multiple similarities: They're both critical computing engines that can handle data, but GPUs specifically accelerate graphics rendering.
Although CPUs can send instructions to a graphics card, they can only handle a few software threads at a time. Multiple processing cores are great for serial processing -- executing a wide variety of workloads or a series of tasks by focusing on completing individual tasks quickly -- but image rendering is complex. A GPU contains many more cores than a CPU, which enables it to tackle thousands of operations at once rather than just a few.
This work breaks down the complex graphics rendering tasks, which involve manipulating computer graphics and image processing simultaneously, consistently and at high speeds. For example, the GPU can accelerate the intensive tasks of ray tracing, bump mapping, lighting computations and smooth decoding to render animations or videos and output them to a display.
GPUs perform parallel operations rather than serial operations. Although the GPU was intended to process computer graphics, its parallel processing architecture made it a clear fit for other complex workloads, such as supercomputing, AI, machine learning (ML), database calculation and big data analysis.
Its ability to handle complex mathematical processes efficiently enables the GPU to enhance performance for data center applications and greatly speed up data center workloads. GPUs can support big data and scientific computing scenarios, streamline container orchestration and process work in a fraction of the time CPUs do.
What is a DPU?
The data processing unit (DPU) offloads networking and communication workloads from the CPU. It combines processing cores with hardware accelerator blocks and a high-performance network interface to tackle data-centric workloads at scale. This architectural approach ensures that the right data reaches its destination in the correct format.
The DPU is essentially designed to process data moving around the data center. It focuses on data transfer, data reduction, data security and data analytics, as well as encryption and compression. This means it supports more efficient data storage and frees up the CPU to focus on application processing.
A DPU can also address server node inefficiency when placed at the heart of data-centric infrastructure. It can mitigate sprawl and deliver high availability and reliability. Additionally, it ensures quick accessibility and shareability of data, regardless of the amount needed for processing and transferring.
DPU processing is specific to uses with large-scale data-processing needs, such as data centers supporting cloud environments or supercomputers driving complex AI, ML and deep learning algorithms.
The future of processing units
The CPU, GPU and DPU were each created to adapt to an evolving IT landscape and meet increasingly complex computing needs. Data centers are the first market segment to adopt DPUs because of the technology's ability to process massive amounts of data. DPUs also offload much of the strain on CPUs and GPUs that power AI and ML applications.
In the future, new processing units might further transform technology operations, but for now, the DPU represents an exciting recent advancement that drives efficiency at scale for data centers.
Editor's note: The site editor updated this piece in 2025 to ensure all information is up to date. A YouTube video was also added to further explain processing units.
Jacob Roundy is a freelance writer and editor with more than a decade of experience with specializing in a variety of technology topics, such as data centers, business intelligence, AI/ML, climate change and sustainability. His writing focuses on demystifying tech, tracking trends in the industry, and providing practical guidance to IT leaders and administrators.








