sound wave
What is a sound wave?
A sound wave is the pattern of disturbance caused by the movement of energy traveling through a medium (such as air, water or any other liquid or solid matter) as it propagates away from the source of the sound.
Sound waves are created by object vibrations and produce pressure waves, for example, a ringing cellphone. The pressure wave disturbs the particles in the surrounding medium, and those particles disturb others next to them, and so on.
The pattern of the disturbance creates outward movement in a wave pattern, like sea water in the ocean. The wave carries the sound energy through the medium, usually in all directions and less intensely as it moves farther from the source.
The idea that sound moves in waves goes back to, at least, the first century B.C. The Roman architect and engineer Vitruvius and the Roman philosopher Boethius each theorized that sound may move in waves. The origin of the modern study of sound is attributed to Galileo Galilei (1564-1642).
Are sound waves longitudinal or transverse?
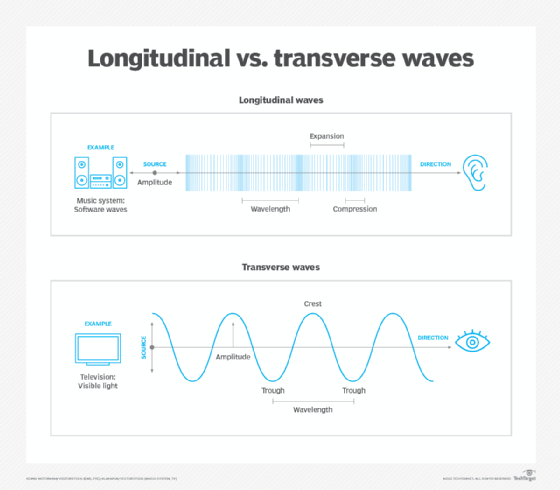
There are two types of mechanical waves: longitudinal waves and transverse waves.
Longitudinal waves
A longitudinal wave is one where all the particles of the medium (such as gas, liquid or solid) vibrate in the same direction as the wave. Sound waves are longitudinal waves.
When longitudinal waves travel through any given medium, they also include compressions and rarefactions. Compression occurs when particles move close together creating regions of high pressure. In contrast, rarefactions occur in low-pressure areas when particles are spread apart from each other. For example, a vibrating tuning fork creates compressions and rarefactions as the tines move back and forth.
Transverse waves
A mechanical wave is transverse when all the particles of the medium, which are solid or liquid (and never gas), vibrate perpendicularly at right angles, up and down, and continue to move in the direction of the wave. For example, the ripples on the surface of a lake are transverse waves. Sound does not move through transverse waves except in special conditions.
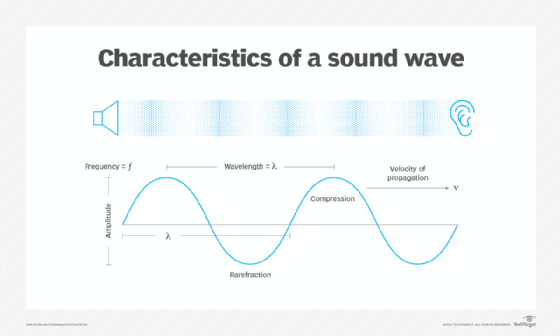
What are the characteristics of sound waves?
Sound waves have several characteristics. These include amplitude, frequency, time, velocity and wavelength. The most important characteristic of a sound wave is wavelength.
The wavelength is the distance between adjacent crests or identical points in the adjacent cycles of a waveform signal transmitted through space or along a wire.
How we hear sound: What happens when sound waves reach the outer ear?
When sound waves reach the outer ear, the auricle or pinna collects and channels them through the ear canal, amplifying the sound. The incoming soundwaves travel to an oval-shaped membrane at the end of the ear canal known as the eardrum.
When the soundwaves reach the eardrum, they cause the eardrum to vibrate. The vibrations are sent to three tiny bones called the incus, malleus and stapes.
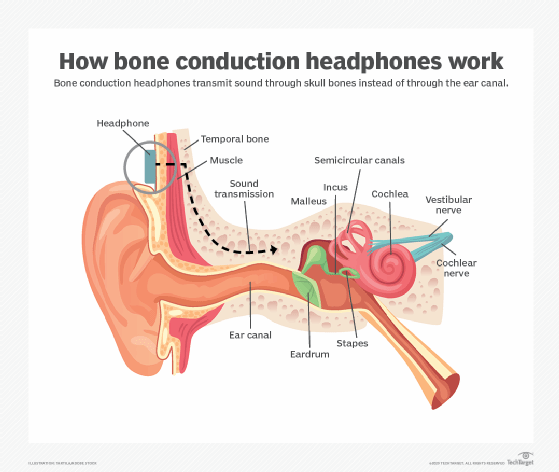
Devices called bone conduction headphones bypass the outer ear by sending sound vibrations through a user's skull directly through the cochlea to the audio nerve. Here, bone -- in effect -- becomes the speaker.
