
Getty Images
SEO vs. SEM: What's the difference?
SEO and SEM strategies help marketers put digital content in front of the right audience. However, SEO strategies focus on organic search, whereas SEM generates paid traffic.
Marketers use SEO and SEM strategies to increase their content's visibility on search engines and reach audiences who frequently use search engines.
Search engine optimization (SEO) and search engine marketing (SEM) techniques both offer ways to increase sales, but they use different approaches. Over time, SEO strategies can help organizations boost their organic search ranking, whereas SEM strategies harness paid advertisements to quickly increase site traffic.
To ensure marketing teams focus on the right strategy for their business needs, they should understand key differences between SEO and SEM, such as the audiences they target, the time it takes to see results and their short- and long-term costs.
What is SEO?
SEO is the process of improving a website to increase its organic -- or unpaid -- visibility on major search engines. Companies like Google and Bing use algorithms to ensure their search engines show relevant, high-quality search results for queries, so marketers use SEO strategies to ensure these algorithms favorably rank their content. The goal of SEO is to organically rank highly on a search engine results page (SERP) for a specific keyword or phrase.
What is SEM?
SEM is an umbrella term for any strategy organizations use to increase their search engine visibility. While SEM includes SEO, people typically use the term in reference to paid advertising.
SERPs on Google and other search engines contain two types of content: organic results and paid advertisements. On Google, paid ads often appear at the top, side or bottom of a SERP. Organizations can pay to have their websites appear in these highly visible locations.
3 key differences between SEO and SEM
Although SEO and SEM both help organizations generate web traffic, marketers should know their key differences.
1. SEO and SEM target different search results
SEO and SEM have the same overarching goal: to increase an organization's visibility on search engines. However, they each focus on different ways to achieve that goal. SEO focuses on the creation and enhancement of webpages to improve their rankings in organic search results. SEM focuses on the use of paid advertisements to rank at the top of SERPs.
To help pages rank organically, marketers use SEO best practices to create content that search engine algorithms tend to favor. Although companies like Google and Bing don't publicly disclose every detail about how they rank pages, the algorithms evaluate dozens of criteria, which include the following:
- Title tags. A page's title should contain the content's main keyword -- or at least a variation of it.
- Content quality. Marketers should create well-written, thorough and well-organized content.
- Mobile friendliness. As people increasingly conduct searches from their mobile devices, search engines prioritize sites that fit in mobile browsers.
- UX. Search engines prioritize websites that offer a UX that is intuitive and easy to navigate.
- Internal links. Up-to-date links that connect one webpage to another page on the same site can improve navigation, audience engagement and, in turn, SEO ranking.
- Backlinks. Google's search algorithm uses backlinks -- links from external websites -- as an indicator of site authority and trustworthiness.
- Site speed. Search engine companies don't want to send users to slow pages, so their algorithms prioritize sites that load quickly.
Marketing teams can use the above criteria to guide their SEO strategy as they create digital content. These best practices can help teams eventually reach the first page or first position on SERPs for their content's keyword or phrase without paying for top spots.
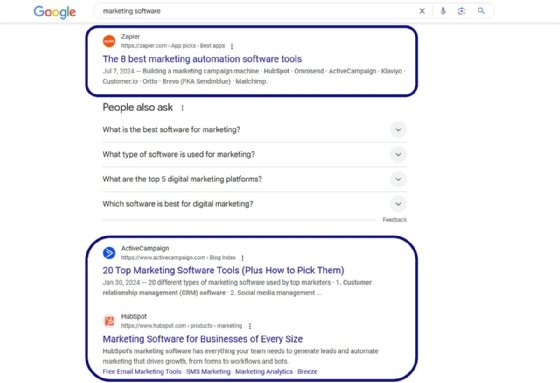
On the other hand, with SEM, marketers use paid ads to automatically appear at the top of SERPs for keywords and phrases related to their content. Two key types of SEM advertising are search ads and shopping ads.
Search ads. Organizations can bid on a keyword or phrase so a link to their page automatically appears on SERPs for that term. These ads follow a pay-per-click (PPC) model in which users pay a fee every time someone clicks on the ad.
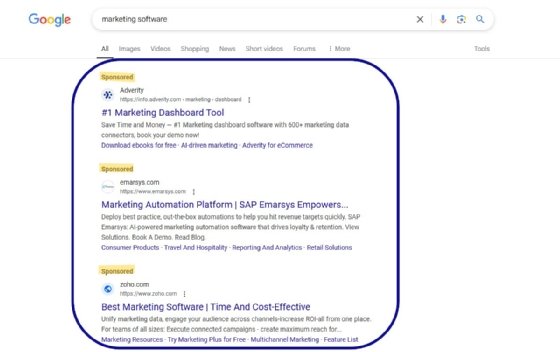
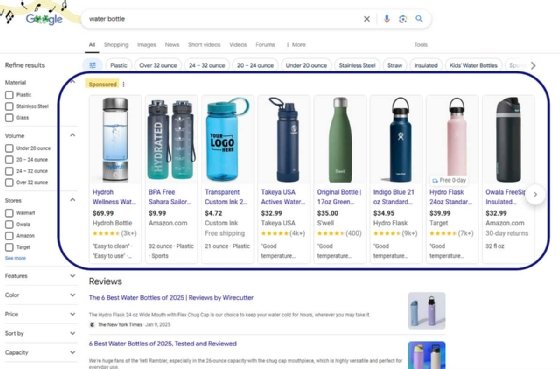
Shopping ads. These ads also follow a PPC model, but they appear on an e-commerce site like Google Shopping and link to an organization's product page. These ads include an image of the product, along with its name and price.
SEM ads offer marketers a quick way to get their brands, content and products in front of their target audiences.
2. SEO takes longer to deliver results than SEM
An SEO strategy can take anywhere from three months to two years to offer significant ranking improvements, whereas an SEM campaign can increase an organization's web traffic within hours.
The digital marketing industry has become highly competitive. To reach the top of a SERP organically, organizations need a comprehensive library of high-quality content, backlinks from external sites and a positive UX for visitors -- all of which take time.
SEM, on the other hand, can generate traffic immediately after marketing teams launch a campaign on a platform like Google Ads. Before a campaign launch, marketers must research their target audience and craft high-quality landing pages for their ads, which can take some time. However, once teams have these landing pages in place, the SEM campaign can immediately bring in paid traffic.
3. SEO costs more than SEM in the short-term
SEO doesn't cost money in the way that SEM ads cost per engagement, but organic visibility requires investing time and effort into SEO. Organizations that want to improve their SEO strategies might need to hire SEO strategists or invest in relevant tools. Because results can take months or years to offer an ROI, SEO has a high upfront cost.
On the other hand, once an organization achieves organic visibility, it can receive lots of traffic for no charge, which makes SEO highly profitable in the long run. With SEM, marketing teams can see instant results. However, when the budget runs out, visibility often drops to where it was before the campaign launch.
Should marketers use SEO or SEM?
For most organizations, an effective marketing strategy focuses on both SEO and SEM because the two processes complement each other. For instance, SEO can help marketers create effective landing pages for their SEM campaigns. Similarly, new sites can use SEM campaigns to generate traffic, which can help them gain backlinks and improve SEO.
In some cases, an organization might only want to use one of these strategies. For example, organizations with a limited marketing budget might want to focus strictly on SEO. On the other hand, marketing teams that need quick results or lack the resources to create optimized content choose to focus on SEM. However, once organizations can supplement their SEO strategies with SEM, they typically do.
Editor's note: This article was originally published in 2022 and was updated to reflect changes in SEO and SEM best practices.
Tim Murphy is associate site editor for Informa TechTarget's Customer Experience and Content Management sites.








