What is RCS messaging (RCS chat)? Explaining how to use it
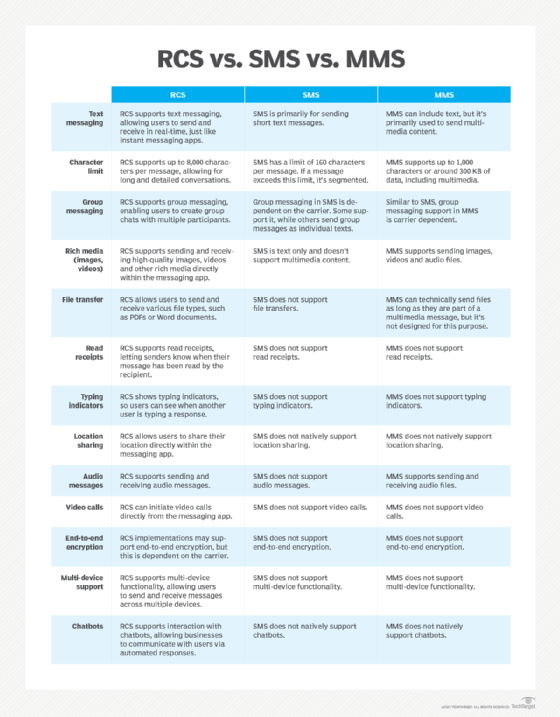
RCS, or Rich Communication Services, is a messaging protocol used in mobile devices. It improves traditional Short Message Service (SMS) text messaging by enabling users to send and receive higher-quality media while providing features such as read receipts, group chats and typing indicators.
RCS was originally developed by the nonprofit GSMA (Global System for Mobile Association) to replace SMS; Google later played a major role in its adoption and standardization across Android devices. RCS is now available on Android and Apple devices.
RCS operates over the internet using mobile data, as opposed to relying on carrier networks like SMS and Multimedia Messaging Service (MMS). This enables RCS to offer features like high-resolution media sharing and end-to-end encryption and allows it to compete with other messaging apps like Apple's iMessage and Meta's WhatsApp.
Why are Rich Communication Services important?
RCS makes messaging more interactive and practical for individuals and businesses. SMS cannot meet most users' expectations for more engaging communications and chat tool options, but RCS can.
Unlike SMS, which is limited to text and relatively low-quality images and audio files, RCS lets users share high-resolution photos and videos, audio messages and files. RCS affords broader participation than SMS, letting users create and coordinate group chats with multiple people simultaneously.
RCS technology is also increasingly prevalent in business activities, from marketing to enabling users to order a product or service directly using a message. Overall, RCS provides a more secure and reliable way for people to communicate in a personalized, interactive fashion.
Enhanced RCS chat features and use cases
RCS has many modern messaging features that users will be familiar with, including the following:
- High-quality media. Compared to SMS/MMS, users can send much higher-quality images and videos to one another using RCS, with limited compression.
- Higher character limits. RCS supports much higher character limits for messages than SMS, which is ideal for users who need to send longer messages.
- Read receipts. RCS shows when a recipient receives and reads a message, which is essential for some users when communicating important information.
- Typing indicators. RCS enables users to see when someone is typing, helping to create a more dynamic messaging experience.
- Encryption. RCS messages have improved security over SMS, offering encryption options like end-to-end encryption. The use of encryption, though, depends on the type of message and carrier and device support.
- Reactions. RCS enables users to react to messages, labeling them with emojis like a thumbs up, a laughing face or a heart.
- Audio messaging. Users can send audio messages during one-on-one or group conversations.
- Location sharing. Users can easily share location information in both one-on-one and group chats.
How does RCS messaging work?
RCS can send messages through mobile data or Wi-Fi. However, it only works when both communicating parties have RCS enabled. Messages sent to another party who does not have RCS will instead be sent as SMS or MMS messages.
RCS also uses the Session Initiation Protocol to create and maintain communication sessions and the Message Session Relay Protocol to send messages and preserve their integrity.
RCS messages are sent through an RCS back-end infrastructure. Originally, users had to rely on their mobile carriers -- like Verizon or AT&T -- to support and provide RCS infrastructure. Available options have since expanded, however. For example, Google's Jibe Cloud platform is a globally offered RCS messaging infrastructure that enables carriers to provide RCS services without building and maintaining their own back end. Likewise, Apple has its own independently implemented RCS back end for Apple devices.
How is RCS different from other messaging protocols?
RCS is not the only available messaging protocol for mobile devices. There are also SMS/MMS, iMessage and Over-The-Top (OTT) messaging protocols.
SMS/MMS
SMS and MMS are two different but commonly grouped protocols. SMS/MMS services use cellular network infrastructures and are limited to the amount of data they transmit. SMS is limited to 160 characters, and MMS can send up to 1,600 characters in text. The media MMS can share is typically constrained to a file size limit, with higher-quality media needing to be heavily downscaled and compressed before sending. SMS and MMS are universally supported, but also lack many modern features.
RCS
RCS acts as an overall upgrade to SMS/MMS. It uses mobile data or Wi-Fi and is much less restrictive than SMS/MMS. RCS does not innately have a character limit for text. Images and videos can be sent in much higher quality, with a file size limit of 100 megabytes (MB) for videos, for example.
RCS also includes modern features not found in SMS/MMS, such as read receipts, typing indicators and end-to-end encryption.
OTT
OTT is a protocol category that refers to third-party messaging apps like WhatsApp, Facebook Messenger or Discord.
These protocols operate over the internet, as opposed to protocols that require traditional carrier networks. Each app uses its protocols, meaning that the amount of data it can send, the amount of compression and the security offered change depending on the app used. OTT messaging apps typically offer text and media sharing, typing indicators and the ability to have group chats.
IMessage
Apple's messaging protocol, iMessage, is based on the Apple Push Notification service. It works over mobile data or Wi-Fi. It has no official character limit and can send high-resolution images and video of about 100 MB with some level of compression. It also has modern message features like read receipts, typing indicators and end-to-end encryption. However, it is limited to Apple devices. Using the iMessage app, messages received from another Apple device appear blue, while messages received from a device using RCS or SMS/MMS appear green.
Benefits of RCS
RCS provides a powerful communication protocol for both individuals and organizations. Its many benefits include the following:
- Enhanced messaging. RCS delivers a more engaging and interactive messaging experience, enabling users to send rich media, such as high-quality images and videos, and engage in group chats, file transfers and voice and video calls.
- Improved customer engagement. RCS enables businesses to send rich media messages -- such as product catalogs, video demos and personalized promotions -- to their customers.
- Increased revenue. RCS allows mobile operators to generate revenue through the sale of enhanced messaging services, such as premium SMS and sponsored messages.
- Better collaboration. RCS enables group chats and file transfer, making it easier for business teams to share information.
- Wide reach. RCS is supported by an increasing number of messaging platforms, including Google Messages, Android Messages and now iOS, making it a widely accessible communication protocol.
- Security. RCS uses advanced security protocols, such as encryption and authentication, to ensure messages are delivered securely and confidentially.
- Future-proof. RCS is designed to enable future updates to support new features and capabilities.
Challenges of RCS
Like any beneficial technology, RCS also has its own set of challenges, including the following:
- Security concerns. RCS supports using advanced security protocols, such as encryption and authentication, to protect messages from interception and eavesdropping. However, the security protocols are uneven among network operators. Some do not implement or fully support these advanced protocols, creating security vulnerabilities.
- Lack of user awareness. Because many users are unaware of RCS or its capabilities, businesses must find ways to circumvent this difficulty and effectively communicate with their customers.
- Competition from other messaging apps. Popular messaging apps like WhatsApp and Facebook Messenger are well-established challengers to RCS.
- Technical complexity. Implementing and maintaining RCS requires technical expertise, making it challenging for small businesses or organizations to adopt and use without Google's Jibe platform.
- Cost. RCS can require additional infrastructure and resources to implement and maintain.
What devices support RCS chat?
RCS is now available on most mobile devices. When it was first rolled out, it was only available from specific mobile carriers on Android devices -- and the Google Messages app became the platform for RCS messages on Android.
Apple did not support RCS messages until recently. Instead, the company pushed its iMessage platform in a walled garden approach -- even going so far as to differentiate when a message was sent using another protocol like SMS by making the message bubble green instead of blue. However, Apple rolled out support for RCS at the end of 2024 with the release of iOS 18. Now, Apple and Android devices can communicate using the same RCS protocol.
Is RCS chat available globally?
Originally, RCS was only available from a select few mobile carriers that dedicated a back end to support it. Since then, however, RCS has seen significant adoption globally. Many carriers support some level of RCS, and Google has increased its accessibility thanks to its Jibe cloud service. Now, organizations that do not have the back end to support RCS can still support it in their messaging services.
This is not an entirely open process, however. Organizations wanting to implement RCS must either license Google's Jibe platform or go through GSMA's licensing and certification process when implementing their infrastructure.
How to turn on RCS chat
The processes of turning RCS on and off differ by device.
How to activate RCS on iOS
On iOS devices using iOS 18, perform the following steps:
- Open the Settings app.
- Scroll down and tap on Apps.
- Then scroll down and tap on Messages.
- Select RCS Messaging under the Text Messaging section.
- There is an option to turn RCS messaging and RCS Business Messages on or off.
How to activate RCS on Androids
The process for turning on RCS messaging on Android devices is generally similar across most Android devices, but there might be small variations depending on the type of device. As an example:
On an Android Phone using Google Messages, perform the following steps:
-
- Open Google Messages.
- Tap on the user's profile picture or icon.
- Select the Messages" setting.
- Select "RCS chats" or "Chat features."
- From here, RCS can be toggled on or off.
RCS history
The development of rich communication services traces back to the aughts, when the mobile industry began exploring ways to enhance SMS messaging. The following are some key milestones in the development of RCS:
- 2007. The basic concept of RCS was introduced by a group of industry promoters led by telecom companies. They aimed to enhance traditional SMS and MMS messaging with features found in popular internet-based messaging apps.
- 2008. GSMA officially adopted RCS and published initial specifications.
- 2011. GSMA released a simplified RCS-e, enhanced version to speed up adoption.
- 2012. Spain's major telecom operators launched RCS-e services under the Joyn brand.
- 2015. Google acquires Jibe Mobile.
- 2016. GSMA launched the RCS Universal Profile to standardize RCS across different mobile networks and devices.
- 2019. Google began releasing RCS to its Android users, quickening the pace of overall adoption.
- 2021. Google enabled end-to-end encryption in Google Messages.
- 2024. Apple began supporting RCS with the launch of iOS 18.
For a time, RCS could have been a factor for businesses deciding on employee devices, but now that Apple supports RCS, it is no longer a factor. Learn more about how iPhones and Androids compare for use in enterprise settings.