What is quantum in physics and computing?
A quantum, the singular form of quanta, is the smallest discrete unit of any physical entity. For example, a quantum of light is a photon, and a quantum of electricity is an electron. Quantum comes from Latin, meaning an amount or how much. If something is quantifiable, it can be measured.
What is quantum in physics?
German physicist Max Planck introduced the modern concept of quantum in physics in 1901. He was trying to explain blackbody radiation and how objects changed color after being heated. Instead of assuming that the energy from heat was emitted in a constant wave, he posed that the energy was emitted in discrete packets or bundles. These were termed quanta of energy. This led to him discovering Planck's constant, which is a fundamental universal value.
Planck's constant is symbolized as h and relates the energy in one photon to the frequency of the photon. Further units were derived from Planck's constant: Planck's distance and Planck's time, which describe the shortest meaningful unit of distance and the shortest meaningful unit of time. For anything smaller than a unit, such as a particle variable, physicist Werner Heisenberg's uncertainty principle postulated that variables of a particle had inherent uncertainty in position and momentum when measured, so these variables couldn't be definitively measured.
The discovery of quanta and the quantum nature of subatomic particles led to a revolution in physics, and to the birth of quantum physics. Before the quantum discovery, the physics world revolved around Albert Einstein's theory of relativity, which described the behavior of macroscopic things. In contrast, quantum theory described the behavior of microscopic particles, which became known as quantum theory, or quantum mechanics. Einstein's theory of relativity and the microscopic focus of quantum theory became the two theories underpinning modern physics. Unfortunately, they deal with different domains, leaving physicists seeking a unified theory of everything.
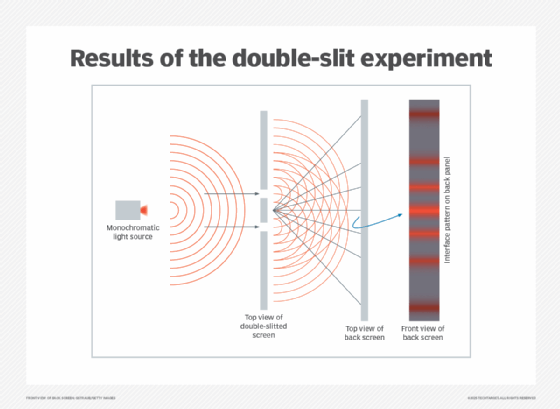
In 1801, English physicist Thomas Young revealed the quantum nature of light in his double-slit experiment. In his experiment, a wave was split into two separate waves and projected upon a screen, demonstrating that light behaves as both a wave and a particle.
Subatomic particles behave in ways that are counterintuitive. A single photon quantum of light can simultaneously go through two slits in a piece of material, as shown in the double-slit experiment.
Schrödinger's cat is a famous thought experiment that describes a quantum particle in superposition, or the state where the probability waveform hasn't collapsed, and where multiple states or probabilities can exist simultaneously. Particles can also become quantumly entangled, causing them to interact instantly over a distance.
What is quantum in computing?
Quantum technology uses the nature of subatomic particles to perform calculations instead of electrical signals like classical computing. Quantum computers use quantum bits or qubits instead of binary bits. By programming the initial conditions of the qubit, quantum computing can solve a real-world problem when the superposition state collapses and where multiple coexisting probabilities resolve into a single outcome.
This enables the processing of complex artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms that are too numerically intensive for the electrical processing workflows of classical computing power to undertake. The forefront of quantum computer research is linking greater numbers of qubits to solve larger, more complex problems.
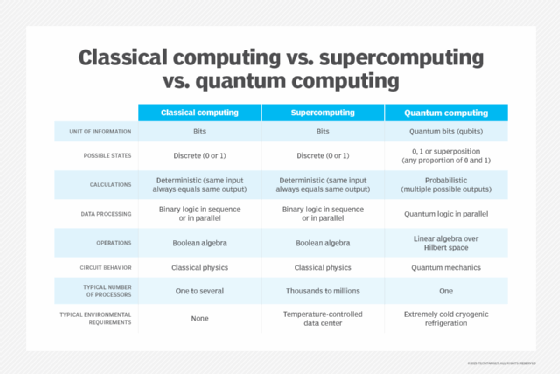
Quantum systems from Google, IBM, Microsoft and others benchmark quantum computer performance by measuring factors such as volume, which in quantum computing means the amount of computational space a circuit can process while still being able to return an accurate result. It's already been ascertained that quantum computers can perform certain calculations much faster than classical computers because they must go through each processing option one at a time. It can take a long time to go through all the options for some types of problems. Quantum computers don't need to try each option; they resolve the answer almost instantly.
Some problems that quantum computers can solve quicker than classical computers are factoring for prime numbers and the traveling salesman problem, which involves processing an algorithm to find the shortest route between a set of points and locations that must be visited. Once quantum computers demonstrate the ability to solve these problems faster than classical computers, quantum supremacy will be achieved.
The future of quantum computing
Market.us reports that the global market for quantum computing will reach $8.28 billion by 2032.
Quantum computing is rapidly growing, driven by public and private sector investments. Industries are realizing its potential in areas that require immense computational capabilities not even possible with the largest supercomputers.
The following highlights potential advancements in the field of quantum computing across various industries and sectors:
- Healthcare and pharmaceuticals. Quantum computing has the potential to accelerate drug development, and quantum-enhanced AI models could enable earlier disease detection.
- Cybersecurity. Quantum cybersecurity uses quantum computing and the laws of quantum mechanics and computer science to develop modern cryptography systems that secure digital communication. Experts expect quantum computers to render existing cryptographic systems insecure and obsolete. Efforts to develop post-quantum cryptography are underway to create algorithms resistant to quantum attacks but can still be used by classical computers. Eventually, full quantum cryptography will be available for quantum computers.
- Supply chain and logistics. Quantum computing can potentially speed up the loading and shipping of goods from one place. Optimizing routes could help reduce fuel consumption.
- Finance. Quantum technology could help optimize financial portfolios and detect fraudulent transactions.
- Climate forecasting. Quantum technology, combined with machine learning, has the potential to enable more accurate weather predictions, helping provide better preparedness for extreme weather events.
Quantum computing has many potential uses. Learn which areas organizations could apply quantum computing technology to increase efficiency and reduce costs.