What is prediction error?
A prediction error is the failure of a model of a system to accurately forecast outcomes. It is the difference between the predicted and measured value. The mean absolute error, mean squared error and mean squared predictive error are among several methods used to calculate accuracy of the predictive model.
Errors are an inevitable element of predictive analytics that should be quantified and presented along with any model, often in the form of a confidence interval that indicates the expected accuracy of predictions. Analysis of prediction errors from similar or previous models can help determine confidence intervals.
It is impossible to eliminate prediction errors. Instead, the goal is to minimize and classify the error. When the potential error is understood, an analyst can have confidence in the values given and make decisions based on the predicted values.
Predictive analytics software processes new and historical data to forecast activity, behavior and trends. The programs apply statistical analysis techniques, analytical queries and machine learning algorithms to data sets to create predictive models that quantify the likelihood of a particular event happening.
Types of prediction errors
The underlying training data is often the source of prediction errors in machine learning (ML) models. Here are some common problems:
- Bias. Bias is a given input that is over- or undervalued compared to an objective value.
- Underfitting. The training model is not complex enough to capture the important characteristics of the data, resulting in overgeneralized guesses as the output.
- Overfitting. With overfitting, the training model is too complex and captures noise or unwanted features of the training data, resulting in an overly sensitive output.
- Variance. Small changes in the training data cause large changes in the final model.
- Generalization error. The model makes poor predictions when given novel data outside the training set.
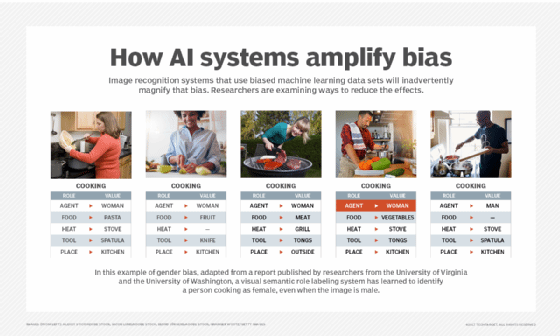
Prediction errors in AI and ML
In AI, the analysis of prediction errors can help guide ML, similarly to the way it does for human learning.
In reinforcement learning, for example, an agent might use the goal of minimizing error feedback as a way to improve. Prediction errors, in that case, might be assigned a negative value and predicted outcomes a positive value, in which case the AI is programmed to attempt to maximize its score. That approach to ML, sometimes called error-driven learning, seeks to stimulate learning by approximating the human drive for mastery.
ML has many more potential uses than statistical analysis. ML tools might be used in speech recognition or machine vision tasks. In such tasks, the parameters and features of the data and model can be examined to determine why the model misclassified a given input.
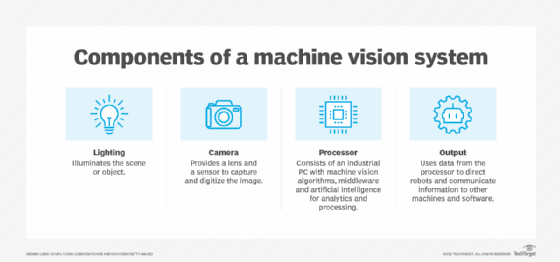
When building a model on table data, it can be difficult to determine what caused the error. The exact correlation between the values and why a specific output is given may not be intuitive.
How to minimize prediction errors
Human analysis of prediction errors is crucial. When predictions fail, humans can use metacognitive functions, examining prior predictions and failures and deciding, for example, whether there are correlations and trends, such as consistently being unable to foresee outcomes accurately in particular situations.
Applying that type of knowledge can inform decisions and improve the quality of future predictions. These additional steps can help minimize prediction errors:
- Data sanitization. Inspect source data for outliers, incompleteness and inaccuracies.
- Data transformation. Normalize and format the data.
- Parameter tuning. Select and test different model training parameters.
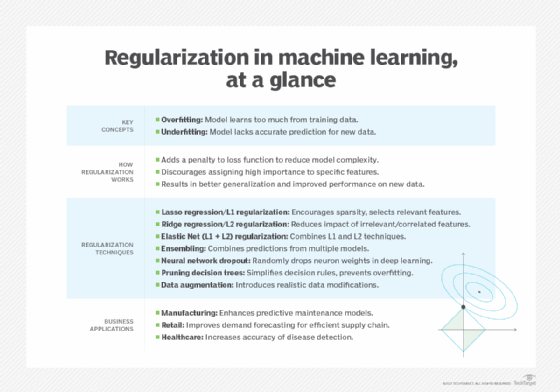
- Regularization. Use L1 or L2 regularization to penalize errors and avoid overfitting.
- Prediction testing. Analyze model outputs in a controlled setting, and refine as needed.
The performance of any predictive model should be evaluated continually. Are the given outputs over an acceptable error threshold? Has the input data changed from when the model was trained? Is the model still meeting key success criteria? Iterating and continually refreshing the model can help to minimize prediction errors.
Regularization in ML represents a valuable set of techniques that can help mitigate the risk of overfitting. By employing these strategies, data scientists can enhance the performance of ML models and reduce potentially costly errors, ultimately benefiting the overall outcome of their work. Learn more about ML regularization with examples.