What is pattern recognition?
Pattern recognition is the ability to detect arrangements of characteristics in data that yields information about a given system or data set. Pattern recognition is a main ability of machine learning (ML), data analytics and AI.
In a technological context, a pattern might be recurring sequences or aspects in data that can be used to make a prediction. These patterns might be simple relationships between variables, or they might be complex multifaceted relationships that use several variables. Pattern recognition is using computers and algorithms to find and make predictions based on the hidden relationships within data.
A simple example of pattern recognition would be an algorithm that tries to determine a person's gender based on their shopping history. It might classify someone who buys makeup and skirts as female, and someone who buys sports memorabilia and work boots as male. This prediction might be then fed into another system to make recommendations for future purchases.
If the process leads to a wrong prediction or it classifies something the wrong way, it is known as a prediction error.
Where is pattern recognition used?
Pattern recognition is one of the most powerful abilities of mathematics and computers. It has found applications in almost every area of modern science, technology and industry.
Over time it can be used to predict trends, find particular configurations of features in images that identify objects, detect frequent combinations of words and phrases for natural language processing (NLP), or locate particular clusters of behavior on a network that could indicate an attack -- among almost endless other possibilities.
Pattern recognition is essential to many overlapping areas of IT, including big data analytics, biometric authentication, security and artificial intelligence.
Some examples of pattern recognition include the following:
- Facial recognition software takes in data related to the characteristics of a person's face and uses an algorithm to match that specific pattern to an individual record in a database.
- Pattern recognition algorithms in meteorological software can detect recurring relationships among weather data that can be used to forecast probable future weather events.
- Intrusion detection systems (IDS) and threat intelligence hunting software rules describe patterns of behaviors and events that can indicate illegitimate network traffic.
- Machine vision uses pattern recognition to classify the input from a camera. A simple system for industrial use might be trained for a very specific purpose, such as determining if an apple is ripe or not. A more complex system might be trained to detect and classify many objects in a live video feed.
- Accounting and financial systems might use pattern recognition to predict sales data or forecast expenses. Other systems might be able to detect fraudulent activity on an account.
- Large language models (LLM) use pattern recognition at their core. They use incredibly large data sets to find the hidden relationships among words and use them to make a prediction of what word to use next based on a given input.
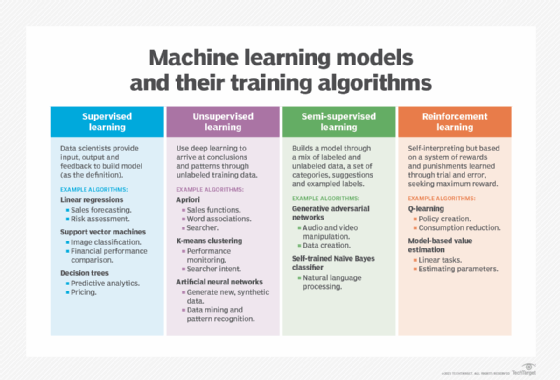
How does pattern recognition work?
There are myriad methods of pattern recognition, but they can be broadly classified as either supervised learning or unsupervised learning.
With supervised learning prelabeled and structured data is used to try to produce specific outputs. In unsupervised learning, the training data is unorganized and the system is used to identify important characteristics.
Some methods use bits of both approaches, called semisupervised learning. In reinforcement learning, the model is further refined as it receives user feedback when it produces good or bad output.
Several steps are typically used while developing a pattern recognition system:
- Data collection. Information is gathered, sorted and preprocessed.
- Feature extraction. Important features of the data are identified and then used to make predictions.
- Classification. The extracted features are analyzed to find the needed relationships and make predictions.
Further post-processing and refinement stages might be applied.
Statistical methods use mathematics to detect and classify the input. For numeric data, this can be simple mathematical regressions or linear mathematics. Other data might be converted into vectors, which can be operated on mathematically.
Neural networks do pattern recognition by simulating a neural pathway. The decision-making is stored as the relationship between the nodes in the network.
In clustering methods, similarities are found in certain attributes that can be used to identify subgroups.
In syntactic methods, the relationships and hierarchy among the data are used. These can be rules or decision trees. This is similar to how the syntax in a language describes how words are grouped.
In fuzzy systems, a level of uncertainty is kept in the process. The output might allow for multiple or incomplete matches. This can help in situations where the data is unclear or organic in nature.
Template matching is the simplest method. Rules for what attributes correspond to what output are developed and applied.
AI is similar to human intelligence, but there are important differences between them. Here are some key ways that AI and human thinking differ.