What is a northbound interface/southbound interface?
A northbound interface (NBI) is an application programming interface (API) or protocol that allows a lower-level network component to communicate with a higher-level or more central component; conversely, a southbound interface (SBI) allows a higher-level component to send commands to lower-level network components. Northbound and southbound interfaces are most associated with software-defined networking (SDN), but can also be used in any system that uses a hub-and-spoke -- also called star -- or controller-and-nodes architecture.
Northbound interface and southbound interface in simple terms
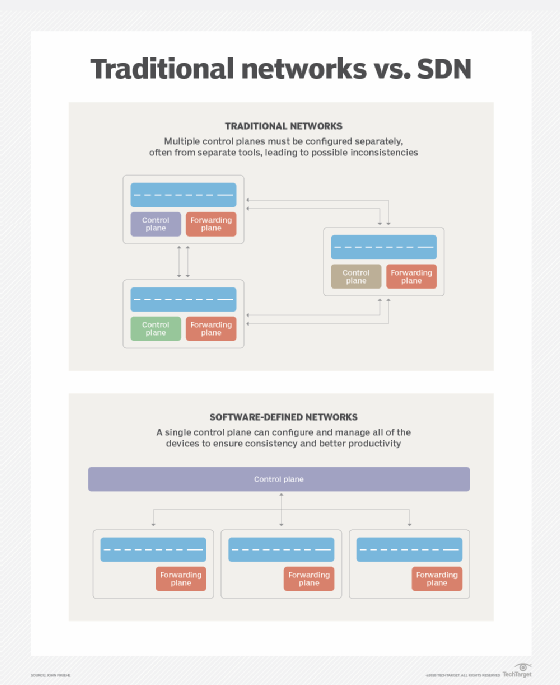
In the context of networking, north and south can be thought of as directions on a map. The north is on the top and south on the bottom of the diagram. Using these cardinal directions helps to visualize internal network communications and how control moves from the top, or north, to the bottom, or south, of a network.
All networks consist of both higher-level elements and lower-level elements. Examples of the former include tools for network automation, network orchestration, administration consoles, network analytics and other management systems. Examples of lower-level elements include switches and routers.
The higher-level elements control the lower-level ones. At the same time, the network's lower-level components need to communicate with its higher-level components using APIs.
Some network designs also have east-west interfaces for communication among peers, also called peer-to-peer communication. These interfaces facilitate communication between the components -- servers, for example -- within the same data center or cloud environment.
What is northbound and southbound traffic in networking?
It is easy to confuse northbound/southbound interface with northbound/southbound data flow or traffic. The interface -- northbound or southbound -- defines the sender, receiver and data format; it expresses the conceptual level of communication and covers the entire bidirectional API.
Conversely, if data or traffic is said to be northbound, southbound or east-west, that merely describes whether it is going toward or away from the network core. It is therefore possible to say that a southbound command went from the core to a node over the northbound interface.
Simply put, north-south traffic refers to traffic coming in and going out of the internal network. For example, data traveling between a network server and an external client over the internet is north-south traffic. In contrast, east-west traffic is the internal traffic moving between devices within a network.
It's important to understand the flows of both north-south and east-west traffic for security reasons. The more north-south traffic there is in a network, the greater the chances of a cyberattack originating from outside that network. Ransomware attacks and data breaches often occur when there are inadequate security controls to manage and control north-south traffic because these attacks typically originate from outside the network.
Benefits of northbound and southbound interfaces
Northbound interfaces abstract the inherent complexities of networks, thus simplifying network management. Also, they provide enhanced flexibility and programmability in system configurations, making them essential for efficiently deploying and integrating the various applications and services in the network.
Other benefits of NBIs include the following:
- Centralized network management and control.
- Efficient resource allocation.
- Faster application and service deployment.
- Easier application customization.
- Real-time monitoring of network infrastructure.
- Network automation and orchestration.
Northbound interfaces help improve network efficiency, flexibility and agility. By reducing unnecessary complexity, they can also reduce the network's operational expenses and improve its return on investment.
Southbound interfaces, on the other hand, play a crucial role in policy implementation. They are also useful for creating actionable and feasible configurations for network devices. Without them, it can be difficult to translate the high-level commands from network management systems into practical configurations. SBIs can also help to improve network control and management.
Northbound and southbound interfaces in software-defined networking
In SDN and virtualized networks, the network logical design and data flows are set by software configurations instead of through hardware or physical cabling changes. SDN helps IT administrators to set up highly flexible network infrastructure, which in turn enables organizations to quickly adapt to evolving business requirements. The configuration of the elements is set by the SDN controller, which sits in the control layer at the center of the network diagram, with north and south established in relation to it.
It is important to note that in SDN, the northbound and southbound interfaces are for networking control commands and APIs. The data or traffic carried by the network stays on the data layer and does not traverse the northbound and southbound interfaces.
Northbound interface in SDN
The northbound interface in SDN provides a standardized approach for communication between the highest application layer and the SDN controller at the middle control layer. It thus enables the efficient exchange of network information between the SDN controller and high-level applications. The application layer consists of network orchestration services, networking design software, operator software or third-party applications that make decisions about the overall structure of the network.
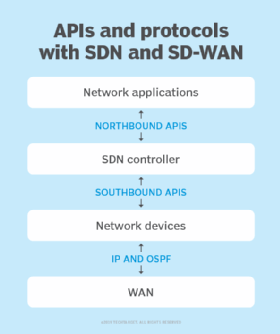
In SDN, the operator or orchestration software does not directly issue commands or configurations to the network nodes. Instead, the operator uses the application layer to issue commands to the control layer over the northbound interface.
The northbound interface is often a representational state transfer API, or REST API, exposed by the SDN controller. Various SDN controllers provide northbound interfaces to enable easy software-defined network management and control. These include the OpenDaylight platform, Open Networking Operating System and Cisco Application Policy Infrastructure Controller.
Southbound interface in SDN
The southbound interface in SDN is the communication between the SDN controller at the middle control layer and the lower networking elements at the data layer. The data layer consists of the physical or virtual network switches and ports.
The SDN controller takes the desired state of the network and translates it into specific commands and configurations that are then pushed to the network devices over the southbound interface. SBIs enable the controller to operate efficiently and to make fast adjustments in response to real-time business requirements.
Popular southbound interface standards are Simple Network Management Protocol, OpenFlow and Open Shortest Path First. Other protocols available for southbound APIs include Network Configuration Protocol, Multiprotocol Label Switching and Intermediate System to Intermediate System.
Examples of northbound and southbound interfaces
An example of how the northbound and southbound interfaces are used is a network engineer defining a specific data route with network orchestration software. The orchestration software sends the instructions to the SDN controller over the northbound interface. The SDN controller then sends the specific configurations to the physical switches over the southbound interface.
A more detailed example is Microsoft Azure software load balancing. The network controller is at the center layer and runs the software load balancer (SLB). The network operator sits at the application layer and uses Windows Admin Center to set the desired state. Windows Admin Center uses PowerShell as the northbound interface to send the commands to the SLB. The SLB then sends Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) updates as the southbound interface to the virtual routers on the data layer. If the SLB finds an error in a router, it can automatically send the new configurations to the other routers through the southbound interface BGP, and then send a notification through the northbound interface to alert the operator of the issue.
Northbound and southbound interfaces in other systems
The concept of northbound and southbound interfaces can also be used in systems with automated control systems and nodes. It can be used when components communicate with different APIs or where an orchestrator is used. The use of separate interfaces contrasts with using a bus architecture.
In a software-defined network, the data center controllers are essential components. When evaluating controller options, consider factors such as performance and compatibility. Learn what SDN data center controllers do in a network.