microphone
What is a microphone?
A microphone is a device that translates sound vibrations in the air into electronic signals and scribes them to a recording medium or over a loudspeaker.
Microphones enable many types of audio recording devices for purposes including communications of many kinds, as well as music vocals, speech and sound recording.
Microphones can be standalone or embedded in devices such as headsets and telephones.
How do microphones work?
The most common type of microphone, the dynamic microphone, uses a coil suspended in a magnetic field that may be attached to multiple membranes for extended frequency response.
Dynamic microphones use electrical energy in the form of induction to produce the audio signal. These microphones are well suited to stage performance.
The microphone capsule contains a small diaphragm connected to a moving coil. When sound waves hit the diaphragm, it vibrates. This causes the coil to move back and forth in the magnet's field, generating an electrical current.
However, how a microphone works ultimately varies depending on its designed purpose.
One of the main considerations, aside from the type of device, is what is being recorded. The directionality of microphones is another consideration in microphone design.
Other types of microphone
Let's now look at a few different types of microphones based on their intended purpose.
Omnidirectional microphones
Omnidirectional microphones are suited to recording all sounds in an area but are poor for focusing on a single subject among background noise.
An example of an omnidirectional microphone is the lavalier microphone, which is often used in television production.
Directional microphones
Directional microphones, also referred to as unidirectional, are better at picking up sounds from a particular direction and are useful in situations where there is significant background noise.
Shotgun microphones are a type of directional microphone often used in film and television production to record audio from a distance.
Cardioid microphones are another type of directional microphone that is commonly used for live music recordings and performances.
Bidirectional microphones
Bidirectional microphones are designed to pick up sounds from two directions, making them ideal for recording conversations.
An example of a bidirectional microphone would be those used for dictation machines.
Condenser microphones
Condenser microphones use the varied electrical charge of a capacitor with a diaphragm acting as one of the plates of a capacitor. The plate is biased by a fixed charge, often from a battery which also amplifies the signal.
The capacitance varies with the movement of the diaphragm in relation to the other plates providing the means to record the sound in the electrical signal.
For example, electret microphones are used in cellphones and computers as a type of condenser microphone that uses a polarized ferroelectric material.
Laser microphones
Laser microphones use the vibrations of surfaces affected by sound waves to capture sound at distances. The lasers return at different angles due to the vibration and these changes are interpreted and translated into sound waves.
Laser microphones are used in situations where sounds need to be recorded from a distance.
Ribbon microphones
Ribbon microphones are made using a thin strip of conductive metal that is suspended in a magnetic field. The ribbon is usually made from aluminum, duralumin or nanofilm.
When sound waves hit the microphone, the ribbon vibrates, which in turn produces an electrical signal.
Ribbon microphones are often used in studios for recording music as they tend to produce a smooth, natural sound.
Microphones vs. speakers
Due to similarities in function, microphones can operate as speakers. Generally, microphone-derived speakers are suited to high-frequency sounds like the STC company's microphone-derived super-tweeter.
Speakers can also operate as microphones, although they are generally suited for the capture of low frequencies.
The history of microphones
The first electronic microphone was a liquid-based mechanism that used a diaphragm attached to a current-charged needle in a diluted sulfuric acid solution. This early microphone was not able to reproduce intelligible speech.
The first viable diaphragm microphones used a sheet of metal attached to a needle that scribed transmitted vibrations to a foil recording medium.
When the needle moved over the foil after the scribing, the process was reversed and translated back to sounds again through the same metal diaphragm.
The crude carbon rod microphone was invented by David Edward Hughes in 1878 and was instrumental in the development of telephony.
These devices used the variable electrical resistance of carbon under pressure between metal plates to translate airborne sound waves into an electrical signal.
Another example of one of the earlier versions of the microphone is the crystal microphone. Crystal microphones use a piezoelectric crystal that generates small amounts of electricity under the compression of a diaphragm to provide the recording signal.
Crystal microphones, like carbon microphones, were also used in early telephones in the 1930s.
Microphones today
With the technological advances in microphone design, there are now many different types of microphones available to meet the needs of a variety of applications.
Digital microphones have also become increasingly popular in recent years as they offer improved sound quality and durability. Additionally, wireless microphones are now commonly used in a variety of settings, from live concerts to television production, although there are still many applications for analog microphones, due to their availability and affordability.
Either way, microphones are an essential piece of technology in today's world and will continue to play a vital role in the years to come.
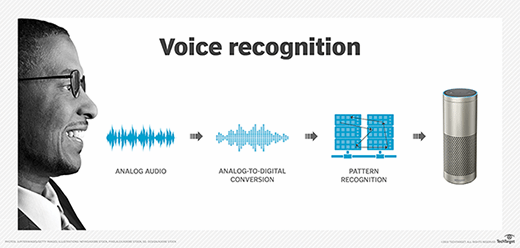
See also: electret microphone, voice recognition, medical transcription, smart speaker, binaural sound, quantum microphone, audio frequency
