
What is lift and shift?
Lift and shift is a strategy for moving an application or operation from one environment to another without stopping to redesign its workflow. The application or operation complexity is a key factor in deciding whether something should be lifted and shifted or re-architected from scratch as a new native cloud app or operation.
Lift and shift is also known as rehosting. It's usually used to move an app and its associated data from an on-premises data center to the public cloud.
In the early days of cloud computing, the lift-and-shift migration approach was often used to replicate on-premises apps in the cloud, while avoiding costly, time-consuming redesign. However, many legacy colocation applications that were lifted and shifted to the cloud couldn't take full advantage of the cost efficiencies of native cloud features, such as autoscaling. While commercial, off-the-shelf applications with easily defined patterns were good candidates for lifting and shifting, re-architecting was a better option for resource-intensive apps, such as those used for big data analytics and image rendering.
In recent years, the role of lift and shift has evolved with enhanced developer efficiency and better pricing models. It continues to be used in specific scenarios, such as large organizations seeking a quick initial migration of legacy applications that are difficult to re-architect and when migrating VMware environments. However, there's a growing recognition that relying solely on lift and shift can't yield the full benefits of cloud computing.
According to Forrester, organizations are focusing increasingly on cloud-native development and application modernization. With those approaches, lift and shift is often used in conjunction with other strategies to achieve long-term cloud adoption goals.
Top lift-and-shift use cases
The lift-and-shift strategy is best suited for specific situations, such as the following:
- Third-party applications that can't be re-factored or modified, only lifted and shifted.
- Legacy applications that are difficult to refactor or replatform because of their age or complexity.
- Businesses operating under a time constraint that must migrate their applications fast and cheaply.
- Hybrid cloud deployments in which an organization must maintain its existing on-premises infrastructure for some workloads, while using the cloud for others.
- Organizations in regulated industries require advanced security, monitoring and compliance capabilities. Migrating their applications to the cloud helps achieve these goals.
Benefits of lift and shift
The lift-and-shift cloud migration strategy offers the following advantages for businesses that have applications they want to move to the cloud:
- Speed. Lift-and-shift migration is often the fastest way to migrate applications to the cloud. By minimizing the need for redesign or modification, businesses can quickly transfer their existing applications and workloads to the cloud platform.
- Simplicity. This migration method often requires minimal changes to the existing application, making it straightforward and efficient. Lift and shift lets businesses focus on other aspects of their digital transformation while ensuring a smooth transition to the cloud.
- Cost savings. Lift and shift is considered a less expensive upfront option for cloud migration service. A lift-and-shift migration strategy enables companies to optimize their spending on IT infrastructure and reduce overall costs.
- Minimal business disruption. Lift and shift doesn't involve substantial changes, enabling organizations to maintain functionality and user experience during migration.
- Scalability. Lift and shift plays a role in overall data management, moving data to cloud storage, which enables on-demand autoscaling, eliminating hardware purchases and over-provisioning.
- Reduced initial risk. Maintaining the existing application architecture reduces the risk of introducing new bugs or compatibility issues, which is especially important for critical applications.
- Improved disaster recovery and backup. Moving workloads to the cloud improves disaster recovery, data redundancy and business continuity strategies.
Disadvantages of a lift-and-shift approach
A lift-and-shift approach has some disadvantages compared with application refactoring, which is also known as re-architecting. While it's usually best to refactor an application as part of a migration to the cloud, sometimes, organizations need to do so retroactively.
- System and environment mismatch. Lifting and shifting is often compared to moving a houseplant from one environment to another -- being in a different habitat can affect whether the plant thrives. Likewise, an IT project that started in an on-premises or original legacy system might not work as well in a new location. For example, a lift-and-shift project that starts without sufficient requirements documentation or operational design can easily go awry. The unfortunate results often involve data that's mismatched to its handling systems or data sets that outgrow their environment.
- Performance-related issues. Resource-intensive apps might need to be redesigned from scratch as cloud-native apps to avoid performance, latency and cloud resource provisioning issues.
- Foregoing cloud-native features. With lift and shift, organizations miss out on the benefits of cloud-native features such as serverless computing, containerization, auto-scaling, automation and microservices. These features significantly improve the performance, scalability and cost-effectiveness of applications.
- Technical debt. Lift and shift can perpetuate technical debt by moving legacy issues and inefficiencies to the cloud, making future modernization efforts more difficult.
- Long-term expenses. While lift and shift can lower initial migration costs, deploying legacy applications on cloud infrastructure without proper optimization can increase cloud expenses over time.
- Refactoring requirements. Refactoring might be necessary when performance fails to meet expectations after a lift and shift, especially when tuning doesn't solve the problem. An application moved to the cloud might benefit from refactoring when costs spike due to application or database inefficiencies. This is also true when vulnerabilities arise because the application can't integrate with native security systems, such as identity and access management tools.
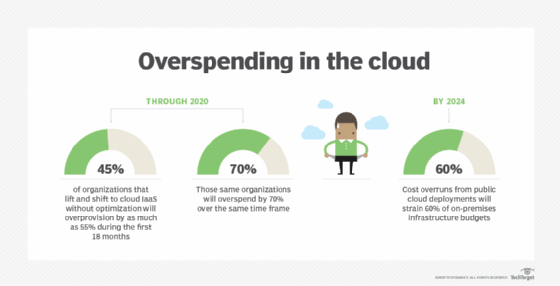
Which cloud migration strategy is right for you?
There are various approaches to cloud migration. Lift and shift is a common strategy. It's an infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) approach to migration that moves an on-premises application as is to a new infrastructure.
Overall, migration strategies are generally grouped into three categories: Lift and shift, refactoring and software-as-a-service (SaaS) offerings. Choosing the right cloud migration strategy depends on an organization's specific needs, existing infrastructure and business goals.
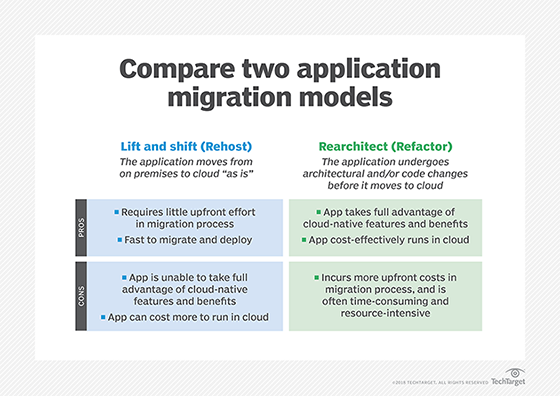
Lift and shift vs. refactoring
Refactoring is a widely used strategy for cloud migration. This approach involves first lifting and shifting applications to the cloud, which helps to reduce on-premises IT infrastructure costs in the short term. After migrating the application to the cloud, the next step is often refactoring it. Refactoring involves modifying components of an application, such as structure, design and code.
Lift and shift and refactoring are also used separately. While lift and shift migrates applications to the cloud with minimal changes, refactoring involves re-architecting applications to take full advantage of the cloud environment. This might mean modifying the application's code or architecture, making it more suitable for the cloud infrastructure and enabling it to use native cloud features.
Lift and shift is cost-effective and requires little upfront effort in the migration process. Refactoring can offer long-term benefits, such as better performance and increased stability. However, these benefits require more upfront time and resources than lift and shift.
Lift and shift vs. SaaS
SaaS is another option for businesses that want to move their applications to the cloud. SaaS offerings are third-party applications that a cloud service provider (CSP) such as Amazon Web Services or Microsoft Azure hosts and maintains. Businesses access and use the software without the need for in-house infrastructure or maintenance.
While lift and shift focuses on migrating existing applications to the cloud, SaaS involves adopting ready-made cloud-based applications that replace the need for on-premises applications. SaaS applications offer several advantages, including reduced costs, faster implementation and simplified management.
However, SaaS might not be suitable for every business or application. Some organizations require more control over their applications or have specific customization needs that SaaS apps can't accommodate. In such cases, lift and shift or refactoring is the more appropriate migration strategy.
Other strategies: The 7 Rs of cloud migration
Besides the three cloud migration strategies mentioned above, organizations use several other approaches. Typically, businesses adopt the seven Rs of cloud migration to guide the transition of applications to the cloud:
- Rehosting. This involves migrating applications to the cloud with minimal modifications. It enables organizations to swiftly transfer their workloads without re-architecting, making it a favorable option for initial migrations.
- Relocating. Similar to rehosting, relocating often involves moving applications to a different environment within the cloud. This may include migrating from one CSP to another or moving from on-premises infrastructure to a cloud service. The emphasis is on shifting the application without making significant modifications.
- Replatforming. Sometimes referred to as "lift-tinker-and-shift," this method optimizes applications during migration to the cloud to ensure compatibility. Replatforming typically involves altering the underlying infrastructure or making minor adjustments to enhance performance, without requiring a complete overhaul.
- Refactoring. This strategy involves re-architecting or redesigning applications to take advantage of cloud-native features. Refactoring is typically based on a platform-as-a-service model. This process requires significant changes to the application's code and architecture, making it more scalable and efficient in a cloud architecture.
- Repurchasing. This approach involves replacing the existing application with a cloud-native option, typically using a SaaS model. Organizations may choose this option when the existing application is outdated or fails to meet their requirements.
- Retiring. Organizations use this method to identify applications that are no longer needed and can be decommissioned. This streamlines the application portfolio and lowers the costs of maintaining unnecessary systems.
- Retaining. Also known as revisiting, this method involves keeping selected applications on premises for various reasons. For example, organizations could choose to retain critical applications for operations or require further evaluation before migrating.
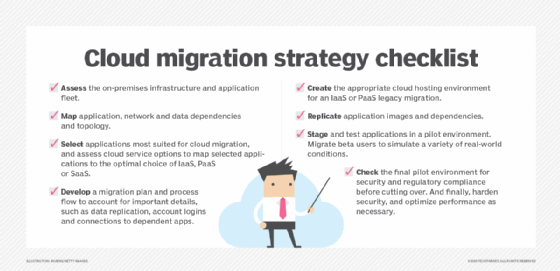
Lift-and-shift preparation
Before undertaking a lift-and-shift migration, businesses should consider taking the following steps to ensure a successful transition:
- Assess applications. Examine the existing applications to determine if they're suitable for lift-and-shift migration or whether they require refactoring or replacement with SaaS applications.
- Develop a migration plan. Build a comprehensive cloud migration strategy that outlines the steps and resources required for the migration process, including timelines, responsibilities and contingencies.
- Ensure security. Review the applications for security vulnerabilities and take measures to protect data and systems during and after migration. Ignoring the importance of security can be a mistake for any cloud migration strategy.
- Select a cloud provider. Pick a CSP that offers the cloud services and support necessary for the organization's specific applications and workloads.
- Monitor and optimize. After the migration, continuously monitor the applications and cloud infrastructure to identify areas for optimization, cost savings and performance improvements.
To ensure a thorough preparation process, organizations should also address the following questions throughout the planning phase:
- Are the applications being considered for lift and shift compatible with the OSes and runtime environments of the target cloud environment?
- What is the expected application or workload lifespan before migrating it to the cloud? This question is important because migrating applications scheduled for retirement within the next 12 months might not be cost-effective or practical.
- Are there any dependencies that could create issues in the cloud?
- Are there licensing concerns that might arise in the cloud environment?
- Does the cloud hosting provider offer automated migration tools to assist with migrations?
- What are the relevant compliance regulations and how will these regulations be met in the cloud?
- How is data in transit and at rest encrypted?
- What access controls are used?
- What are the options for data backup and disaster recovery?
- What is the expected timeline for the migration?
By adopting this structured approach and carefully addressing these questions, organizations can significantly enhance the chances of a successful lift-and-shift cloud migration.
Lift and shift is just one approach to cloud migration. Learn the key steps for a successful cloud migration.