laser printer
What is a laser printer?
A laser printer is a popular type of computer printer that uses a non-impact photocopier technology where there are no keys striking the paper.
When a document is sent to the printer, a laser beam "draws" the document on a selenium-coated drum using electrical charges. The drum is then rolled in toner, a dry powder type of ink that adheres to the charged image on the drum. The toner is transferred onto a piece of paper and fused to the paper with heat and pressure.
The laser printer was popularized in the mid-1980s as a standalone printer for use with personal computers. It typically replaced an impact dot matrix printer or a non-impact inkjet printer. Laser printers are still often connected directly to a single PC, but today many are linked to local area networks (LAN), supporting workgroups or entire departments.
In some cases, a laser printer is used as a multifunction peripheral with printing, scanning, photocopying and fax capabilities. These devices are known as multifunction printers (MFP). They usually have MFP or MFC for multifunction center as part of their model numbers.
How a laser printer works
Laser printers can be used in a home office or a small business office. Office connectivity is typically via an Ethernet connection. In a home office or small business, a cable or Wi-Fi are used to connect the printer to computing devices. Wi-Fi is also used to connect mobile devices to printers for mobile printing.
Laser printers can handle both black and white and color printing, though color laser printers are more expensive than monochrome laser printers. Typically, laser printers are used for printing whereas newer all-in-one printers can function as a printer, copier, scanner and fax. Many have user-friendly touchscreen displays.
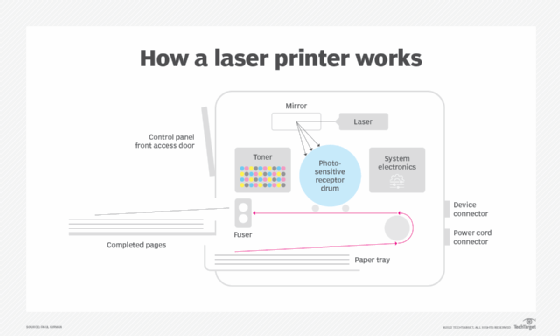
The following steps detail how a laser printer works:
- A photo, graphic or text image is sent to the printer, which begins the process of transferring that image to paper using a combination of positive and negative static electric charges.
- The revolving drum gets a positive charge.
- The system's electronics convert the image into a laser beam.
- The laser beam bounces off a mirror onto the drum, drawing the image on the drum by burning a negative charge in the shape of the image.
- Then the drum picks up the positively charged toner from the toner cartridge. The toner sticks to the negatively charged image on the drum.
- Paper entering the printer receives a negative charge.
- As the paper passes the drum, the paper's negative charge attracts toner from the positively charged drum; the toner literally sits on top of the paper.
- The paper's charge is removed and a fuser permanently bonds the toner onto the paper.
- The printed paper is released from the printer.
- The electrical charge is removed from the drum, and the excess toner is collected.
Printer selection guidelines
When buying the best laser printer for the needs of a business, some important features to consider, in addition to price and warranty, include the following:
Print speed and capacity
Personal laser printers are sufficient for printing an average of 200 pages per week. These are low-end and cost $120 and up. They can print up to 20 to 25 pages per minute (ppm). A workgroup printer is needed if an average of 1,000 pages per week is needed. These print up to 55 ppm and cost $500 to $1,000.
Production printers are used by commercial publishers to print 50,000 or more pages per week. These are expensive and can print up to 75 to several hundred pages per minute. They cost $25,000 to $150,000. They can print 24 hours a day, seven days a week.
Resolution
The standard resolution in most laser printers today is 600 dots per inch (dpi). This resolution is sufficient for normal everyday printing, including small desktop publishing jobs. A high-end production printer might have a resolution of 2400 dpi. Some laser printers still use a resolution of 300 dpi. This resolution can cause jagged lines to appear on the outer edge of an image.
Hewlett Packard created Resolution Enhancement Technology (RET) to correct this. RET inserts smaller dots at the edges of lines and to smooth the rough edges. RET does not improve the resolution, but the document looks better. If you purchase a printer with 300 dpi, make sure it has RET.
Printer languages
Printer Control Language (PCL) is the standard printer language for Hewlett Packard and most other laser printers, most of which are HP-compatible. PCL is used for printing letters, database printouts, spreadsheets and simple graphics.
Postscript printers are used with desktop publishing software and drawing packages. Postscript printers are the norm for Apple MacIntosh-connected printers. A laser printer that comes with Postscript installed is more expensive and is likely to be used for high-definition images.
A laser printer that uses PCL can be upgraded to Postscript by installing a software driver provided by the manufacturer of the laser printer. The printer might require more memory when upgraded to use Postscript. This is because a laser printer needs the entire image in memory before printing, and a Postscript printer requires more memory to process than a PCL printer. The application being used must support Postscript for the laser printer to print Postscript documents.
Paper handling
Paper handling is important when shopping for a laser printer. Most laser printers use letter-size -- 8.5 by 11-inch -- and legal-size -- 11 by 14-inch -- cut-sheet paper. High-end production printers use continuous sheet fed paper.
Laser printers can print on transparencies, adhesive labels and lightweight cards. A laser printer with automatic duplex printing can print on one side of the paper, turn the paper over and print on the other side. Many laser printers, however, use simple printing with manual duplex printing. Manual duplex printing is achieved by changing the print options in the printer's properties or printing one side and taking that same paper and reinserting it into the printer to print on the other side.
Warm-up time and first paper out time (FPOT)
When a laser printer is turned on, it needs time to warm up the fuser to operating temperature. If the printer has a standby mode or is turned off between printing jobs, the warm-up time becomes even more important. Large workgroup and production printers can take five to 15 minutes to warm up. This waiting period can hinder overall productivity.
Similarly, the FPOT is also an important consideration when looking for a high-quality printer. It refers to how long it takes to print the first piece page of a print job. When a laser printer receives data from the computer to print, it takes five to 30 seconds to prepare the printer to print a new job. This is in addition to the time it takes to actually print the document.
Laser printers vs. inkjet: Which is better?
A laser printer is different from an inkjet printer in several ways, including the following:
- The toner or ink in a laser printer is dry. In an inkjet, it is wet.
- The upfront purchase price of an inkjet printer is less than a laser printer. However, over time, an inkjet printer is about 10 times more expensive to operate than a laser printer because ink needs replenishing more frequently than toner cartridges, particularly if high-yield toner cartridges are used.
- The printed paper from an inkjet printer will smear if wet, but a laser-printed document will not.
Both types of printers operate quietly and allow fonts to be added by using font cartridges or installing soft fonts. If your printing needs are minimal, an inkjet printer is sufficient. But if your printing volume is high, consider buying a laser printer.
History of laser printers
IBM introduced the first laser printer in 1975 for use with its mainframe computers.
In 1984, Hewlett-Packard revolutionized laser printing technology with its first HP LaserJet, a compact, fast and reliable printer that PC users could afford.
Since then, laser printers have decreased in price and increased device and print quality. Hewlett Packard continues to be the leading manufacturer with competitors such as Brother, Canon, Lexmark and Xerox.
Learn how to use remote print management effectively with a hybrid workforce.
