instantiation
What is instantiation?
In programming, instantiation is the creation of a real instance or particular realization of an abstraction or template, such as a class of objects or a computer process. To instantiate is to create such an instance by, for example, defining one particular variation of an object within a class, giving it a name and locating it in some physical place.
What is instantiation in object-oriented programming?
In object-oriented programming (OOP), an object is essentially an instance of a class. In OOP languages, a class is like a blueprint where variables and methods are defined, and each time a new instance of the class (instantiation) is created, an object gets created -- hence the term object-oriented. All objects of a class have a particular set of associated variables or properties, accessories or means to access those variables, and functions or methods.
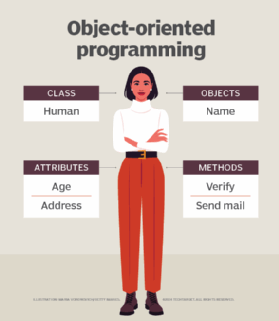
These properties (or variables) can be viewed as data describing the objects that are created from a class. For example, a class may represent a new employee. In this instance, the properties of this class may include job title, role, responsibilities, wages and so on.
An instance of an object can be declared by giving it a unique name that can be used in a program. This process is known as instantiation. A class can also be instantiated to create an object, a concrete instance of the class. The object is an executable file that can run on a computer.
One use of instantiation is data modeling and programming before OOP. Another is making a real (data-filled) object from an abstract object as is done by creating an entry in a database table (which can be thought of as a kind of class template for objects).
What is instantiation in Java?
In Java, an OOP language, the object that is instantiated from a class is, confusingly enough, called a class instead of an object. In other words, using Java, a class is instantiated to create a specific class that is also an executable file that can run on a computer. However, Java's equivalent of a class attribute is a static attribute. Generally, static variables are referred to with the Java class name.
What is instantiation in Python?
In OOP, the creation and initialization of objects of a given class is a fundamental step. In Python, everything is an instance or an object. Class constructors, which are like blueprints, allow software engineers to create and initialize objects of a given class. This instantiation process follows the steps of instance creation and instance initialization and makes those objects ready to use.
When a copy of a class is created that inherits all the class properties and functions, it is called instantiating a class. To instantiate a class in Python, the class like it is called a function, passing the arguments defined by the __init__ method. The newly created object is the return value.
What is instantiation in C++?
In C++, the creation of a new instance of the class is called instantiation. Memory is allocated for that object and the class constructor runs. Programmers can instantiate objects on the heap with a new keyword or on the stack as a variable declaration. Whenever an object of that class is instantiated, the compiler will call special class members.
What is instantiation in C#?
In the OOP language C#, instantiation describes the processes of creating a new object for a class using a new keyword.
What is instantiation in JavaScript?
In JavaScript, instantiation describes the creation of an object. JavaScript programmers can achieve this by using one of the five available patterns:
- Functional
- Functional-shared
- Prototypical
- Pseudoclassical
- ES6
This approach helps programmers manage inheritance effectively while enabling code reusability when creating several instances of objects. When used correctly, these patterns can decrease the amount of code in memory. The term "class" was included in ES6, but prior to that, developers had to use function calls to create objects.
What is instantiation in Verilog?
In Verilog, a hardware description language, the process of creating a unique object using a module template whenever a module is invoked is called instantiation. The objects are called instances, and these objects have their own names, parameters, variables and input/output (I/O) interface.
See also: code, source code, compiler, decompile, yet another compiler compiler, parser, software toolchain, native code, assembler
