vulnerability assessment
What is a vulnerability assessment?
A vulnerability assessment is the process of defining, identifying, classifying and prioritizing vulnerabilities in computer systems, applications and network infrastructures.
Vulnerability assessments provide organizations with the necessary knowledge, awareness and risk backgrounds to understand and react to threats to their environment.
A vulnerability assessment intends to identify threats and the risks they pose. It typically involves using automated testing tools, such as network security scanners, whose results are listed in a vulnerability assessment report.
Organizations of any size, or even individuals who face an increased risk of cyberattacks, can benefit from some form of vulnerability assessment, but large enterprises and organizations subject to ongoing attacks will benefit most from vulnerability analysis.
Because security vulnerabilities enable hackers to access IT systems and applications, it is essential for enterprises to identify and remediate weaknesses before they can be exploited. A comprehensive vulnerability assessment, along with a vulnerability management program, can help companies improve the security of their systems.
Importance of vulnerability assessments
Vulnerability assessments provide organizations with details on security weaknesses in their environments. They also provide directions on how to assess the risks associated with those weaknesses. This process offers the organization a better understanding of assets, security flaws and overall risk, reducing the likelihood a cybercriminal will breach their systems.
Types of vulnerability assessments
Vulnerability assessments discover different types of system or network vulnerabilities. The assessment process includes using a variety of tools, scanners and methodologies to identify vulnerabilities, threats and risks.
Types of vulnerability assessment scans include the following:
- Network-based scans identify possible network security attacks. This type of scan can also detect vulnerable systems on wired or wireless networks.
- Host-based scans locate and identify vulnerabilities in servers, workstations or other network hosts. This scan usually examines ports and services that could be visible on network-based scans. It offers greater visibility into the configuration settings and patch history of scanned systems, even legacy systems.
- Wireless network scans focus on points of attack in wireless network infrastructure. In addition to identifying rogue access points, a wireless network scan also validates a company's network is securely configured.
- Application scans test websites to detect known software vulnerabilities and incorrect configurations in network or web applications.
- Database scans identify weak points in a database to prevent malicious attacks, such as SQL injection attacks.
Vulnerability assessments vs. penetration tests
A vulnerability assessment often includes a pen testing component to identify vulnerabilities in an organization's personnel, procedures or processes. These vulnerabilities might not normally be detectable with network or system scans. The process is sometimes referred to as vulnerability assessment/penetration testing, or VAPT.
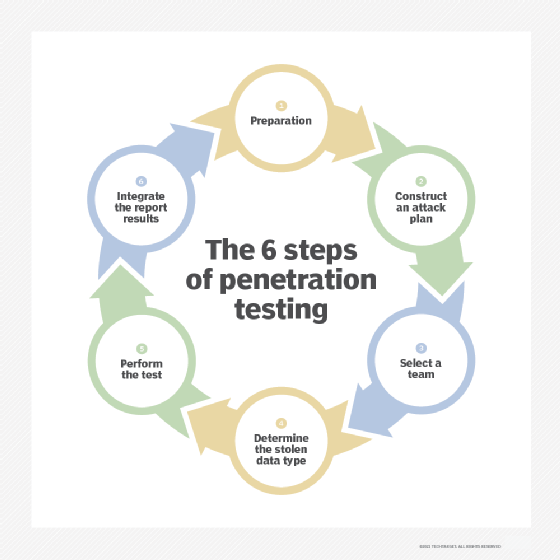
Pen testing is not sufficient as a complete vulnerability assessment and is, in fact, a separate process. A vulnerability assessment aims to uncover vulnerabilities in a network and recommend the appropriate mitigation or remediation to reduce or remove the risks.
A vulnerability assessment uses automated network security scanning tools. The results are listed in a vulnerability assessment report, which focuses on providing enterprises with a list of vulnerabilities that need to be fixed. However, it does so without evaluating specific attack goals or scenarios.
Organizations should conduct vulnerability testing on a regular basis to ensure the security of their networks, particularly when changes are made. For example, test when services are added, new equipment is installed or ports are opened.
In contrast, pen testing involves identifying vulnerabilities in a network and then attempting to exploit those vulnerabilities to attack the system. Although sometimes carried out in concert with vulnerability assessments, the primary aim of pen testing is to check whether a vulnerability exists. In addition, pen testing tries to prove that exploiting a vulnerability can damage the application or network.
While a vulnerability assessment is usually automated to cover a wide variety of unpatched vulnerabilities, pen testing generally combines automated and manual techniques to help testers delve further into the vulnerabilities and exploit them to gain access to the network in a controlled environment.
This article was written by a TechTarget Contributor in 2021. TechTarget editors revised it in 2024 to improve the reader experience.







