
Getty Images
Data center cooling challenges and how to solve them
Data centers that are not properly cooled can see equipment work inefficiently or become damaged. Learn some common cooling challenges and assess ways to solve them.
IT equipment generates heat, and as its capacity increases, it produces more. Some organizations reduce their data center's physical size to fit more into cabinets. Even smaller data centers now see heat densities they never imagined 10 years ago.
Properly cooling computing hardware has always been challenging, but when only some cabinets are hotter than others, it gets even more difficult, especially in legacy data centers still running 20-year-old cooling equipment. There are common data center cooling challenges but also ways to ensure they don't get in the way of efficient cooling.
Beware of lost cooling air
First, have your cooling systems optimized to get the most out of what you have. Run close to ASHRAE TC 9.9 guidelines if you can as a guide, and then look to other areas on improvement. Don't invest in new equipment if existing equipment can still do the job. Let's start with the biggest challenge: existing raised-floor cooling.
Clean out the underfloor space so air conditioners can deliver air unimpeded. It's a multistep process but can make an amazing difference. Have the floor realigned, tightened and re-leveled, and seal all openings to ensure minimal waste of cool air. Good products exist to close gaps around existing cables and pipes. Producing cool air is expensive, so wasting it through leaky floors is costly and reduces cooling effectiveness.
Ensure efficient data center air flow
Understand air flow tiles, and balance the data center's air flow. A fully open adjustable damper on a 25% open tile reduces its effective open area to only 16%, so consider installing undampered tiles. Also, 63% open grate tiles can help in front of higher-heat cabinets but also reduce underfloor air pressure to nearby tiles. Too many of them can air-starve the rest of the floor.
Fan-boosted tiles can be problem-solvers when they are correctly used. Fans take the air they want, so they may leave little air for other cabinets. Tiles with temperature-controlled fans can help. But they're expensive, and organizations may need a lot of them to balance a room.
Act to ensure cooling air is sufficient
For continuing problems or for non-raised floor rooms, there are ways to supplement cooling in specific areas, but they all have challenges.
Adding in-row coolers requires rearranging cabinets. Front- or rear-door pre- or post-coolers can reduce heat load. But both require piping and a chilled water or refrigerant cooling source. These can be far more effective, however, than adding or replacing large computer room air conditioners or computer room air handlers and less expensive as well. Simply adding air conditioners, especially to underfloor systems, can impair cooling unless experts have optimized air flow designs using computational fluid dynamics air flow modeling.
Aisle containment is another option to ensure cooling air is sufficient to regulate equipment temperatures. There are two major decisions in doing this.
1. Full or partial containment
Full containment can be difficult to implement in existing facilities. If fire protection heads are in alternate aisles, above-cabinet air containment barriers will stop sprinkler or gas discharge from reaching adjacent aisles. There are three options:
- Install partial containment. Enclosing aisle ends -- but not closing above cabinets -- can be nearly as effective as full containment in some situations.
- Add fire protection heads and sensors. This is the best option but is expensive and potentially disruptive in an operating data center.
- Consider products that automatically remove containment barriers in the event of a fire. Unfortunately, most of these don't comply with National Fire Protection Association 76, which is an advisory standard and not code-enforceable. Only truly compliant options are recommended.
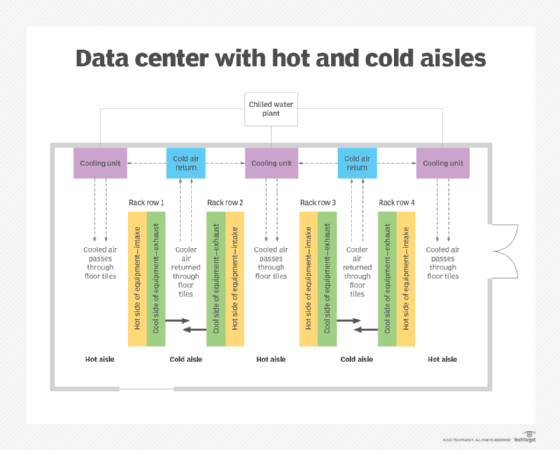
2. Hot or cold aisle containment
There are proponents of each, but cabinet configuration may dictate. Cold aisle containment requires good air balance and ensures that all the cool air goes to cabinets. But the rest of the room is hot -- perhaps 100 degrees Fahrenheit (37.8 degrees Celsius) or more.
Hot aisle containment is more energy-efficient but requires a clear return air path back to the air conditioners. Existing installations often find cold aisle containment more practical to retrofit.
Overhead coolers are effective in delivering cool air directly in front of high-heat cabinets, but they require large heat loads to operate. They also use special piping that can be difficult to install in existing facilities.
Monitor the cooling environment
Most importantly, install good environmental monitoring -- data center infrastructure management software -- and mount sensors on cabinets. Modern smart power distribution units make this easy. Adjust cooling with real data, not just on how an area feels. Good data enables organizations to operate near the top of the ASHRAE Thermal Guidelines -- 27 degrees Celsius or 80.6 degrees Fahrenheit inlet temperature to the IT equipment -- using less cooling energy but also getting more capacity out of cooling units.
Self-cooled cabinets can work in data centers that only have a few cabinets that contain high-density equipment. They are large and may be nonredundant. If cooling stops, doors swing open to access room cooling until organizations fix the cabinet system.
Total immersion cooling runs servers in a vat of nonconductive liquid that can handle high heat densities. They're like horizontal 42U cabinets, but their weights may make floor loading a problem. For a full rack of high-performance servers, however, they may be the easiest solution of all.
There are many ways available to solve challenging cooling problems, but the biggest challenge may be deciding which to choose. Examine your budgets and requirements of the facility to determine the best way to fix common cooling issues.







