What is a forensic image?
A forensic image (forensic copy) is a bit-by-bit, sector-by-sector direct copy of a physical storage device, including all files, folders, and unallocated, free and slack space. Forensic images contain all the files visible to the operating system (OS), as well as deleted files and pieces of files left in the slack and free space.
Forensic imaging is one element of computer forensics, which is the application of computer investigation and analysis techniques that forensic examiners use to gather digital evidence for presentation in a court of law.
Not all imaging and backup software creates forensic images. For example, Windows backup creates image backups that aren't complete copies of the physical device. Forensic images can be created through specialized forensic tools, such as forensic software. Some disk imaging utilities not marketed for forensics also make complete disk images.
Forensic imaging in cybersecurity
In the case of cybercrime, additional evidence might be discovered other than what's available through an OS. This type of original evidence includes incriminating data that has been deleted to prevent electronic discovery. Unless the data is deleted securely and overwritten, it's often recoverable with forensic or data recovery software.
Creating forensic images and backing them up prevents data loss from drive failures. The loss of data as evidence can be detrimental to legal cases. Forensic digital image files can also prevent the loss of critical files in general.
Types of forensic images
Three types of forensic images can be created when capturing the contents of a storage device. Which approach is used depends on the technology available and business requirements. The three types of images are the following:
- Physical image. This image captures a storage device's contents, including active data, unused or unallocated space, and deleted data that might still reside in the storage unit.
- Logical image. This image captures usually active data by scanning a storage device.
- Targeted image. Specific data, such as that required for a legal examination, is identified and imaged.
Forensic image format types
Several different types of forensic image formats serve different needs. The key forensic image formats include the following:
- Raw image. Also referred to as DD, this image type is a simple, uncompressed clone that includes deleted files and unallocated space and is widely supported by tools like Autopsy.
- EnCase image. This is also referred to as E01. It's a compressed format with metadata and integrity checks common in legal investigations.
- Advanced forensic format. AFF is an open source format that supports compression and encryption, and stores data and metadata together.
- SMART. This format includes compression and segmentation. It's used in specific forensic tools for large data sets.
- FTK Forensic Toolkit. FTK is Exterro's proprietary imager format with hash verification, which is best suited for evidence integrity.
Capturing and creating a forensic image
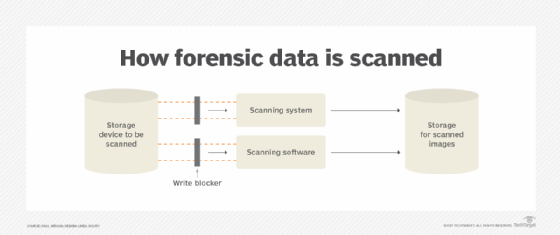
Generating a digital forensic image of a storage device requires tools and software to scan the device, capture the desired content and provide an exact copy to another storage device. Almost any device with a storage function or capability can create a forensic image. For example, hard drives, CD-ROMs, flash drives, mobile phones, computers, smartphones and even web pages can all do this.
For example, OpenText EnCase Forensic software creates an image format for storage and future forensic analysis. A successful forensic image has the following characteristics:
- The device being scanned and the scanning technology are successfully connected.
- The source device and its data haven't been modified.
- The scanning technology generates a true copy of the data to be scanned.
Write blocking is a technology that prevents any changes to the source device before and during the scanning process. Write blockers are typically between the source and the scanning system, and are available for different storage devices.
Why is forensic imaging important?
Forensic imaging prevents the loss of original data. These imaging tools and techniques are the only way to ensure that electronic data can be successfully admitted as evidence in a court or legal proceeding.
A detailed image of a memory system or primary storage device provides accurate information on its contents, enabling forensic experts to diagnose existing and potential problems. Law enforcement needs accurate and verifiable data for a legal or compliance audit as part of a forensic investigation.
Challenges of forensic images
Forensic imaging comes with several challenges. The most important are the following:
- Preserving authenticity, including ensuring exact replicas when encryption or antiforensic tools are involved, can be difficult.
- Large image sizes, especially raw formats, can strain storage demands and access logistics.
- Time constraints occur when imaging large drives, potentially delaying urgent investigations.
- Tool compatibility issues arise as not all software supports every format.
- Legal complexity can be an issue, including meeting chain-of-custody standards while avoiding data tampering.
Learn more about the tools and techniques required in a cloud computing forensics investigation.