
What is an algorithm?
An algorithm is a procedure used for solving a problem or performing a computation. Algorithms act as an exact list of instructions that conduct specified actions step by step in either hardware- or software-based routines.
Algorithms are widely used throughout all areas of IT. In mathematics, computer programming and computer science, an algorithm usually refers to a small procedure that solves a recurrent problem. Algorithms are also used as specifications for performing data processing and play a major role in automated systems.
An algorithm could be used for sorting sets of numbers or for more complicated tasks, such as recommending user content on social media. Algorithms typically start with initial input and instructions that describe a specific computation. When the computation is executed, the process produces an output.
How do algorithms work?
Algorithms work by following a set of instructions or rules to complete a task or solve a problem. They can be expressed as natural languages, programming languages, pseudocode, flowcharts and control tables. Natural language expressions are rare, as they are more ambiguous. Programming languages are normally used for expressing algorithms executed by a computer.
Algorithms use an initial input along with a set of instructions. The input is the initial data needed to make decisions and can be represented in the form of numbers or words. The input data gets put through a set of instructions, or computations, which can include arithmetic and decision-making processes. The output is the last step in an algorithm and is normally expressed as more data.
For example, a search algorithm takes a search query as input and runs it through a set of instructions for searching through a database for relevant items to the query. Automation software acts as another example of algorithms, as automation follows a set of rules to complete tasks. Many algorithms make up automation software, and they all work to automate a given process.
What are different types of algorithms?
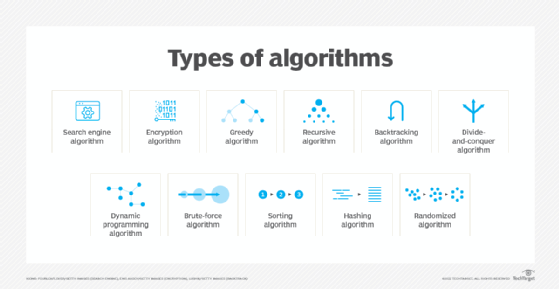
There are several types of algorithms, all designed to accomplish different tasks:
- Search engine algorithm. This algorithm takes search strings of keywords and operators as input, searches its associated database for relevant webpages and returns results.
- Encryption algorithm. This computing algorithm transforms data according to specified actions to protect it. A symmetric key algorithm, such as the Data Encryption Standard, for example, uses the same key to encrypt and decrypt data. If the algorithm is sufficiently sophisticated, no one lacking the key can decrypt the data.
- Greedy algorithm. This algorithm solves optimization problems by finding the locally optimal solution, hoping it is the optimal solution at the global level. However, it does not guarantee the most optimal solution.
- Recursive algorithm. This algorithm calls itself repeatedly until it solves a problem. Recursive algorithms call themselves with a smaller value every time a recursive function is invoked.
- Backtracking algorithm. This algorithm finds a solution to a given problem in incremental approaches and solves it one piece at a time.
- Divide-and-conquer algorithm. This common algorithm is divided into two parts. One part divides a problem into smaller subproblems. The second part solves these problems and then combines them to produce a solution.
- Dynamic programming algorithm. This algorithm solves problems by dividing them into subproblems. The results are then stored to be applied to future corresponding problems.
- Brute-force algorithm. This algorithm iterates all possible solutions to a problem blindly, searching for one or more solutions to a function.
- Sorting algorithm. Sorting algorithms are used to rearrange data structures based on a comparison operator, which is used to decide a new order for data.
- Hashing algorithm. This algorithm takes data and converts it into a uniform message with a hashing.
- Randomized algorithm. This algorithm reduces running times and time-based complexities. It uses random elements as part of its logic.
What are examples of algorithms?
Machine learning is a good example of an algorithm, as it uses multiple algorithms to predict outcomes without being explicitly programmed to do so.
Machine learning uses supervised learning or unsupervised learning. In supervised learning, data scientists supply complex algorithms with labeled training data and define the variables they want the algorithm to assess for correlations. Both the input and the output of the algorithm are specified.Unsupervised machine learning involves algorithms that train on unlabeled data and sift through it to look for patterns that can be used to group data points into subsets. Most types of deep learning, including neural networks, are unsupervised algorithms.
Machine learning used in artificial intelligence also relies on algorithms. However, machine learning-based systems may have inherent biases in the data that feeds the machine learning algorithm. This could result in systems that are untrustworthy and potentially harmful.
Although algorithms are used extensively in computer science, AI and machine learning scenarios, they're also employed frequently in everyday life.
The following are some examples of algorithms used in real life:
- Following a recipe. Recipes provide a series of steps to achieve a particular objective, such as preparing blueberry muffins or making spaghetti sauce from scratch. Recipes aim to produce consistent results and help individuals -- regardless of their background -- create a specific dish by following detailed instructions. In this way, recipes mirror computer science algorithms, which outline steps for generating reproducible outcomes.
- Tying shoelaces. Tying shoelaces is another example of following an algorithm. For example, there are a finite number of steps that lead to a properly tied traditional shoelace knot, which is often referred to as the "bunny rabbit" or "loop, swoop and pull" knot.
- Facial recognition. Facial recognition is widely used in iPhone logins as well as Snapchat and Instagram filters. It works by projecting facial traits from a photo or video onto a biometrics map using an algorithm. The program then looks for a match between this map and a database of faces to confirm the user's identification. If facial recognition is used for Snapchat or Instagram filters, there is no need for searching the database because the algorithm simply builds a map of the face and applies the filter to it.
- Traffic signals. Traffic signals use smart algorithms to manage traffic flow. These algorithms group different algorithms or movements, such as going straight or turning right, into phases, which helps ensure safety and efficiency. For example, when a motorist approaches a red light, the traffic signal is cycling through these phases. By evaluating the volume of traffic, an algorithm decides when it's safe for the vehicle to move forward.
- Sorting documents and papers. This is a great example of how algorithms can be used for various tasks and purposes, such as sorting files alphabetically, by word count, by date, or by any other specifications. When someone arranges their personal or professional documents according to a set of instructions, they are applying algorithmic thinking to simplify the organization process by using small tasks.
- Searching for a book in the library. Finding a library book is like following an algorithm or a step-by-step plan. For example, there are different ways to do it, such as using the library's computer system or looking for labels on the shelves that show the book's genre, subject or author. No matter which method one chooses, if it can be explained and done by others, then it can be classified as an algorithm.
Discover how AI algorithms work and provide a competitive edge for businesses. Explore the main types and learn the importance of evaluating both the benefits and risks associated with these algorithms.
