entity
What is an entity?
An entity is a single thing with a distinct separate existence. It can be real or abstract. In many contexts, the term entity is used to describe things or units that have no ready label or are difficult to classify under a single other word. For example, a customer relationship management (CRM) system might use the word entity as a generic way to describe persons, corporations, government agencies or nonprofit organizations (NPOs).
The word entity is from a root in Latin, ens, meaning an existing thing; it makes a distinction between a thing's existence and its qualities.
Entity in IT context
In a technology and business context the word entity is used in many different ways.
An entity relationship diagram (ERD) is a graphical way to show the relationship between objects or entities. They are often the starting point for creating many business or computer projects. Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a popular way to create entity diagrams.
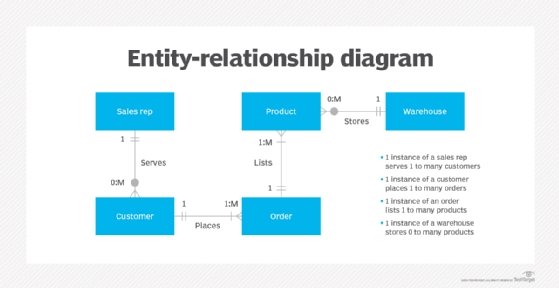
In databases, an entity is a single person, place, or thing about which data can be stored. Entity data can be stored in a single row or involve a large data structure in a relational database. In data modeling (the first step in the creation of a database), an entity is some unit of data that can be classified and has stated relationships to other entities.
A named entity is a single thing that can be clearly identified as distinct. Data mining and machine learning use named entity recognition (NER) to identify and classify named entities. These systems identify distinct entities then assign real-world data to them. This lets these systems begin to understand how things work and interact together.

In the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model of network communication, an entity is an active element within a subsystem that communicates with other entities using a defined protocol.
IBM uses the term entity in several products to describe a user, group, or resource. Entity might be further defined or set by the product.
In Fortran, almost every program element is referred to as an entity, such as a procedure, an operator, an interface block, an input-output unit, a symbolic constant, and a statement label.
Entity in a business context
An entity type describes the type of legal structure a business has. The entity type is important for tax and legal reasons. Examples of entity types are sole proprietorship, C corporation, S corporation, or limited liability corporation, i.e. an LLC. Persons are also considered an entity.
Named entity recognition is a critical part of natural language processing. Learn how NLP benefits enterprise analytics.
