What is NoSQL (Not Only SQL database)?
NoSQL is an approach to database management that can accommodate a wide variety of data models, including document, graph, key-value and columnar formats.
A NoSQL database generally means that it's non-relational, distributed, flexible and scalable. Additional common NoSQL database features include the lack of a tabular database schema, data clustering, replication support and eventual consistency, as opposed to the typical ACID (atomicity, consistency, isolation and durability) transaction properties of relational and structured query language (SQL) databases. Many NoSQL database systems are also open source.
The term NoSQL originally could be taken at its word -- that is, SQL wasn't used as the application programming interface (API) to access data. However, the ubiquity and usefulness of SQL caused many NoSQL databases to add support for SQL. Today, it's commonly accepted that NoSQL stands for "not only SQL."
What are the types of NoSQL databases?
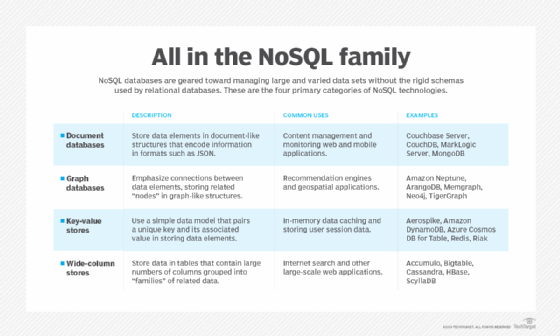
There are four types of NoSQL database systems. Each uses a different type of data model, resulting in significant differences between each NoSQL type, noted as follows:
- Document databases. Also called document stores, these databases store semi-structured data and descriptions of that data in document format. They enable developers to create and update programs without needing to reference the master schema. The use of document databases has increased along with the use of JavaScript and JavaScript Object Notation (JSON), a data interchange format that has gained wide currency among web application developers. Document databases are used for content management and mobile application data handling, such as blogging platforms, web analytics and e-commerce applications. Amazon DynamoDB, Couchbase Server, Google Cloud Firestore and MongoDB Atlas are examples of document-based databases.
- Graph databases. Graph data stores organize data as nodes, which are similar to rows in a relational database, and edges, which represent connections between nodes. Because the graph system stores the relationship between data or nodes, it can support richer representations of data relationships. Also, unlike relational database models that rely on strict schemas, the graph data model can evolve over time and use. Graph databases are applied in systems that must map relationships, such as social media platforms, reservation systems or customer relationship management. Amazon Neptune, ArangoDB and Neo4j are examples of graph databases for enterprises.
- Key-value stores. Also known as key-value databases, these systems execute a simple data model that pairs a unique key with an associated value. Because this model is simple, it can be used to develop highly scalable and performant applications. Key-value databases are ideal for session management and caching in web applications, such as those needed when managing shopping cart details for online buyers or for managing session details for multiplayer gaming. Deployments differ in the way they're oriented to work with RAM, solid-state drives or disk drives. Examples of key-value databases include Aerospike, Amazon DynamoDB, Memcached, Microsoft Azure Cosmos DB and Redis.
- Wide-column stores. These databases use familiar tables, columns and rows such as relational database tables, but column names and formatting can differ from row to row in a single table. Each column is also stored separately on disk. As opposed to traditional row-orientated storage, a wide-column store is optimal when querying data by columns and is optimized for those apps that need large data volumes and low latency. Typical applications where wide-column stores can excel include recommendation engines, catalogs, fraud detection and event-logging. Apache Accumulo, Apache Cassandra, Apache HBase and ScyllaDB are some options for wide-column databases.
These basic NoSQL database classifications are only guides. Over time, vendors have mixed and matched elements from different NoSQL database families to achieve more generally useful systems. That evolution is seen, for example, in MarkLogic from Progress Software, which added a graph store and other elements to its original document databases. Couchbase Server supports both key-value and document approaches. Apache Cassandra has combined key-value elements with a wide-column store and a graph database. Sometimes NoSQL elements are mixed with SQL elements, creating a variety of databases that are referred to as multimodel databases.
Advantages of NoSQL
There are several advantages to using NoSQL databases, including the following:
- Simplified application development. NoSQL databases simplify application development, particularly for interactive real-time web applications, such as those using a RESTful API and web services.
- Flexibility. These databases provide flexibility for data that hasn't been normalized, which requires a flexible data model or has different properties for different data entities.
- Scalability. They offer scalability for larger data sets, which are common in analytics and artificial intelligence applications.
- Developer friendly. NoSQL databases are developer friendly, as they enable developers to modify specific apps, especially in cloud computing environments to speed up development. They're also better suited for mobile, social media and big data environments.
- Ease of use. NoSQL databases are designed for specific use cases and don't have a rigid schema, which makes them easier to use than general-purpose relational or SQL databases for those types of applications.
- Venture funding and cost management. NoSQL companies are often venture-funded and adopting the NoSQL model can lead to a better fundraising experience and more manageable costs for startups.
Disadvantages of NoSQL
Disadvantages of using a NoSQL database include the following:
- Less standardized. Each NoSQL database has its own syntax for querying and managing data and lacks a uniform query language. This is in contrast to SQL, which is the lingua franca for relational and SQL database systems.
- Lack of a structured schema. A schema with some sort of structure is required in order to use the data. With NoSQL, this must be performed by the application developer instead of the database administrator. The lack of a rigid database schema and constraints removes the data integrity safeguards that are built into relational and SQL database systems.
- Reduced consistency. Because most NoSQL databases use the eventual consistency model, they don't provide the same level of data consistency as SQL databases. At times the data won't be consistent, which means they aren't well-suited for transactions that require immediate integrity, such as banking and automated teller machine transactions.
- Fewer industry standards. Because NoSQL databases are newer, there are no comprehensive industry standards as with relational and SQL DBMS offerings.
- ACID transactions. Most NoSQL databases don't perform ACID transactions, which are tried-and-true techniques for ensuring data consistency across the entire database. Instead, NoSQL relies on the principle of eventual consistency, which can pose the risk of data becoming out of sync between different database nodes.
NoSQL vs. SQL: What's the difference?
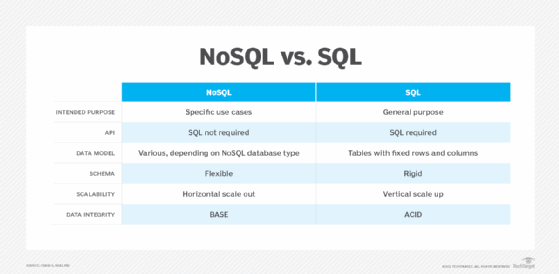
At a high level, SQL databases are general purpose, whereas NoSQL databases are engineered for specific use cases. The primary differences between NoSQL and SQL can be summed up in the following five categories. Each deploys a different approach to these aspects of data storage and retrieval.
- API. For NoSQL, SQL isn't required as an API to the data in the database, although many NoSQL databases offer a SQL-like query language. For SQL databases, SQL is typically the only, or predominant, interface to the data.
- Data model. With NoSQL database systems, data isn't modeled as tables with fixed rows and columns, as with a SQL DBMS. Instead, depending on the NoSQL database, data can be modeled as JSON documents, graphs with nodes and edges, or key-value pairs. Wide-column stores use the table and row concept, but columns can be dynamic from row to row within a table.
- Schema. The schema for a NoSQL database is flexible, meaning there's no fixed structure to the data, data types and lengths for data elements. Data can be stored in a free-form, or schemaless, manner. This approach offers programmers a higher degree of flexibility, which can ease development efforts. With SQL databases, the schema is fixed, with rigid data types and lengths for each column, and every row must match the defined column layout and structure. For example, if a column is defined as an integer, only integer data can be stored in the column and the DBMS will reject any attempt to do otherwise. This approach delivers better data quality because the DBMS enforces rules as data is added.
- Scalability. NoSQL databases usually execute horizontal scaling, also known as scaling out. Scaling out involves adding more hardware to a system, usually in the form of new commodity servers. Horizontal partitioning using sharding is frequently used in NoSQL systems to break large databases into smaller pieces spread across multiple servers. The SQL approach typically is vertical scaling, also referred to as scaling up. With vertical scaling, additional resources are added -- such as a more powerful CPU or additional memory -- to handle additional workload or to improve performance.
- Data integrity. NoSQL and SQL databases use different approaches to protect the integrity of data as it's created, read, updated and deleted by applications and users. Most NoSQL database systems manage data integrity with an approach known as BASE (Basically Available, Soft State with Eventual Consistency). Using BASE, data can stay inconsistent for some time, but database replication eventually updates all copies of the data to be consistent. Some applications can tolerate this type of inconsistent data, whereas others can't.
SQL databases use the ACID approach, which NoSQL databases don't follow. Each of its four qualities -- atomicity, consistency, isolation and durability -- contribute to the ability of a transaction to ensure data integrity in SQL databases. Using ACID, each transaction -- when executed alone, in a consistent database state -- either completes, producing correct results, or terminates, with no effect. In either case, the resulting condition of the database always will be a consistent state.
NoSQL vs. RDBMS
NoSQL and relational database management systems (RDBMSes) are different database systems, each having their own strengths and weaknesses. The major differences between the two include the following:
- Structure. RDBMSes store data with rows and columns in tables and follow the ACID properties to ensure data integrity. NoSQL databases can store data in various formats, including key-value pairs, document-oriented, column-oriented or graph-based. They're designed for flexibility and scalability.
- Schema. RDBMSes require a predefined schema, which means that the tables and relationships between them are defined before data insertion. NoSQL databases have a flexible schema and can therefore handle semistructured and unstructured data efficiently.
- Query language. SQL is typically used to interact with RDBMSes, as it provides powerful capabilities for querying and manipulating structured data. While some NoSQL databases have their query languages, many use simpler APIs for data access. Some support querying similar to SQL, but not to the same extent as RDBMSes.
- Scalability. Relational databases typically scale vertically. This means they're scaled by increasing the power of the server hardware, which can be expensive. NoSQL databases are often chosen for their ability to scale horizontally, which enables them to handle large amounts of data by adding more servers to the database cluster.
Evolution of NoSQL
SQL and relational database systems are pervasive because they deliver a general-purpose mechanism for supporting most data management requirements. They're designed to be reliable, accurate and useful for planned applications as well as ad hoc and complex queries. Nevertheless, some SQL and relational requirements -- for example, rigid schema and strict ACID -- can make them less suitable for applications that require flexible data and high speed.
NoSQL database systems arose to address these needs, many developed by companies such as Amazon with its DynamoDB, Meta and its Apache Cassandra, and Google with its Bigtable database to address their specific needs. Another early influential NoSQL database system is Berkeley DB, developed at the University of California, Berkeley, beginning in the 1990s. Berkeley DB is described as an embedded database that closely supports specific applications' storage needs. This open source software provides a simple key-value store. Berkeley DB was commercially released by Sleepycat Software in 1999. The company was acquired by Oracle in 2006. Oracle continues to support open source Berkeley DB.
The NoSQL term can be applied to some databases that predated the RDBMS, but it more commonly refers to the databases built in the early 2000s for the purpose of large-scale database clustering in cloud and web applications.
NoSQL databases are becoming more common in cloud computing settings. Examine the wide range of NoSQL database options in the cloud that leading providers and other vendors offer.







