What is ESG (environmental, social and governance)?
Environmental, social and governance (ESG) is a framework used to assess an organization's business practices and performance on various sustainability and ethical issues. It also provides a way to measure business risks and opportunities in those areas. In capital markets, some investors use ESG criteria to evaluate companies and determine their investment plans, a practice known as ESG investing.
While sustainability, ethics and corporate governance are generally considered to be non-financial performance indicators, the role of an ESG program is to ensure accountability and the implementation of systems and processes to manage a company's impact, such as its carbon footprint and how it treats employees, suppliers and other stakeholders. ESG initiatives also contribute to broader business sustainability efforts that aim to position companies for long-term success based on responsible corporate management and business strategies.
Although ESG is often associated with investing, it's also an important consideration for a broader audience, including customers, suppliers and employees, who are concerned with an organization's sustainability.
ESG's three core principles
As the number of ESG funds for managing investments increases, business and IT leaders are increasingly paying attention to ESG as a functional approach to doing business. Each aspect of ESG plays an important role in the effort to increase a company's focus on sustainable and ethical practices. The following are details on common ESG criteria companies and investors use.
This article is part of
ESG strategy and management guide for businesses
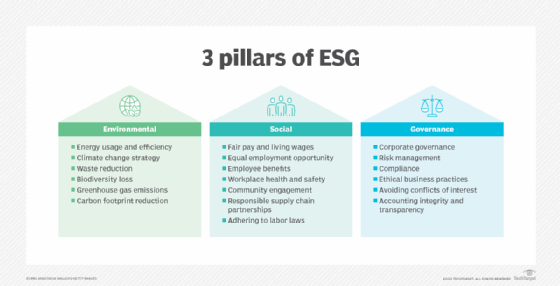
Environmental
Environmental factors involve considerations of an organization's overall effect on the environment and the potential risks and opportunities it faces because of environmental issues, such as climate change and measures to protect natural resources. Examples of environmental factors that can be ESG criteria include the following:
- Energy consumption and efficiency.
- Carbon footprint, including greenhouse gas emissions.
- Waste management.
- Air and water pollution.
- Biodiversity loss.
- Deforestation.
- Natural resource depletion.
Social
Social factors address how a company treats different groups of people and its social impact, including employees, suppliers, customers and community members. The criteria used include the following examples:
- Fair pay for employees, including a living wage.
- Diversity, equity and inclusion programs.
- Employee experience and engagement.
- Workplace health and safety.
- Data protection and privacy policies.
- Fair treatment of customers and suppliers.
- Customer satisfaction levels.
- Community relations, including the organization's connection to and impact on the local communities in which it operates.
- Funding of projects or institutions that help poor and underserved communities.
- Support for human rights and labor standards.
Governance
Governance factors examine how a company polices itself, focusing on internal controls and practices to maintain compliance with regulations, industry best practices and corporate policies. Examples include the following:
- Company leadership and management.
- Board composition, including its diversity and structure.
- Executive compensation policies.
- Financial transparency and business integrity.
- Regulatory compliance and risk management initiatives.
- Ethical business practices.
- Rules on corruption, bribery, conflicts of interest, and political donations and lobbying.
- Whistleblower programs.
Why is ESG important for businesses?
ESG has become an important aspect for businesses to pay attention to, as people are becoming increasingly concerned about environmental, social and governance-related issues. Concerns like climate change, human rights and compensation have become bigger topics of conversation amongst broader audiences. Other important business factors ESG initiatives consider include the following:
- Transparency. ESG reports provide more transparency for investors, enabling them to make informed business decisions.
- Long-term sustainability. ESG frameworks help businesses evaluate their impact on the world while also providing a way to track progress on goals. Likewise, consumers are more likely to show more brand loyalty to organizations with worthy ESG initiatives.
- Risk management. A well-implemented ESG framework helps businesses identify and mitigate sustainability and ESG risks.
- Regulatory compliance. Governments and other regulatory bodies are implementing more regulations related to factors that ESG typically addresses. Having an ESG framework in place helps an organization avoid fines or other legal issues.
Pros and cons of ESG
The pros of ESG practices for investors and companies include the following:
- Investment returns and sustainability can mix. Sustainability funds can achieve similar or better returns compared to traditional funds. According to global financial services company Morgan Stanley, in 2023, sustainable funds outperformed traditional funds across all major asset classes and regions.
- ESG can attract new customers for additional growth. Consumers and business customers who factor ESG considerations into their buying decisions are likely to seek out products or services provided by companies that are focused on ESG.
- ESG investing pushes companies to make other positive investment decisions. Organizations with ESG initiatives tend to focus on a wide range of environmental issues and ethical practices. For example, ESG aligns with the triple bottom line, a sustainability-focused accounting framework that companies can use to measure the overall economic value they create and their social and environmental impact.
- Helps companies attract and retain high-quality employees. It can boost employee motivation and increase overall productivity by giving workers a sense of purpose.
- Reduces costs. When ESG practices are incorporated into the fabric of an organization, operating expenses, energy bills and other costs can be reduced over time.
Potential cons of ESG practices include the following:
- Doesn't follow a one-size-fits-all approach. One company's approach to ESG might not work for another, which complicates both management of ESG initiatives and ESG investing. The need to weave ESG efforts into both day-to-day business practices and long-term strategies adds more complications.
- ESG strategies that aren't authentic can backfire. Organizations that focus on ESG inconsistently, use it as a brand image ploy or disconnect it from their business strategy likely won't be successful. For example, a company that engages in greenwashing -- making false or misleading claims about environmental actions -- could face customer backlash that affects revenue and the value of its stock.
- Strong stock market performance isn't guaranteed. While there are success stories, focusing on ESG doesn't guarantee strong performance by a company's stock. In addition to other internal factors, changes in market conditions, business trends and the overall economy can negatively affect the performance of companies and ESG funds alike.
- Creating a diverse investment portfolio can be difficult. For investors focused on an ESG-led investment strategy, it might be harder to create a balanced portfolio that aligns with long-term goals.
- Detailed performance reporting across different ESG criteria can be challenging. Most ESG factors aren't tied directly to financial data, resulting in additional effort to provide tangible performance results. Further, knowledge gaps reside between ESG information and the supply chain as reporting standards and frameworks aren't consistently applied.
How to define ESG goals
Defining ESG goals and setting solid timelines is a strategic process that must align with a company's mission, values and long-term objectives. This process should include the following steps:
- Establish ESG needs. The organization should first conduct a baseline assessment to evaluate its current needs.
- Identify key areas for ESG frameworks. The organization should identify any areas for potential improvement such as regulatory compliance initiatives, greener data centers, sustainable supply chains, carbon offsetting or net-zero emission pledges.
- Set goals. These goals should align with business strategies and be considered SMART -- specific, measurable, achievable, realistic and time-bound.
- Determine responsibilities. The organization should plot out responsibilities and governance structures, which helps ensure accountability.
- Create a timeline. ESG goals should be broken down into different periods to ensure accountability. These terms can be short, or one to two years; medium, or three to five years; and long, or five plus years.
- Measure and adjust. Once implemented, the organization should keep track of performance and make periodic adjustments as needed.
ESG initiatives typically require an extended period to see a return on investment. Long-term projects, such as achieving net-zero emissions, can take several years to transition into. This requires a consistent commitment to continuous monitoring, reporting and adjusting.
How to collect and report on ESG data
A formalized ESG data collection process provides a framework for structured data collection, aggregation, analysis and cleaning, which helps enable accurate ESG reporting.
The data collection strategy used might differ depending on the framework, but some common data collection strategies include the following:
- Data aggregation. Data should be gathered from any key area pertaining to ESG initiatives. This can cover different departments like data from operations, human resources (HR) and finance teams.
- Centralized data management system. A centralized data management system is used to consistently consolidate and access data from multiple sources.
- Surveys, audits and business reports. A collection of tools can be used to send out and analyze ESG-related data. These, for example, could be employee surveys, environmental audits or regular business reports.
- Automation. Automated data collection tools can be used to automatically collect and process ESG data. This also helps enable real-time data monitoring.
There are also several different ESG reporting frameworks that an organization can consider, including the following:
- IFRS Sustainability Disclosure Standards. Developed by the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) Foundation, this framework creates a consolidated and comprehensive view of sustainability efforts in reporting organizations. It's at the heart of ongoing efforts to simplify the ESG reporting process by consolidating, integrating or aligning various frameworks.
- SASB Standards. This framework is an approach to providing data for financial reporting on an organization's sustainability efforts. It was originally developed by the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) but is now part of the IFRS Foundation. The IFRS standards build on the SASB ones, but the latter framework is also still being updated.
- CDSB Framework. Created by the Climate Disclosure Standards Board (CDSB), this framework was designed to help measure the environmental side of ESG reporting. The CDSB has also been consolidated into the IFRS Foundation, and the CDSB Framework's technical guidance was used in developing an IFRS climate disclosure standard. The framework is still available for use but is no longer being updated.
- GRI Standards. Developed by the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), this framework provides a set of sustainability standards for reporting. Joint work is underway to identify and align common disclosures in the GRI and IFRS standards, but the two frameworks will remain separate.
- TCFD Recommendations. This framework for reporting on financial risks posed by climate change includes four focus areas -- governance, strategy, risk management, and metrics and targets. It was developed by the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures, a group commonly known as the TCFD that was created by the Financial Stability Board. The recommendations were incorporated into the IFRS standards, and the TCFD has now disbanded.
- CDP. This framework is a disclosure platform for reporting on business risks and opportunities related to climate change plus water security and deforestation issues. It was developed by the Carbon Disclosure Project, which also is now known simply as CDP. The questionnaire that companies fill out when using the CDP framework has been aligned with the IFRS climate standard.
- Streamlined Energy and Carbon Reporting. This framework developed by the U.K. government provides guidance for ESG reporting by qualifying companies based there.
- U.N. Guiding Principles Reporting Framework. This United Nations framework focuses on ethical governance and issues related to human rights.
What types of industries can benefit from ESG initiatives?
Small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) might assume their lack of resources could be a hindrance to ESG adoption, and that any ESG efforts won't pay off in the long run, but that isn't necessarily the case. While larger organizations might have extra resources to set up ESG policies and form high-level sustainability partnerships, SMBs can still attract socially conscious investors without going through the same level of bureaucracy and red tape that larger organizations face.
Aside from business size, ESG initiatives are applicable to many different industries. Resource-intensive industries and those that have large environmental impacts can greatly benefit from ESG efforts. For example, the following industries typically see benefits from implementing ESG initiatives:
- Energy. Oil, gas companies and even renewable energy-based companies can focus on reducing carbon emissions with ESG frameworks in place. The fossil fuel industry, for example, can also focus on adopting and transitioning to renewable energy sources.
- Financial. Financial services can incorporate ESG criteria into investment decisions, financial reporting and risk management practices. Banks, insurance companies and asset managers, for example, can use ESG criteria to assess businesses that pose financial risk, with those that have more sustainable opportunities for long-term growth.
- IT. Information technology businesses can benefit from implementing ESG initiatives by adopting more energy-efficient technologies, reducing electronic waste or ensuring an increased level of data privacy and security.
- Manufacturing. Manufacturing businesses can use ESG to improve cost savings, operational efficiency and reduce waste. These companies can focus on implementing sustainable production practices and ensure safer working conditions.
- Agriculture. ESG initiatives can be implemented in agriculture industries to improve yield, reduce environmental affects and help protect those businesses from climate change. This is done by implementing more sustainable farming practices, water conservation and using fair labor practices.
- Retail. Retailers benefit from ESG frameworks by using sustainable sourcing, reducing waste, using fair labor practices and improving transparency in the supply chain. These practices can also appeal to consumers who are more environmentally or socially conscious, improving brand loyalty.
- HR. HR departments that adopt ESG practices could see benefits such as better employee satisfaction and reduced turnover. This might be done by focusing on improving diversity and inclusion, ensuring fair treatment and compensation of employees and promoting a more positive workplace culture.
- Supply chains. Supply chains used in different industries can also be improved by adopting ESG practices that focus on providing more sustainable sourcing, reducing carbon footprints and working with more ethical suppliers.
What's the difference between ESG and sustainability initiatives?
Sustainability is an idea that focuses on an organization's efforts to minimize its effect on the Earth. Sustainability typically focuses on balancing long-term environmental, social and economic needs.
The main differences between ESG and sustainability have to do with their scope and purpose.
Sustainability as a term can be used broadly, but typically refers to protecting the planet and people. Meanwhile, ESG is primarily focused on how the world affects companies or investments. ESG also broadens its focus beyond environmental sustainability; it also considers social and governance factors.
ESG is used as a framework to evaluate a company's performance on non-financial issues that could lead to a financial impact in the short and long term. Sustainability, however, places an increased importance on environmental issues and the organization's effect on the planet. Sustainability is meant to reduce negative environmental impacts while also ensuring that business practices don't compromise future generations.
ESG reports are also typically meant to be used by investors and financial stakeholders to make better-informed decisions, while sustainability initiatives are meant for investors, employees, consumers or any regulatory bodies. ESG also typically involves specific ESG metrics that are measured and reported on, while sustainability practices don't have to encompass formal reporting.

Alternatives to ESG investing
While ESG investing is now a prominent form of sustainable investing, it isn't the only option for those interested in similar approaches. Although ESG investing and the following alternatives are often talked about interchangeably, some differences exist:
Socially responsible investing. SRI focuses specifically on investments in organizations that match an investor's environmental, ethical and social values. For example, it excludes companies that manufacture certain products or profit from practices that harm the environment. SRI concentrates on the investor's values above a company's financial performance. Comparatively, ESG investing strategies focus on high standards of corporate behavior but often also consider business performance together with ESG criteria. In addition, ESG investing typically is based on more quantitative data because of the use of ESG scores and metrics.
Impact investing. This strategy focuses on helping an organization achieve specific goals that have social or environmental benefits. For example, impact investing could support a company that's working to develop renewable energy technology or promises to donate a percentage of its profits to charitable groups. Impact investing can also help promote corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives in companies. CSR is a self-regulating approach that emphasizes doing good and taking positive actions, such as a shoe company giving away a pair of shoes for each pair purchased.
Conscious capitalism. Unlike the previous strategies, conscious capitalism refers to a socially responsible economic and political philosophy. It focuses on the premise that businesses should operate ethically while pursuing profits. The strategy emphasizes that an organization should serve its entire ecosystem, not just shareholders, other prominent stakeholders and company leadership. Other conscious capitalism beliefs include the following:
- Organizations should have a higher purpose beyond pure profits to inspire and engage their key stakeholders.
- The focus should be on the entire business ecosystem to create and optimize value for all stakeholders.
- Conscious leadership follows the collective we vs. me mentality to drive the business.
History of ESG investing, regulations and standards
Socially responsible investing practices began to take shape in the 1960s and 1970s. Activists started pushing academic institutions and companies to divest their stock holdings in organizations that did business in South Africa to protest the apartheid system then in place there.
In 1971, two United Methodist ministers opposed to the Vietnam War launched the Pax Fund, the first U.S. mutual fund open to the public that used social and environmental criteria in investment decisions. Initially, the fund avoided investing in weapons manufacturers -- it later added tobacco, alcohol and gambling companies and heavy polluters to the list. Still in existence, it's now owned by London-based Impax Asset Management and named the Impax Sustainable Allocation Fund.
The South Africa divestment campaign accelerated in the 1980s, and a broader push to divest holdings in tobacco makers began among public health organizations, universities and public pension funds. In 1990, investment research firm KLD Research & Analytics created the Domini 400 Social Index to help guide socially conscious investors -- one of the first SRI indexes, it included 400 companies that prioritized social and environmental responsibility. It's now namedthe MSCI KLD 400 Social Index and is owned by MSCI Inc., which acquired KLD in 2010.
In 1995, the Washington-based Social Investment Forum, now known as the U.S. SIF Foundation, published a report on sustainable investing trends in the U.S. that said $639 billion in total assets were being managed using SRI strategies. The latest version of the now-biennial report, published in December 2022, put that figure at $8.4 trillion for ESG and sustainable investments overall, which U.S. SIF said amounted to 12.6% of all the investment assets under professional management in the U.S.
The sustainable investing movement gained more momentum with the founding of the Carbon Disclosure Project in 2000. Now known simply as CDP, it created a platform for companies to report on their carbon emissions and footprints. Two years later, a group of 35 institutional investors requested climate disclosures from 500 large companies, which helped to normalize such reports.
The term ESG was popularized by "Who Cares Wins," a report first published in 2004 by a group of 18 banks and investment firms that was organized by the United Nations. The report offered recommendations on how to better incorporate ESG issues into asset management, brokerage services and related research activities. It was followed a year later by the so-called "Freshfields Report," another U.N.-backed document that was prepared by the London-based law firm Freshfields Bruckhaus Deringer and outlined a legal framework for integrating ESG criteria into investment decisions.
The U.N. then asked another group of institutional investors to develop the Principles for Responsible Investment (PRI), a set of six ESG investing principles that was published in 2006 and continues to be promoted by the PRI Association. The evolution and growth of ESG investing picked up pace with the formation of more ESG reporting initiatives, including the CDSB in 2007, the SASB in 2011, the TCFD in 2015 and the Workforce Disclosure Initiative in 2016.
More recently, key developments include the following:
- 2020. The World Economic Forum and the Big Four accounting firms released a standardized set of stakeholder capitalism metrics to make ESG reporting by companies more consistent and easier to compare.
- 2021. The European Union's Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation went into effect, creating new sustainability reporting requirements for financial services and investment firms.
- 2022. The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission similarly proposed rules amendments with more detailed disclosure and reporting requirements for investment funds that use ESG criteria. The CDSB and the SASB standards were consolidated into the IFRS Foundation, which plans to create a unified set of IFRS Sustainability Disclosure Standards.
- 2023. The EU's Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive went into force in January. Eventually, it will require 50,000 companies to file annual reports on their business risks and opportunities related to social and environmental issues and how their operations affect people and the environment.
- 2024. Another sustainability-related measure went into force in the EU -- the Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive (CSDDD). Starting in 2027, qualifying companies that operate in the EU will be required to identify and act on adverse human rights and environmental impacts. The CSDDD applies to both internal operations and supply chains. It requires annual reporting on due diligence activities.

Hundreds of ESG funds are now available to investors in the U.S. alone. However, ESG investing has become a political issue. On Sept. 19, 2024, the Republican-led U.S. House of Representatives approved H.R. 4790, the Prioritizing Economic Growth Over Woke Policies Act, preventing retirement fund managers from considering ESG factors in their investment decisions. This legislation now goes the U.S. Senate.
Since its conception, ESG has become a critical framework for guiding businesses toward sustainable practices in environmental, social and governance-related tasks. Learn more about the history behind ESG investing.