What is digital transformation? Everything you need to know
Digital transformation is the incorporation of computer-based technologies into an organization's products, processes and strategies. Organizations undertake digital transformation to better engage and serve their workforce and customers, and thus, improve their ability to compete. In challenging economic times, operational efficiency and cost optimization can also become important transformation objectives.
Often large in scope, a digital transformation initiative can require an examination and reinvention of all facets of an organization, from supply chains and workflows, to employee skill sets and org charts, to customer interactions and value proposition to stakeholders.
Successful digital transformations yield ongoing business benefits: Digital technologies and processes enable organizations to adeptly respond to customer demands in the present and as demands evolve. Digital transformation also builds the infrastructure and skills required for taking advantage of fast-evolving technologies that could confer a competitive advantage.
A digital transformation strategy positions organizations to survive and thrive in a future where technology is the critical economic driver.
But transformation requires cultural adjustment as well as technology adoption. Business leaders must build agile organizations able to deal with change and uncertainty as permanent fixtures of corporate life. In doing so, they'll be better equipped to navigate rapidly emerging developments such as the latest generation of artificial intelligence (AI). AI is poised to have an enormous influence on the methods and goals of digital transformation.
"AI is fundamentally changing the landscape of digital transformation by revolutionizing how businesses operate," said Angelic Gibson, CIO of AvidXchange, a fintech in Charlotte, N.C.
Why is digital transformation important?
The digitization of society started in the late 20th century and underwent rapid acceleration in the first two decades of the 21st century, spurring a growing need for digital transformation across industries.
Indeed, many organizations believe they must either adapt to the changing market forces driven by digitalization or face extinction. According to an IDC report, 82% of organizations believe they "must invest in digital transformation or be left behind." The 2023 Insight Intelligent Technology Report, commissioned by integrator Insight Enterprises, polled 1,000 senior business executives. Nearly half of those respondents cited the ability to keep pace with technological innovation as one of the greatest threats they face over the next 12 months.
"The survey results indicate that people are getting ready to invest again in innovation," said Matt Jackson, global CTO at Insight Enterprises.
The urgency of innovation is exemplified in the oft-cited case of Blockbuster LLC, which, in the early 2000s, was a global entity with video rental stores throughout the United States and around the world. But its presence and relevance precipitously declined from about 2005 onward, as Netflix and others harnessed emerging technologies and capitalized on the consumer appetite for on-demand entertainment delivered via highly profitable streaming video services. The power of digital technologies to disrupt is also evident in the rise of Amazon from online bookseller to an electronic commerce (e-commerce) juggernaut that redefined the retail industry.
More recent examples of digital disruptions include the emergence of fintech companies challenging traditional financial institutions and fast fashion retailers using AI to overtake long-established apparel providers.
The danger of market leaders being displaced and disrupted is expected to continue, as emerging technologies enable new business models, more engaging customer experiences, novel products and services, and other innovations.
As a result, enterprises are boosting their spending on digital transformation. Grand View Research forecasted the worldwide market to reach $4.6 trillion by 2030, expanding at a 26.7% compound annual growth rate.
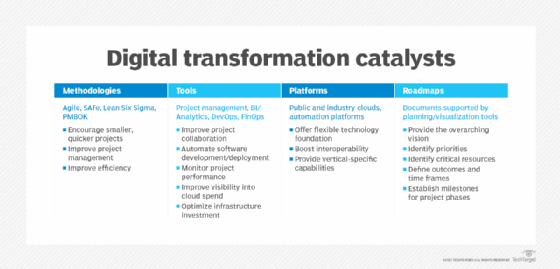
What drives digital transformation?
Digital transformation emerged more than a decade ago as an antidote to digital disrupters. The threat of disruption continues to drive today's initiatives. But several other factors can also inspire organizations to roll out digital technology to change important processes or revamp entire business models.
Those include the traditional business virtues of reducing waste and eliminating redundant processes. Enterprise Strategy Group's "2023 Technology Spending Intentions Survey" identified operational efficiency as the top driver for digital transformation initiatives. More than half of the 700-plus IT professionals that TechTarget's Enterprise Strategy Group surveyed cited that factor.
Customer-facing initiatives are also ripe for digital innovation. Organizations are motivated to transform customer experience (CX), through modernizing contact centers and launching new digital offerings for buyers. The ability to create data-driven products and services ranked second on the list of digital transformation drivers, according to the Enterprise Strategy Group survey. Providing a better and more differentiated CX placed third.
What are the goals of digital transformation?
The drivers behind digital transformation point an organization toward a key goal or goals. The actual objectives, however, will depend on what business leaders consider the proper scope of an initiative and the resources at their disposal.
For example, an organization could focus strictly on the goal of transforming a business process, eliminating redundant activities or automating manual hand-offs to prevent data-entry errors. A revamped business process, enabled by digital technologies, increases productivity and business velocity. This type of transformation harkens back to the business process reengineering projects of the 1990s.
A step up from business process transformation, business model transformation seeks to reinvent a segment of a business or, potentially, the entire operation. The transition from a brick-and-mortar company to a digital business provides one example of wide-ranging transformation. Initiatives at this scale will require more funding and a wider range of skill sets.
An enterprise may also seek a middle path, selecting and transforming related processes within a particular business concern such as CX. Other types of transformation include domain transformation and cultural transformation, with the latter goal featuring in nearly all initiatives.
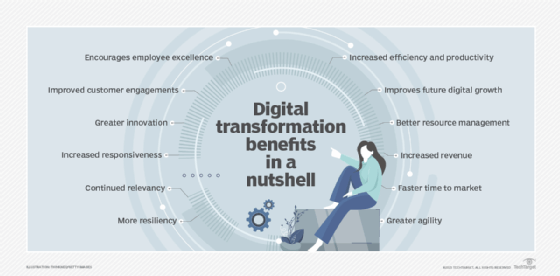
What are the benefits of digital transformation?
Digital leaders that reach their transformation goals stand to gain several advantages. The core digital transformation benefits -- all interrelated and interdependent -- include:
- Increased efficiency and productivity.
- Better resource management.
- More resiliency.
- Greater agility.
- Improved customer engagement and personalization.
- Increased responsiveness to market demands.
- IT modernization.
- Greater innovation.
- Faster time to market with new products and services.
- Increased revenue.
- Continued relevancy.
Overall, digital transformation enables organizations to succeed in this digital age: For businesses, that success means higher revenue and bigger profits. Other types of organizations, such as nonprofit institutions and government agencies, can better meet the needs of stakeholders or improve citizen services.
What are digital transformation technologies?
Technology drives both the need for digital transformation and supports the digitalization of an organization. Although no single application or technology enables transformation, several digital transformation technologies are critical to digitalization:
- Cloud computing. With its elastic compute and data storage services, cloud computing often provides the foundation for transformation initiatives, along with offerings such as cloud-based CRM and ERP systems.
- Commoditized information technology. Gives an organization the ability to focus investment dollars and people resources on the IT customizations that differentiate it in the marketplace.
- Mobile platforms. Enable work to happen wherever and whenever.
- Machine learning (ML) and AI. When fueled by comprehensive data programs, provide organizations with insights for faster, more accurate decisions around sales, marketing, product development and other strategic areas.
- Edge computing. Provides another tier for enterprise compute and storage, enabling use cases in industries including manufacturing, healthcare and retail.
- IoT. Generates vast amounts of data through sensors embedded in myriad devices; the resulting big data collection can fuel cloud- or edge-based data analytics.
- Hyperautomation. Includes technologies such ML and AI, RPA and business process management for scaling automation across an enterprise.
Additional emerging transformational technologies help organizations to move faster, work more efficiently, and create new products and services, including the following:
Transformation technologies are often used in combination, rather than as isolated deployments. A manufacturer, for instance, might use 5G to boost connection speed to make more data available from IoT devices. That business could then analyze the data in the cloud to gain insight into operations across factories, while also performing analytics at the edge to understand conditions at the local plant. ML could be used for predictive maintenance, with the computer vision aspect of AI playing a quality management role.
"Any innovation project is always a combination of different technologies and thoroughly designed processes aiming to achieve business goals," said Max Ivannikov, head of IoT at DataArt, a software engineering firm based in New York.
Digital transformation examples
Digital transformation can take different forms, but it generally falls into one or more of several categories: digitalizing the customer experience, opening new market opportunities, enabling innovation and increasing operational efficiency.
Examples of digital transformation success in business are plentiful. Here are four high-profile examples:
Toyota Motor North America (TMNA). The automaker tapped hyperautomation as the cornerstone of its digital transformation initiative. The company had been on the AWS cloud for several years but used many manual processes for handling cloud provisioning and other developer requests. TMNA, however, automated those functions, deploying a development platform built on Spotify Backstage, an open-source technology for creating developer portals. Developers now use self-service features instead of filling out request forms. The resulting cost savings let TMNA boost its investment in data science and analytics.
Capital One. The bank has made ML an integral part of its digital transformation program. Capital One uses ML to scan for anomalies across its business lines, detect credit card fraud and boost demand generation. This ML investment is part of a decade-long technology transformation at Capital One, which now uses cloud-based platforms such as Snowflake's data warehouse as the core infrastructure on which developers build models.
Nespresso. The maker of specialty coffee machines and operating unit of Switzerland-based Nestlé Group, Nespresso deployed a cloud-based customer CRM system that offered customers omnichannel access to shopping and customer service. Customers can reach the company whether they use the website, use a mobile device or visit a store. Having a 360-degree view of each of its customers enabled Nespresso to move into more markets and improve sales.
Domino's Pizza. The pizza company successfully transformed itself for the digital age, launching innovative tech-driven services, such as its Domino's Tracker, and mobile technologies that helped fuel significant growth in the past decade.
How to develop a digital transformation strategy
A digital transformation strategy is a carefully planned approach to using digital technologies and tools in order to achieve specific business goals and objectives. While each organization's vision of success will differ, the following five steps are broadly useful for developing a strategic plan:
- Understand the market and the organization's place in it, as well as its existing and potential customers.
- Analyze where the market is heading so the organization can anticipate the potential for digital disruption and how it can be the disruptor instead of being disrupted by others.
- Identify the existing and potential value proposition through internal evaluation and external research.
- Develop a vision for what the organization should be in the future, including how its products and services should evolve to meet customer needs and expectations.
- Create a digital transformation roadmap that offers a way to move from current to future state.
As part of this strategic planning, executives should assess the organization's existing capabilities -- from employee skills to its existing IT stack, articulating what additional capabilities will be needed and devising a plan to obtain those capabilities. Organizational leaders will need to draw on a number of traditional disciplines, such as project management, as well as newer techniques, such as Agile methodologies, in order to successfully bring their organization, its culture, its people and its technologies into the future.
Digital transformation is not a one-time exercise. Experts agree that organizations must evaluate their digital transformation process and strategy on an ongoing basis and adjust it to maximize business value.
What are common digital transformation challenges?
Most organizations pursue some level of digital transformation, but the evidence suggests getting there can prove difficult.
Gartner's 2023 Board of Directors survey found 30% of digital leaders have "significantly advanced toward digital transformation goals." Similarly, the IDC-Insight report noted few of the business leaders polled expect to reach the goal of becoming a digital business "disruptive in the use" of new technologies and business models -- at least in the near term. Only 23% of the survey respondents said they expect to realize digital at scale by 2024.
Cultural roadblocks and changing customer expectations rank among the top digital transformation challenges, contributing to a failure rate that industry analysts put in the 70% to 80% range. The following are the most common reasons experts cited for why digital transformation failures happen:
- Lack of executive (CXO) sponsorship.
- Not having a collaborative culture.
- Not hiring digital transformation talent.
- Lack of clear digital transformation goals.
- Failing to think through the required technology.
- Adopting a fail-fast attitude.
- Overfocus on technology fads.
- Unclear understanding of the role of digital technologies in transformation.
- Lack of broader organizational alignment.
- Not investing in appropriate oversight.
- Not figuring out the right value and objectives and key results.
Another digital transformation hurdle: legacy applications that don't support digital initiatives but can't easily be replaced. If the leadership group refuses to pay to replace old technologies or fails to garner the necessary executive- and board-level support for investing in a technology overhaul, digital transformation is unlikely to happen.
In the IDC-Insight survey, half of business leaders said "infrastructure complexity" inhibited the completion of digital initiatives, while 46% said legacy technology hindered organizational strategy.

The importance of digital transformation culture
Building a digital transformation culture is frequently cited as the single most important task for organizations engaged in transformational change. Leaders need to create an organizational culture where continual improvements happen and where stakeholders are open to ongoing change. Everyone must be willing to identify and abandon dated and ineffective processes and replace them with something better.
Many organizations, however, struggle to build a digital culture capable of supporting and sustaining transformation.
TEKsystems' 2023 "State of Digital Transformation Report," found organizations cited cultural factors as their main transformation obstacles. The 855 technology and business decision-makers surveyed ranked the complexity of the current environment/siloed mindset and behaviors, creating a culture of continuous learning, and change management and implementation complications as their top three challenges.
Without attention to such critical cultural requirements, an organization could end up with modern technologies that enable more efficient or effective processes -- such as ordering raw materials, taking inventories or handling payments -- without truly transforming how the organization operates, what it has to offer its stakeholders and what value it produces for all involved.
Creating a culture of innovation requires organizations to adopt a higher risk tolerance as they evaluate emerging technologies. In that regard, a portfolio mindset that accepts wins and losses is important for encouraging lasting transformation. The absence of meaningful cultural change can result in backsliding on transformation initiatives.
"People have a certain way of working that they're used to -- the status quo," said David Chou, director of cloud capabilities at Leidos, a technology, engineering and science solutions and services provider based in Reston, Va. "If you don't focus on 'how do I change the way people interact with work?' they'll go back to their mental playbook on how they used to do things."
Digital transformation team roles
Building the right team for a transformation effort is the most important component of a successful digital transformation strategy, according to Metrigy CEO and principal analyst Robin Gareiss. The effort "starts with good leaders -- typically C-level executives with budget, influence and respect," she said. The chief executive officer (CEO) usually appoints the person in charge of the digital transformation initiative.
At some companies, this might be the chief digital officer (CDO) or a person hired specifically to work on digital transformation, or the project might be the responsibility of the CIO, CTO or chief operations officer (COO), who spearheads the initiative in addition to their other duties. In addition, some enterprises have begun to appoint chief AI officers to manage AI strategy.
IT teams handle a significant amount of the work associated with the selection, implementation and management of the technologies that enable and drive the initiative. The IT team working on a digital transformation initiative must be able to innovate, test, deploy and scale projects quickly.
Critical IT roles for digital transformation include the following:
- Cloud architects.
- Data architects.
- Digital product managers.
- Information security (infosec) leaders.
- Scrum masters.
- Systems integrators.
- User experience (UX) engineers.
How to measure digital transformation ROI
Digital transformation is a broad undertaking with no singular endpoint; it typically requires multiple ongoing initiatives that involve investments in new technologies, new skills, an updated workplace culture and even organizational restructuring.
Despite the overarching nature of digital transformation, organizations can indeed measure how well they're doing on their digital transformation journey and whether their investments are delivering returns.
Executives can measure ROI delivered by digital transformation initiatives as they would quantify ROI on more conventional projects. The steps for doing so include:
- Identifying the business problem or opportunity.
- Determining the objectives the initiative should address; setting goals for a digital transformation initiative helps organizations allocate resources and measure progress.
- Determining the components and associated costs to deliver on the initiative.
- Identifying the value metrics that show the return on the budgeted digital investment.
- Establishing a project timeframe and calculating the ROI.
The ability to demonstrate a convincing financial return on a digital transformation initiative will become increasingly critical as leaders compete for funding with other priorities in a fast-changing business environment.
How did the COVID-19 pandemic affect digital transformation?
The onset of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 made digital transformation a matter of survival, as enterprises scrambled to enable remote work and serve customers in lockdown.
"It woke up a lot of C-suite officers, alerting them to stop dragging their feet on their digital transformation efforts, because they saw that the companies that were more mature in their digital transformation suffered much less disruption and much less costly disruption," said Rick Pastore, research principal at SustainableIT.org, about the effect of the pandemic on transformation initiatives.
The COVID-19 pandemic sped up digital transformation, as organizations across nearly all industries were forced to limit or even abandon in-person transactions and virtualize as many interactions as possible. According to a Gartner survey, more than two-thirds of boards of directors accelerated their digital business initiatives in the wake of COVID-19 disruption, and about half predicted changing their organizations' business models as a result of the pandemic.
Other effects of the pandemic on digital transformation include:
- Wider use of contactless technologies as businesses overhauled payment systems.
- Higher adoption of self-service options in CX and omnichannel strategies.
- Pursuit of advanced e-commerce platforms and supply chain transformation to navigate shifts in customer demand and supplier disruption.
- Increased interest in AI in data analysis for predictive modeling.
- Evolution of the CIO from enabler to trusted partner in achieving business goals.
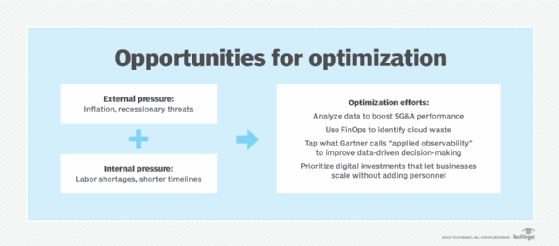
Current trends in digital transformation
The COVID-19 pandemic ushered in an era of increasing instability as organizations were compelled to deal with multiple, simultaneous crises. Inflation became an important concern starting around 2021 -- along with economic uncertainty stemming from the threat of recession. Environmental and geo-political threats also came into play.
Rapid developments in technology, generative AI in particular, compounded matters. The need to deal with fast-moving, unpredictable events and economic constraints changed the nature of digital transformation.
"The speed of business doesn't wait for you to finish up your programs," said Linh Lam, CIO of Jamf, an Apple device security company based in Minneapolis.
The main trends include the following developments:
- A shift from large-scale, open-ended projects to smaller, well-defined initiatives.
- Shorter delivery timelines for faster ROI.
- Wider use of Agile methods and digital transformation frameworks to guide projects amid changing business conditions.
- Adoption of FinOps and other cost optimization methods to keep cloud expenditures in check.
- Use of digital platforms and industry clouds to boost time to market.
- Greater reliance on hyperautomation to curb spending and free up funding for innovation.
Against this backdrop, promoting a culture of adaptability and planning for constant change now rank among the best practices for digital transformation.
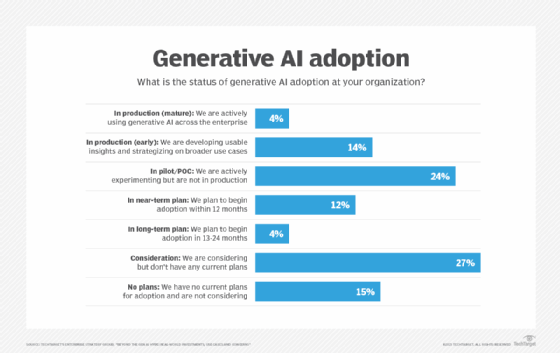
The future of digital transformation
The ascent of generative AI -- and its quick adoption among many enterprises -- promises to recast digital transformation.
The next few years are likely to see a closer coupling between the two movements. Over time, the lines may blur to the point that digital transformation becomes AI transformation. The changes will affect the digital transformation's objectives and the tools for achieving those goals.
The rapid uptake of generative AI will influence digital transformation as enterprises look to reinvent business processes, improve productivity and gain competitive advantage. TechTarget's Enterprise Strategy Group discovered that 54% of the organizations it polled will have adopted generative AI within the next 12 months. The market researcher's August 2023 report, "Beyond the GenAI Hype: Real-world Investments, Use Cases and Concerns," surveyed 670 technology and business decision-makers.
Improving customer experience and developer productivity are poised to become early prominent use cases for generative AI. The increasing use of generative AI in the tools practitioners use to deliver digital transformation projects should accelerate results.
The rise of generative AI also threatens to widen the gap between leaders and laggards along the technology adoption lifecycle. The possibility of falling farther behind could inspire digital transformation initiatives in which trailing organizations seek to catch up with technology.
"If you continue with the old ways of doing things, you are going to miss the boat," said John Cannava, CIO at Ping Identity.
Jason Sparapani contributed to this article.






