
What is data loss prevention (DLP)?
Data loss prevention (DLP) -- sometimes referred to as data leak prevention, information loss prevention or extrusion prevention -- is a strategy to mitigate threats to critical data. DLP is commonly implemented as part of an organization's plan for overall data security.
Using a variety of software tools and data privacy practices, DLP aims to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information. It does this by classifying the different content types within a data object and applying automated protection policies.
A multilayered DLP strategy ensures sensitive information remains behind a network firewall. Creating a DLP plan lets an organization review and update its data storage and retention policies and maintain regulatory compliance. It also helps organizations meet various challenges, such as the remote work trend and increasingly sophisticated cyberattacks.
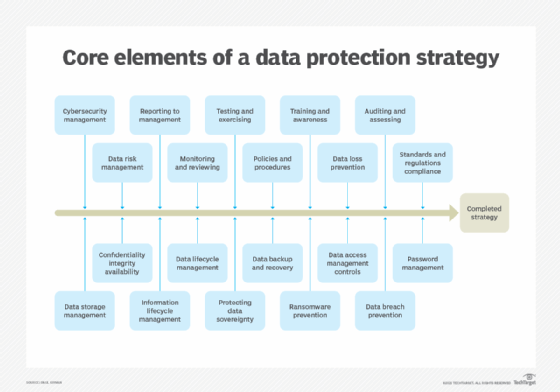
How does data loss prevention work?
DLP software monitors, detects and blocks sensitive data from leaving an organization. That means monitoring both data entering an organization's networks as well as data leaving the network.
This article is part of
What is data security? The ultimate guide
Most DLP software focuses on blocking actions. For example, if an employee tries to forward a business email outside the corporate domain against company policy, or they try to upload a corporate file to a consumer cloud storage service such as Dropbox also against company policy, permission would be denied.
DLP software can block employee computers from reading and writing to USB thumb drives to prevent unauthorized copying.
Detection primarily centers on monitoring incoming emails to look for suspicious attachments and hyperlinks that indicate phishing attacks. Most DLP software will flag inconsistent content for staff to manually examine or the system can block questionable content outright.
In the early days of DLP, security teams set the rules around detection and blocking, but those were simplistic and often circumvented. Newer software uses machine learning-based artificial intelligence, which can learn and improve detection and blocking over time. These tools can automate responses and provide near real-time monitoring and alerts.
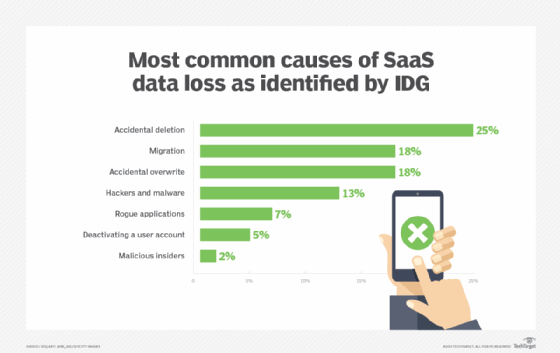
Common causes of data loss in the enterprise
The root causes of data loss vary, ranging from well-meaning employees making mistakes to malicious actors and man-made or natural disasters:
- Cyberthreats. Malicious actors can orchestrate various types of cyberattacks on an organization handling sensitive data, such as customer or client Social Security and credit card numbers. These attacks are becoming increasingly sophisticated. Organizations must be prepared for both external and internal threats.
- Human error. Employees do make mistakes when entering data, which can lead to gaps and other issues.
- Natural disasters. Floods, hurricanes, earthquakes and service provider outages are out of an organization's control. However, it's possible to anticipate such events and have a disaster recovery plan in place.
- Software and hardware malfunctions. An organization that doesn't frequently update or upgrade software can eventually experience performance bugs or failures which can inadvertently lead to data loss.
- Unsecured or stolen devices. Devices, especially portable ones, can be stolen and lead to data loss and exposure. It's imperative that policies dictate acceptable use of these devices to prevent theft and compromised data.
Benefits of DLP
DLP platforms have advantages for organizations that manage sensitive data:
- Improving visibility and incident response. DLP platforms provide a user interface that lets users view the status of their data sources. These platforms typically send out alerts and expedite incident responses when there's a data breach or cyberattack.
- Assisting with compliance. DLP platforms help organizations store, classify and use data in ways that comply with local, state and federal standards for handling sensitive data, such as the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).
- Limiting access to authorized personnel. DLP tools have authentication and access control features that only allow trusted employees to use sensitive data.
- Preventing data leaks. DLP reduces the likelihood that an organization will suffer a data breach or other attack, and thus be liable for financial costs or reputational harm associated with compromised or lost data.
Challenges of DLP
Despite these benefits, there are also challenges with both implementing and maintaining DLP systems:
- Complexities. Configuration and management of many data sources can become complicated depending on how much data an organization is handling and how many employees are using the platform, each with their own levels of access.
- Employee training. These systems require employee training and regular messaging with updates. This is an extra expense and effort.
- False positives. False positives can occur with DLP platforms, as benign activities can be flagged as threats, causing alert fatigue as employees divert time and resources unnecessarily.
Why is data loss prevention important?
Data loss can result in hefty fines and possibly criminal penalties. It also can negatively affect an organization's business and reputation, and even put it out of business.
In 2017, personally identifiable information (PII) of nearly 150 million people was stolen from an unpatched Equifax database. The company failed to fix the vulnerability promptly, then failed to inform the public of the breach for weeks after it was discovered. In July 2019, the credit agency was fined $575 million.
Data loss could cause executives to lose their jobs. Top execs at Target and Equifax resigned following major data breaches that involved customers' personal data and cost the companies millions in fines.
The average total cost of a data breach was $4.45 million in 2023, a 15% increase since 2020, according to an IBM and Ponemon Institute report. If the fines and other economic losses don't hurt a business, the loss of customer and public faith well might.
What are the types of data loss prevention?
Various data security products and techniques are available to provide corporate network DLP. These include the following:
- Data identification. DLP is only useful if it's told what is and isn't sensitive. Businesses should use an automated data discovery and classification tool to ensure reliable and accurate identification and categorization of data rather than leaving it to humans to decide.
- Protecting data in use. Data is moved around quite a bit internally, and bad actors conducting external breaches often rely on this to reroute the data. DLP software can help ensure that data in motion isn't routed someplace it shouldn't go.
- Protecting data at rest. This technique secures data at rest, such as data residing in databases, other apps, cloud repositories, laptops and other computers, mobile devices and storage.
- Endpoint DLP. This type of DLP functionality protects data at the endpoint device level -- including computers, mobile phones and tablets. It can block data from being copied and encrypt data as it's transferred.
- Data leak detection. Data leakage detection techniques involve setting a baseline of normal activity, then actively looking for unusual behavior.
- Cloud DLP. These services have evolved to manage and protect critical data in software-as-a-service and infrastructure-as-a-service applications.
Trends driving DLP adoption
More than 35% of all DLP implementations fail, according to Gartner. Such failure can lead to severe consequences for a business, including fines, penalties and a degraded reputation. It's these factors that drive DLP adoption, including the following:
- Cost of a data breach. As previously mentioned, the average total cost of a data breach is nearly $4.5 million. The long-term costs related to reputational damage can be higher.
- Compliance. The growing list of global regulations -- including PCI DSS, HIPAA and the EU-based General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) -- increases the need for DLP to help meet data governance legal requirements.
- Expanding data volumes. Companies produce more data than ever that generates a great deal of value. Sophisticated hackers are on the prowl to find ways to steal data for profit, including tactics such as identity theft, insurance fraud and other economic crimes.
- Chief information security officers (CISOs). Companies are hiring professional security specialists known as CISOs to create and oversee governance policies that secure intellectual property and other confidential data and information. CISOs typically use DLP as one of their security tools.
- Talent shortages. Skilled data security professionals are in demand and difficult to find. To compensate, organizations often outsource DLP to vendors that provide managed IT services.
- Wider attack surfaces. Cloud services, endpoint devices and third-party vendor tools are vulnerable to ransomware, malware and other cybersecurity threats.
- Insider threats. These can be intentional or malicious, but often they aren't. Employees transmitting important data using various communications tools can unintentionally put data at risk.
Data loss prevention best practices
Organizations can take the following five steps to implement a DLP program:
- Conduct an inventory assessment. Businesses can't protect what they don't know they have. A complete inventory is a must. Some DLP products -- from vendors such as Barracuda Networks, Cisco and McAfee -- will do a complete scan of the network.
- Classify data. Organizations need a data classification framework for both structured and unstructured data. Such classification categories include PII, financial data, regulatory data and intellectual property.
- Establish data handling and remediation policies. The next step after classifying the data is to create policies for handling it. This is especially true with regulated data and in areas with strict rules -- such as the EU's GDPR and the California Consumer Privacy Act.
- Implement a single, centralized DLP program. Many organizations implement multiple DLP plans across different departments and business units. This leads to inconsistent data and information protection and a piecemeal picture of the network. There should be one overarching program.
- Educate employees. Unintended actions are more common than malicious intent. Employee awareness and acceptance of security policies and procedures are critical to DLP.
Data loss prevention tools and technologies
There are two types of DLP solutions on the market today: dedicated and integrated.
Dedicated products are standalone ones that are in-depth and complex. Integrated products are more basic; they work with other security tools to provide DLP policy enforcement and are less expensive than dedicated DLP tools.
DLP software products use business rules to enforce regulatory compliance and classify and protect confidential and critical information. This means unauthorized users can't accidentally or maliciously share data that poses an organizational risk.
It's doubtful one tool will meet all of an organization's data loss prevention needs. Many DLP vendors have one area of focus, while others have suites of tools that fit together. Businesses can assemble a set of best-of-breed tools or use an all-in-one suite.
Some of the top DLP providers and products, according to TechTarget market research, are Digital Guardian DLP by Fortra, Forcepoint DLP, Palo Alto Networks Enterprise DLP, Proofpoint Enterprise DLP, Symantec Data Loss Prevention by Broadcom, Trellix Data Security and Zscaler Data Protection.
One of the primary causes of data loss is natural disasters. Learn about backup strategies organizations can implement to mitigate data loss.