What is data curation?
Data curation is the process of creating, organizing and maintaining data sets so people looking for information can access and use them. Curation involves collecting, structuring, indexing and cataloging data for users in an organization, group or the general public. Data is curated to support business decision-making, academic needs, scientific research and other purposes.
Data curation is part of the overall data management process. It is sometimes incorporated into data preparation work that gets data sets ready for use in business intelligence (BI) and analytics applications. In other cases, prepared data is fed into the curation process for ongoing management and maintenance. Some organizations have formal data curator positions. In ones that don't have a data curator, data stewards, data engineers, database administrators, data scientists or business users fill that role.
The data curation process stems from the centuries-old practice of selecting, organizing and presenting objects as part of collections, such as artwork in a museum or books in a library. The term curation dates to ancient times and comes from the Latin word curae, meaning care for -- a meaning it still has today, including in relation to data.
What is the purpose of data curation?
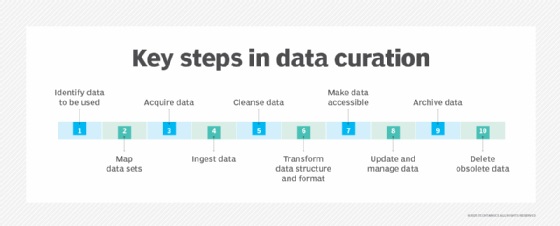
In business, data curation is a key component of an enterprise data strategy. It helps ensure the organization can make good use of its data and comply with data-related regulatory and security requirements.
Curation achieves those objectives because it makes data findable and accessible. It also provides the ability to trace information on data lineage and classifies data by various characteristics, such as whether it's public, proprietary or protected.
Data curation focuses partly on understanding and organizing metadata, the set of details that provides information about the data itself. As such, data curation practices center on understanding where and how data is generated and stored. That includes creating searchable indexes on the data sets being curated. A data catalog might also be built to provide an inventory of all data assets.
These features provide visibility into an organization's data-- a critical requirement as the volume of data generated and the number of data collections continue to grow. Visibility also helps optimize data use; BI and data science teams, business executives and other employees can find and access the data they need for analytics applications and operational decision-making.
Effective data curation also engenders more trust in the data because users know it's accurate, reliable and up to date. This then creates more faith in the accuracy of data-driven decisions and speeds up business action and innovation based on data analytics.
Why is data curation important?
In many organizations, data is generated and collected from various sources, including databases, customer relationship management systems, data repositories, market data and edge computing devices connected to the internet of things. Big data systems often store a combination of structured, unstructured and semistructured data for analysis. To effectively derive insights and train machine learning (ML) models, it's essential to curate this data. Without properly curated data, organizations struggle to manage their data quality assurance.
Curation brings order to what could otherwise be a chaotic process of data cleaning, ingestion and use. In doing this, it keeps organizations from being overwhelmed by proliferating data sources and exploding data volumes. Without it, an organization could lose track of data sets, and users wouldn't have access to the information they need to do their jobs.
That could result in wasted resources as users spend time searching for and understanding data. It could also lead to inaccurate analytics, flawed business decisions, lost opportunities and other problems that affect business performance.
What are the main steps of data curation?
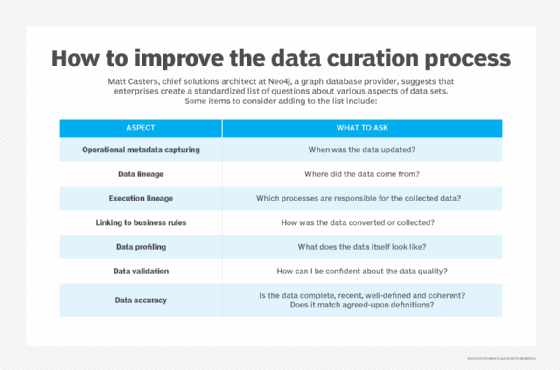
The process of curating data sets includes a variety of tasks, which are broken into the following 10 steps:
- Data identification. This initial step identifies relevant data required for analytics applications.
- Mapping data sets. This step maps the data sets, labeling and cataloging them with the related metadata.
- Data acquisition. The next step is to acquire the identified data sets, collecting them from internal databases, application programming interfaces and external sources.
- Data ingestion. This step involves putting acquired data into a data warehouse, a data lake or another system.
- Data cleansing. The data is cleansed to fix inconsistencies, anomalies and errors, such as invalid entries, missing values, duplicate records and spelling variations.
- Data transformation. After cleansing, it's important to model, structure and transform the data into a suitable format for analysis.
- Data accessibility. During this step, searchable indexes of the data sets are created to make them available to users.
- Ongoing management. In this step, data is maintained and managed according to ongoing analytics, data privacy and security requirements.
- Archiving. Preservation of data sets is one of data curation's primary aims.
- Deleting. Disposing of data sets when they're no longer needed or become obsolete is a final step.
Examples and applications of data curation
Data curation plays a vital role across many industries. Here are some real-life examples and use cases of data curation:
- Healthcare. Data curation in medical applications ensures the accuracy and completeness of patient records, including medical histories, diagnoses and treatment plans. The process standardizes terminology, corrects errors through automation and protects data privacy, which is essential for both patient care and medical research. In medical imaging, data curation helps with annotating X-rays and MRIs, maintaining image quality, and organizing data and images for research and diagnostics.
- Government data management. Public sector agencies manage extensive amounts of data, including census information, legal documents and historical records. Data curation ensures this information is accessible and usable. Additionally, by standardizing data formats, correcting inaccuracies and eliminating redundancies, data curation enhances the accuracy and reliability of government data.
- Financial services. Financial institutions collect and organize transaction data to detect fraud, comply with regulations, analyze market trends and assist with investments and loans. Proper curation ensures accuracy for financial institutions, facilitates data security and creates audit trails.
- Scientific research. Researchers depend on curated data sets to conduct studies, ensure data quality and support advanced findings. For example, in climate change research, data curation integrates diverse sources, such as ice core samples and ocean temperature measurements, to facilitate comprehensive analyses.
- ML and AI. Data curation helps build and manage ML models. Companies curate data sets to ensure they're accurate, consistent and high-quality, which leads to better-performing models. For example, a tech company could curate image data sets for training computer vision algorithms to ensure the images are labeled correctly and represent diverse scenarios.
Data curation vs. data management
Both data curation and management contribute to extracting value from data while ensuring data integrity and compliance. However, they're distinct concepts with key differences.
Data curation
Data curation focuses on the quality and usability of data sets. It ensures research data is accurate, reliable and accessible for purposes such as scientific research and decision-making. Curation activities include processes such as enriching and cleaning data, data transformation, metadata creation, data validation and data preservation for reuse.
Data management
Data management encompasses the entire data lifecycle, from creation to disposal. It takes a broader organizational approach to data management, including overall data handling processes, such as storage, security and governance. Data management activities include database administration, as well as data warehousing, security, governance, backup and recovery.
What is a data curator and what does one do?
Some organizations, particularly large ones with mature or expansive analytics programs, have created data curator positions responsible for the many tasks associated with curating data. A data curator typically identifies required data sets and ensures they're collected, cleansed and transformed as needed.
The curator is responsible for making the data sets and information about them, such as their metadata and lineage documentation, available to users. Curators develop strategies for long-term storage, management and accessibility to safeguard essential data for future access and use.
The data curator's main objective is to ensure users can access the right data for analysis and decision-making. Curators work with other members of the data management team and the IT and security teams to build reliable and secure data pipelines. They also set and maintain appropriate data governance, privacy and security workflows and standards for each data set.
An organization may have multiple data curators: some responsible for data sets in specific domain areas. One or more lead curators are responsible for metadata management and overall data curation performance.
Big data is a valuable asset. It contributes to informed business decisions and operational enhancements. Explore some of the ways big data is transforming business practices.