What is continuous learning, and what are its benefits?
Continuous learning is the ongoing expansion of knowledge and skill sets. In the context of professional development in the workplace, it's about developing new skills and knowledge while also reinforcing what has been previously learned.
The definition of continuous learning is broad. The continuous learning process can be formal or informal and structured or unstructured in nature. Activities involved include taking a formal course, observing more experienced employees, asking for assistance with an unfamiliar topic, exploring new and alternative work methods, studying, having casual conversations and practicing a skill.
Daily habits and practices form the foundation of continuous learning. This type of learning works through any means of knowledge intake and can continue as lifelong learning.
Continuous learning initiatives in the workplace have the potential to increase employee engagement, job satisfaction and knowledge retention. To stay competitive, organizations must continually adapt to changing social and economic environments. Because an organization's success depends on its people, it's important for employee skill sets to evolve to meet the demands of the business climate. Continuous learning is one way to do that.
Principles of continuous learning
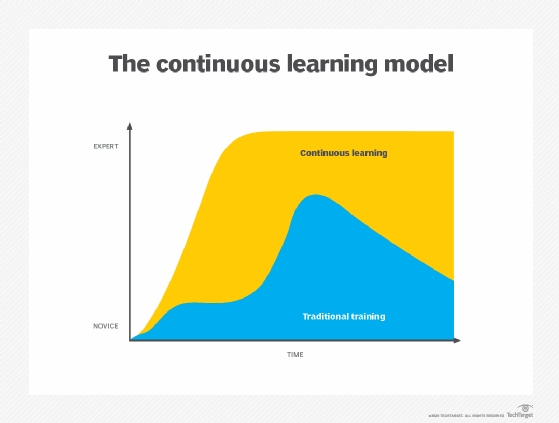
In traditional employee training, the level of employee knowledge rises to a peak right after a specific training course or event and then gradually falls off over time from a lack of reinforcement. In continuous learning, employees retain knowledge at a higher level because they participate in multiple learning events that reinforce one another.
The premise of continuous learning in the workplace is for employees to retain knowledge and skills over time. They attain higher levels of knowledge and retain that knowledge longer with reinforcement activities.
Some key elements are required to create a continuous learning environment. They include the following:
- Readily accessible learning opportunities for whenever the need arises.
- Continuous opportunities for learners to apply their knowledge and test their new skills.
- A culture that fosters learning with repeatable, sustainable practices.
- Collaboration opportunities so learners share knowledge and perspectives.
- Regular feedback mechanisms from both instructors and students.
Benefits of continuous learning
Continuous learning in the workplace has the potential to expand employee skills, increase skill and knowledge retention, generate new ideas and perspectives, boost morale and raise overall employee performance. For individual employees, continuous learning is beneficial in the following ways:
- It helps them achieve career development goals.
- It lets them obtain or update professional licenses or certifications.
- It encourages them to explore new opportunities and perspectives in their work and personal development.
- It enables them to develop marketable professional skills through upskilling and reskilling.
For the organization, continuous learning has another set of benefits:
- It contributes to achieving organizational goals.
- It encourages a forward-thinking, innovation culture.
- It makes employees feel valued.
- It keeps costs down because it's less expensive to invest in the ongoing development of current employees than to train new employees.
- It enhances competitiveness as employees become more skilled and productive.
Challenges of continuous learning
Continuous learning programs don't always run smoothly. They can experience the following challenges:
- Resistance to new skills. Employees can be resistant to learning new skills if they find the topic uninteresting or difficult. In this case, employers should explore alternative training methods and tools.
- Evolving requirements. Business needs change frequently, so having employees learn new skills that might become irrelevant over time isn't productive.
- Time constraints. Employees might find it difficult to fit additional training into their schedules. Courses that are broken into smaller, manageable lessons are easier to incorporate. However, if courses conflict with other tasks, challenges can arise.
- Budget issues. Employers might have limited budgets for training and software. In such instances, employees might have to settle for cheaper training software with fewer features and shortened course durations.
- Lack of personalized learning. Employees learn differently, but continuous learning courses often aren't designed to be personalized. A flexible and personalized upskilling program is the best approach.
Continuous learning modeling
Examples of continuous models include Deloitte's Continuous Learning Model, which features three different categories for learners' needs:
- Immediate. Learning that's needed to be successful today.
- Intermediate. Learning that's needed to expand skill sets and grow in current positions.
- Transitional. Learning that's needed to reach long-term organizational goals, advance up the career ladder or make a career switch.
Paradigms are the different ways employees learn. They consist of the following:
- Education. This is traditional learning and development often done in classrooms or e-learning experiences. This type of learning is typically trackable and has a clearly defined beginning and end.
- Experience. This is learning through workplace events, such as special projects, job rotations and stretch assignments.
- Exposure. This is learning through social relationships and interactions.
- Environment. This involves the tools and systems that support employee learning in the workplace.
Continuous learning strategies
There are multiple strategies that apply continuous learning techniques, including the following:
- Structured learning. These formal learning methods are preorganized for specific goals and purposes. They include school courses, online courses, workshops, seminars, webinars, conferences and employee and managerial training programs. Structured learning is offered through educational institutions, such as universities and community colleges, or through employer-sponsored courses.
- Social learning. This involves the ways people learn through interacting and observing others. It can be formal or informal, in person or over virtual mediums. Social learning includes discussion, coworking, collaborative problem-solving, mentoring and on-the-job training.
- Self-directed learning. These are independently administered approaches that employees can use to expand their skills and knowledge. This type of learning can occur sporadically based on on-demand course offerings, or it can follow a structured schedule. It includes research, reading, experimentation and practice testing.
How to build a continuous learning strategy
A continuous learning strategy begins with business leadership or those tasked with training employees developing long-term goals for their continuous learning plans. Then, a learning infrastructure is implemented that includes various courses and tools to achieve those goals.
Organizations must create a supportive continuous learning environment, as employees focused on meeting their immediate work deadlines might be hesitant to pick up new learning opportunities. Business leaders can focus on the following areas to encourage continuous learning:
- Planning. Map out a course of action to show employees that the organization is investing effort and resources into continuous learning. This should include who the learning plans are for, such as individual employees, teams, departments and the entire organization. There should be ongoing dialogue between management and employees to clarify objectives and priorities.
- Leadership. A continuous learning culture starts from the top, so it's important for management to communicate their full support for these activities.
- Sustainability. Provide ongoing resources to support and maintain a continuous learning culture.

Building a culture of continuous learning
Once the scope of a continuous learning strategy is determined and a plan devised, the following components will help to ensure employees take full advantage of it:
- Flexibility when implementing learning plans. Flexibility is key to accommodating as many employees as possible and ensuring their participation. Flexible approaches include accounting for people's busy schedules and personal lives by allotting sufficient time to complete assignments. Another example would be providing easily accessible forums or discussion boards for collaboration and interaction among learners who live far apart.
- Useful technology tools and resources. Learning management systems (LMSes) and other types of learning platforms are particularly useful for cohort learning, which helps train or educate multiple employees at the same time. Systems that enable virtual and hybrid learning are also useful.
- Collaborative and collective learning efforts. LMSes have capabilities that foster collaboration and interactive assignments with features such as forums and gamification. When learners engage in fun activities and interactions, they're more likely to retain what they're learning.
Continuous learning for artificial intelligence and machine learning
The concept of continuous learning applies to artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) systems. Ongoing learning is a key part of these systems. ML systems use algorithms to learn to analyze data on their own. Algorithms help them distinguish important insights and learn what predictions they can make from that information.
In a static learning process, once an ML algorithm is trained on a specific data set, it assumes every future data set it analyzes is similar. However, the world and knowledge aren't static. Therefore, in the same way humans are retrained and reskilled through continuous and constant learning, ML systems also undergo continuous training as part of the ML operations process.
An ML model is deployed once and then continuously monitored and retrained to adapt to constantly changing data. There are different techniques and tools that developers use to automate this retraining process.
The continuous learning process for ML requires periodic oversight from a human developer. There are also drawbacks to this type of retraining, as it requires expensive technology and can be time-consuming. However, the ongoing learning process is important to ensure the efficiency of AI and ML systems.
Continuous vs. lifelong learning
The term lifelong learning is often used interchangeably with continuous learning, yet there are differences.
Continuous learning applies to employers or institutions that offer courses to improve a person's knowledge or skill sets, including both hard and soft skills. Lifelong learning instead focuses on an employee's or student's personal development as they cultivate skills and obtain new knowledge that isn't necessarily required or useful for career development.
For example, a person working in a field that doesn't require coding skills might take e-learning courses on computer languages, such as HTML5, for web development side projects and to fill skill gaps. This type of structureless personal development qualifies as lifelong learning. When similar courses are offered through an employer with set dates and sessions, and the course content pertains to the employee's day-to-day tasks and competencies, this exemplifies continuous learning.
A newer, AI-driven approach to teaching employees new skill sets is the learning experience platform. Find out what it is, how it works and how it differs from traditional LMSes.