consignment inventory
What is consignment inventory?
Consignment inventory is a supply chain model where the supplier retains ownership of the products until they are sold by the retailer, reducing the financial risk for retailers and allowing suppliers to access broader markets.
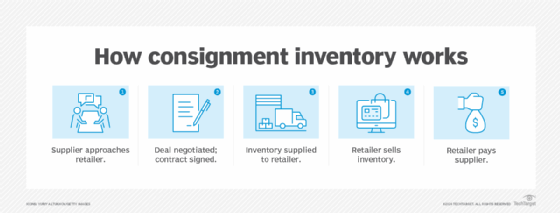
Consignment inventory involves a partnership where the supplier, or consignor, entrusts their goods to a retailer, or consignee, who sells the goods to the end consumer. The retailer does not purchase the inventory upfront; instead, the supplier retains ownership of the goods until they are sold.
This arrangement allows retailers to manage inventory without significant initial investments and reduces the financial risks associated with unsold goods, as they can be returned to the supplier.
Key benefits of the consignment inventory model
Consignment inventory offers benefits to both retailers and suppliers:
- For retailers: The model is especially beneficial to retailers when customer demand is uncertain; it allows the retailer to offer customers a greater variety of products and place a greater emphasis on sales. By carrying the product on consignment, the retailer takes a smaller financial risk since they do not pay for the product unless it is sold.
- For suppliers: The model benefits suppliers by placing their products in more retail locations, thus increasing product exposure and potential sales. However, consignment inventory poses a delay in payment until goods are sold.
Components of the consignment inventory model
In a consignment partnership, a crucial part of the process is inventory management. It involves regular monitoring and reporting of inventory levels, sales and returns. This ensures that both the consignor and consignee maintain accurate records and understand the product flow.
The relationship between the consignor and consignee is governed by a contract that outlines the terms of the consignment arrangement. Key elements of the contract include the following:
- Commission rates. Defines if and what percentage of the sales revenue the retailer will retain as a commission for selling the goods.
- Duration of consignment. Specifies how long the retailer can hold the unsold goods before they must be returned to the supplier.
- Payment terms. Details the frequency and method of payments from the retailer to the supplier for sold goods.
Modern consignment inventory practices are supported by specialized software that manages the complexities of tracking inventory levels, managing customer and supplier details, and handling the financial aspects of the consignment.
These software solutions are available for businesses of all sizes and can significantly enhance the efficiency and accuracy of consignment operations.
Challenges and considerations for consignment inventory
While the consignment model expands market access for suppliers, it also introduces risks related to delayed payments and dependency on the retailer's ability to sell the goods. Suppliers must select reliable retail partners and establish clear contractual terms to mitigate these risks.
On the other hand, retailers must efficiently manage consigned goods to ensure they maximize sales and minimize returns. They also need to maintain good relationships with suppliers by providing transparent sales reporting and timely payments.
As markets evolve, this model will continue to provide a flexible approach to inventory management that can adapt to changing consumer demands and market conditions.
As with any other retail model, inventory management is important when managing consignment inventory. Learn about five important inventory management software features.
