component
What are components?
In computer science and engineering disciplines, a component is an identifiable part of a larger program or construction. Usually, a component provides a specific functionality or group of related functions.
In software engineering and programming design, a system is divided into components that are made up of modules. Component test means testing all related modules that form a component as a group to make sure they work together.
In object-oriented programming and distributed object technology, a component is a reusable program building block. These building blocks can be combined with other components in one or several computers in a distributed network to form an application.
Examples of component-based development include a single button in a graphical user interface (UI), a small interest calculator and an interface to a database manager. Components can be deployed on different servers in a network and communicate with each other for needed services.
Physical items, such as smartphones, are built with a variety of components. These include a case, battery, main circuit board, a display and a backlight assembly. Various components are themselves made up of other components. For example, a smartphone's circuit board is comprised of components such as memory and a processor.
What are the major software components?
There are many ways to classify software components. A common approach is to identify component types:
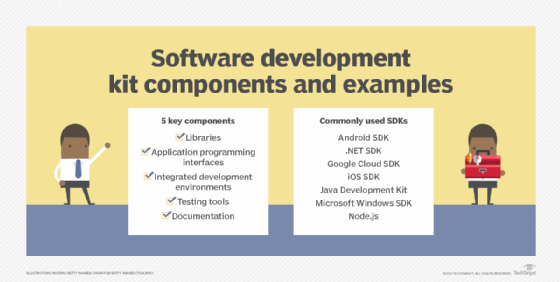
- Application programming interfaces (APIs) enable applications to communicate and interoperate.
- Connectors facilitate interoperability between software systems.
- Controls are graphical elements that let users interact with applications and systems. These are often elements like drop-down menus, buttons and sliders.
- Frameworks offer defined structures and tools for building applications, such as the React framework used with JavaScript.
- Libraries are added with a codebase to provide established sets of reusable code, such as NumPy or a math library for performing complex computations.
- Modules provide segments of code designed to offer specific features and functions, such as a UI module or an algorithm.
- Plugins are small segments of software that are added to an existing application to tailor or refine the application for various purposes. Device drivers are sometimes considered plugins, because they connect an operating system (OS) to computer hardware devices.
- Services offer modular and well-defined functions, such as Docker for creating and managing containers, or a firewall for network traffic management.
In other cases, software components can be classified by their function:
- Algorithms include components that perform computations, analyses or data processing. For example, a data graphing algorithm can be built as a separate and reusable software component.
- Drivers provide the code that enables software to interact with specific hardware devices. For example, an application might need a driver to communicate with a printer. While drivers are usually used for hardware-to-OS connections, they also let applications directly connect with hardware.
- Interfaces include the UI, such as menus and controls, that let a user interact with software and ensure its usability. There are also interfaces between software components, such as APIs, that let them interact.
- Main application support is often the main body of the application that calls or uses software components. It also serves as a central point of interconnection for the many components of the application.
What are the characteristics of a software component?
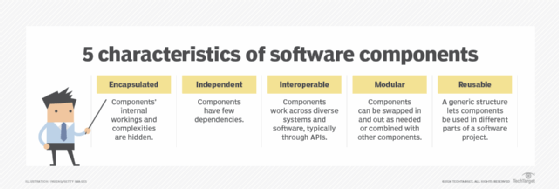
Just as there are various ways to classify software components, there are different approaches to defining the characteristics of software components. One common methodology identifies software components according to the following five characteristics:
- Encapsulated. Components hide their internal workings and complexities. They often take data and return results through a well-defined interface, such as an API, to prevent unintended interactions with other software elements.
- Independent. A component might be a dependency, but it rarely has any dependencies of its own. This eases updates and software maintenance, while also reducing the need for time-consuming regression testing when components are changed.
- Interoperable. Interoperability enables components to work across diverse systems and software, typically through an API. This lets them be used in more ways, and allows for mixing and matching of components among projects, and even lets them be shared and monetized.
- Modular. When components are modular, it means they can be swapped in and out as needed, or combined with other components to form an interchangeable and flexible environment.
- Reusable. Components tend to be generic and can be reused in different parts of a software project -- or even across different software projects. This reduces the need for developers to duplicate their efforts on every project and facilitates software reuse.
The Sun Microsystems JavaBeans API defined how to create components. It described a component model as typically providing these major types of services:
- Component interface exposure and discovery. During application use, one component can interrogate another to discover its characteristics and how to communicate with it. This lets different companies -- possibly independent service providers -- create components that interoperate with the components of other companies without either component having to know in advance exactly which component it will be working with.
- Component properties. This lets a component make its characteristics publicly visible to other components.
- Event handling. This lets one component identify to other components that an event, such as a user pressing a button, has occurred so that the component can respond to it. For example, Sun said a component that provided a button UI for a finance application would raise an event when the button was pressed, resulting in a graph-calculating component gaining control, formulating a graph and displaying it to the user.
- Persistence. This preserves the state of components for later user sessions. This capability is sometimes called stateful. However, stateless components and modules that don't have persistence are often used for complex or distributed software projects.
- Application builder support. A central idea of components is that they're easy and flexible to deploy in a distributed network. However, they also let developers use iterative methods to create new components and see the properties of existing ones.
- Component packaging. Since a component can comprise several files, such as icons and other graphical files, Sun's component model included a facility for packaging the files in a single file format that could be easily administered and distributed. Sun called its component package a Java Archive or JAR file.
What are the benefits of software components?
A component-based approach to software architecture can provide numerous advantages:
- Faster development time. Developers can use a library of existing or reusable components to develop applications far faster and with less testing and fewer bugs than teams that must create their own code. A component library might form organically over time as developers create and maintain components. Or developers can access open source or third-party libraries of components.
- Easier and faster maintenance. Developers can create separate components and then integrate them into a software project. The modular environment makes for easier maintainability where only an individual component or code base needs to be changed and tested, not the entire code or all components. This makes change and validation faster and easier, improving component maintenance.
- Lower development costs. Faster development, better code quality using proven and tested components and a reduced need for testing all mitigate project development costs and facilitate ongoing software project management and maintenance.
- Team flexibility. A component-based software design approach makes team separation, specialization and independence easier. One team can work on certain components, another team can work on other components, and yet another team can work on the main project that uses those components.
- Design consistency. Reusable components help to ensure that software projects deliver a consistent user experience through components like the UI or a major processing-intensive compute component, such as a math or data processing task.
What are the challenges of software components?
Despite the many benefits of a component-based software engineering approach to software design, developers must also grapple with different component limitations and challenges:
- Limited compatibility. Ideally, a component inputs and outputs certain data, but the reality is that the format and content of the call or request to the component aren't always compatible with the component. Some software projects require components to perform tasks that they aren't fully capable of supporting, necessitating an update or the creation of a new component.
- Inconsistent data. It's important for components to handle the same data structures in the same manner. For example, an application designed to support floating-point math tasks shouldn't use a component designed to work with integer numbers. This introduces errors and data inconsistencies that can lead to application problems.
- Security concerns. Simple components, such as a library of math functions linked to a codebase, might not pose many security concerns. However, in the context of broader software projects -- such as integrating the components of distributed applications -- components can expose software to security issues.
- Scalability problems. Applications perform processing tasks, which can create processing bottlenecks that slow performance, especially when too many components exchange data at once. Developers must be able to gather performance metrics, and then find and remediate bottlenecks that limit application scalability.
How do components improve software quality?
Software quality is typically enhanced through consistency and testing. Consistency ensures that the same tasks are performed in the same way at the same level of performance throughout the software development process. The software testing process helps to ensure that code is validated and proven.
When a task is encapsulated into a software component, that component becomes an independent and well-understood element. Each time that component is used or reused, it performs the same task in the same way, ensuring that the component's appearance and output are consistent. As that component is applied to different projects, that consistency is carried over into those other projects.
Testing components for bugs and performance is just as important as with any other application. The advantage of testing components is in scope: A component is a relatively small segment of code intended to perform a specific job. This makes it easier and faster to test a component compared with testing a full application. When a component is changed or updated, it's only necessary to retest the component, not all of the applications that use the component.
Conversely, when an application using a component is changed or updated, only the application must be tested, not all of the components that the application uses. Thus, components tend to be well-proven and reliable software elements, elevating software quality and reducing bugs in software development projects.
Software design documents are an important part of the software development lifecycle and software quality assurance. Learn the role software components play in their effectiveness.
