backward compatible (backward compatibility)
What is backward compatible (backward compatibility)?
Backward compatible (also known as downward compatible or backward compatibility) refers to a hardware or software system that can successfully use interfaces and data from earlier versions of the system or with other systems.
For example, Perl, the scripting language, was designed to be backward compatible with Awk, an earlier language that Perl was designed to replace.
Another example is the Microsoft Xbox Series X and Series S, as well as the Xbox One X, which are backward compatible with all original Xbox games.
Backward compatibility is more easily accomplished if the previous versions have been designed to be forward compatible, or extensible, with built-in features such as hooks, plugins, or an application program interface that allows the addition of new features.
It's important to note that the term backward compatible has occasionally been used to describe hardware or software that is designed without regard for compatibility with earlier versions, causing the older version and new version to fight (or combat) each other.
In this case, the two versions cannot share data easily and may have functionality that causes errors or crashes when they are installed on the same computer, often because the computer does not understand which version is being referred to. Even if the older hardware is removed, the remaining vestiges of it may cause problems in running the newer version.
An adjacent concept is forward compatibility, which refers to creating software and hardware with a roadmap directed at compatibility with future products.
Applications of backward compatibility
The following are a few examples of backward compatibility seen in everyday applications.
Processors and operating systems
The X86 family of microprocessors has backward compatibility with the 16-bit Intel 8086 processors released in 1978. This is an important capability because backward compatible processors can execute the same binary software instructions as their predecessors, without needing new applications or operating systems.
Video games and consoles
For gamers, upgrading to the latest consoles can mean games or components that are no longer compatible. Therefore, in order to boost customer satisfaction, there are numerous cases of backward compatibility in video game design and consoles.
The following are a few examples:
- The Atari 2600 with the Atari 5200 and 7800
- The Sega Genesis with the Sega Master System via add-on component
- The Nintendo Game Boy Color with the original Game Boy
- The Microsoft Xbox 360 and the Xbox One can support some games released for their predecessors with emulation functionality
- The Sony PlayStation 2 and PlayStation 3 consoles are compatible with the original PlayStation and, with Emotion Engine installed, the PS3 can play PS2 games
- The PlayStation 5 can play all PlayStation 4 games, as well as use PS4 components
3G, 4G and 5G devices
According to the U.S. Federal Communications Commission, the 5G phones available today are backward compatible with earlier generation networks in areas beyond the current 5G coverage. Furthermore, 4G phones will still work for those carriers planning to invest in more 5G towers.
Unfortunately, most carriers have plans to phase out 3G coverage. So, if your phone is more than a few years old, it's best to check with your carrier to confirm what type of service you have and what their plans are for phasing out 3G connectivity.
Additionally, it's important to note that 3G and 4G are not forward compatible. To obtain 5G service, users will be required to upgrade to a 5G device.
Wi-Fi networking protocols
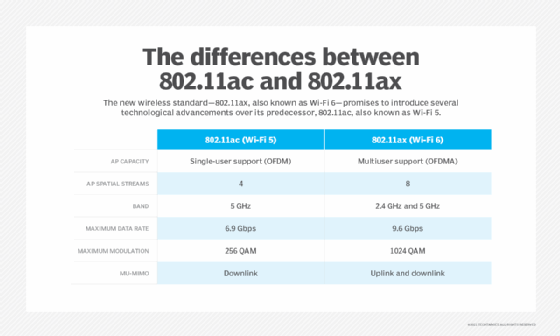
The latest wireless standard, Wi-Fi 6, or 802.11ax, has backward compatibility with previous generations of devices, according to the Wi-Fi Alliance. However, it's not quite as simple as that.
For example, you wouldn't be able to connect an 802.11b device to a wireless local area network (WLAN) without significant performance degradation, due to the varying data rates.
Some legacy devices need speeds of 1 to 2 megabits per second, so, while they are technically compatible, most wireless networking professions running high-speed environments simply opt to turn off the slower rates in order to let the higher rates prevail.
So, while Wi-Fi 6 is backward compatible, most networks will be configured in favor of performance, as opposed to creating backward compatibility.
3DES encryption
In cryptography, Triple DES, or Triple Data Encryption Algorithm, is a symmetric-key block cipher that uses the Data Encryption Standard (DES) cipher algorithm three times per data block. This is a much stronger version of the traditional DES, which was created in 1977 for government agencies to use to protect sensitive data.
There are three keying options for Triple DES, or 3DES, only one of which is backward compatible with DES.
Option 1
In option 1, all three keys are independent, triple-length keys. This is signified as 3TDEA.
This is the strongest form of encryption available in the 3DES model.
Option 2
Option 2 is a double-length key. Only the first two keys are dependent. This is signified as 2TDEA.
This provides a shorter key length of 112 bits and a middle-of-the-road solution compared to DES and keying option 1.
Option 3
In this option, all three keys are identical, which makes this the only version that is backward compatible with DES, because two of the operations cancel one another out. This is also why this is the weakest form of 3DES encryption.
The pros and cons of backward compatibility
There are both benefits and tradeoffs for this form of technology.
Pros
- It preserves the investment made in older software or older hardware.
- It adds value and incentive to purchase new hardware, especially if buyers know in advance that not only can they use previous software, but they will also be able to count on forward compatibility for future generations.
- Newer hardware that can use older applications or games may also have better visuals or frame rates, allowing the user to have a better experience without having to purchase new applications or games.
Cons
- The cost of supporting old software is a huge drawback for the developer.
- Increased complexity can increase the time to market for the product.
- There can also be technological hurdles and slower innovation.
Because of these drawbacks, numerous gaming console manufacturers have started transitioning away from backward compatibility or only including it for the first couple of generations.
For example, the original PlayStation is only compatible with PS2 and PS3. The same is true for PS4 and PS5. Doing this can also help boost sales -- at the cost of customer satisfaction, however.
The future of backward compatibility
Due to the decline of sales inherent in creating systems with backward compatibility, as well as the rise in digital storefronts, industry forecasters believe backward compatibility will be obsolete in the near future. This is most prevalent in the gaming community.
To appease gamers, many console manufacturers have begun releasing emulation systems, as well as remastered consoles so those who are nostalgic for classic games can play remasters at minimal cost, with better quality.
This not only appeases older gamers, but introduces a new, younger audience to classic games and systems.
