What is binary and how is it used in computing?
Binary describes a numbering scheme in which there are only two possible values for each digit -- 0 or 1 -- and is the basis for all binary code used in computing systems. These systems use this code to understand operational instructions and user input, and to present a relevant output to the user.
The term binary also refers to any digital encoding and decoding system in which there are exactly two possible states.
What is a binary system in computing?
The binary numbering system is one of the many numbering systems in use today. These include the decimal system (base 10), duodecimal system (base 12) and hexadecimal system (base 16). In the 17th century, Gottfried Leibniz, a German mathematician and scientist, refined the binary system. He believed that the system represented Christianity's view of God (1) versus nothing (0) and documented its basics and benefits in a paper titled Explanation of binary arithmetic in 1703.
In mathematics and computing, a binary digit, or bit, is the smallest unit of data. Each bit has a single value of either 1 or 0, which means it can't take on any other value. Computers can represent numbers using binary code in the form of digital 1s and 0s inside the central processing unit (CPU) and RAM. These digital numbers represent data in a machine-readable form. Specifically, they are electrical signals that are either on (1) or off (0) inside the CPU or RAM, telling those components what to do. Without those signals, the CPU and RAM will not work. For this reason, the binary system is considered the foundation of modern-day computing and electronics.
In digital data, memory, storage, processing and communications, the 0 and 1 values are sometimes called low and high, respectively. In transistor technology, 1 refers to a flow of electricity while 0 represents no flow of electricity.
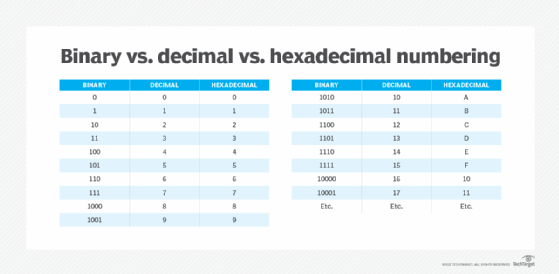
Binary vs. decimal
Since the binary system uses only two digits or bits and represents numbers using varying patterns of 1s and 0s, it is known as a base-2 system. The digit 1 refers to "on" or "true," while 0 refers to "off" or "false."
In contrast, the decimal numbering system is a base-10 system, where each possible place in a number can be one of 10 digits (0-9). In a multidigit number, the rightmost digit is in the first place, the digit next to it on the left is in 10th place, the digit further left is in 100th place and so on.
For example, in the four-digit number 1,980, these are the places occupied by each digit:
| 1 |
9 |
8 |
0 |
| 1,000th place |
100th place |
10th place |
1st place |
The importance of binary code
The binary number system is the base of all computing systems and operations. It enables devices to store, access and manipulate all types of information directed to and from the CPU or memory. This makes it possible to develop applications that enable users to do a variety of tasks, such as the following:
- View websites.
- Create and update documents.
- Access software.
- Perform calculations and data analyses.
- Play games.
- View streaming video and other kinds of graphical information.
The binary schema of digital 1s and 0s offers a simple and elegant way for computers to work. Any instructions given to a computer are first converted into binary language using an assigned American Standard Code for Information Interchange (ASCII) code. ASCII codes allow a computer to understand an instruction and to act appropriately on it. The system also offers an efficient way to control logic circuits and to detect an electrical signal's true (1) and false (0) states.
How binary numbers work
The binary system is the primary language of computing systems. Inside these systems, a binary number consists of a series of eight bits. This series is known as a byte. In the binary schema, the position of each digit determines its decimal value. Thus, by understanding the position of each bit, a binary number can be converted into a decimal number.
In decimal numbers, each additional place is multiplied by 10 as we move from right to left (first place, 10th place, 100th place, etc.). But, in binary numbers, each additional place while moving from right to left is multiplied by two. The two examples below explain this idea.
Example 1: Here's how the decimal values are calculated for an 8-bit (byte) binary number 01101000.
In this number, the first digit is at the far right, while the eighth digit is at the far left. The second (0) to the seventh (1) digits are read from right to left.
| Bit position |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
| Bit |
0 |
0 |
0 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
| Binary-to-decimal calculation (exponent) |
20 |
21 |
22 |
23 |
24 |
25 |
26 |
27 |
| Decimal value (x2) |
1 |
2 |
4 |
8 |
16 |
32 |
64 |
128 |
As the bit position increases from one to eight, the previous decimal value is multiplied by two. That's why the first bit has a value of 1, the second bit has a value of 2, the third bit has a value of 4 and so on.
The final value of the decimal number is calculated by adding the individual values from the above table. However, only those values where the bit equals 1 should be added. These values represent the "on" position. The 0s represent the "off" position, so they are not counted in the decimal value calculation.
So, for the binary number 01101000, the decimal value is calculated as:
8 + 32 + 64 = 104
Example 2: In this example, the decimal values are calculated for the binary number 11111111.
| Bit position |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
| Bit |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
| Binary-to-decimal calculation (exponent) |
20 |
21 |
22 |
23 |
24 |
25 |
26 |
27 |
| Decimal value |
1 |
2 |
4 |
8 |
16 |
32 |
64 |
128 |
For this binary number, every bit has a value of 1, so all of the individual values are added, yielding this decimal value:
1 + 2 + 4 + 8 + 16+ 32 + 64 +128 = 255
What is a binary formula?
A binary formula is a formula that's used to convert binary numbers to decimal, duodecimal or hexadecimal numbers. The formula is different for different conversions.
To convert a binary number to decimal form:
- Every digit of the number is multiplied by 2 raised to the power of that digit's position in the number.
- The results of the multiplications for each digit are added together.
Consider a binary number B = bn-1….b3b2b1b0. Here's how the binary formula will look:
For B = bn-1….b3b2b1b0
D = (bn-1 × 2n-1) +…+(b3 × 23) + (b2 × 22) + (b1 × 21) + (b0 × 20)
Suppose B = (1101011)2
Here,
n = 7
n - 1 = 6
D = (1 × 26) +(1 × 25) + (0 × 24) + (1 × 23) + (0 × 22)+ (1 × 21) + (1 × 20)
= 64 + 32 + 0 + 8 + 0 + 2 + 1
D = 107
Thus, (1101011)2 = (107)10
The formula for converting binary to hexadecimal and octal numbers is much less straightforward and can be tedious to do manually.
Representing decimal numbers in binary format
As noted, the binary numbering system only works with 1s and 0s. However, the position of just these two digits can represent many more numbers. The examples in the previous section show how any decimal number from 0 to 255 can be represented using binary numbers. Numbers larger than 255 can also be represented by adding more bits to an 8-bit binary number.
Here are the decimal numbers from zero to 20 and their binary equivalents.
| Decimal number |
Binary number |
Decimal number |
Binary number |
| 0 |
0 |
11 |
1011 |
| 1 |
1 |
12 |
1100 |
| 2 |
10 |
13 |
1101 |
| 3 |
11 |
14 |
1110 |
| 4 |
100 |
15 |
1111 |
| 5 |
101 |
16 |
10000 |
| 6 |
110 |
17 |
10001 |
| 7 |
111 |
18 |
10010 |
| 8 |
1000 |
19 |
10011 |
| 9 |
1001 |
20 |
10100 |
| 10 |
1010 |
--- |
--- |
The ASCII values for 0 through 31 (binary: 000 0000 through 001 1111) are non-printing control codes.
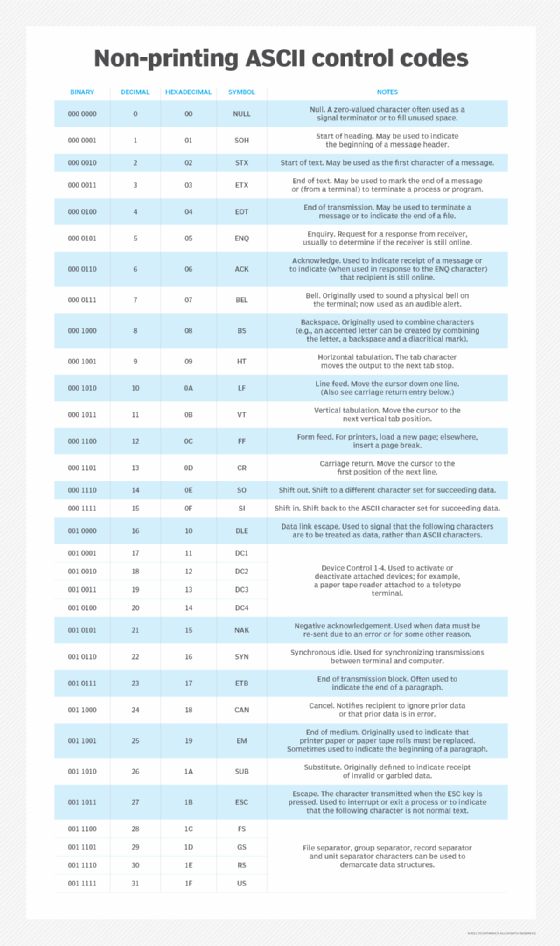
Converting binary numbers into text characters
Binary numbers can be translated into text characters using ASCII codes to store information in the computer's RAM or CPU. ASCII-capable applications, such as productivity software, e.g., word processors, can read text information from the RAM or CPU. They can also store text information that can then be retrieved by a user at a later time. ASCII codes are stored in the ASCII table, which consists of 128 text or special characters. Each character has an associated decimal value.
ASCII characters include the characters a-z, A-Z, 0-9 and an assortment of punctuation marks.
In the first example of the previous section, the binary number is 01101000 (decimal number 104). In ASCII, that number would produce a lowercase h.
To form words, more letters are added to h; in binary terms, that means adding more binary numbers to the binary number for h. The binary code for ASCII lowercase i is 01101001. So, to create the word hi, the binary number for i is added to the binary number for h, which yields the following binary number:
01101000 + 01101001 = 0110100001101001
In decimal terms, the decimal numbers for h and i are 104 and 105, respectively.
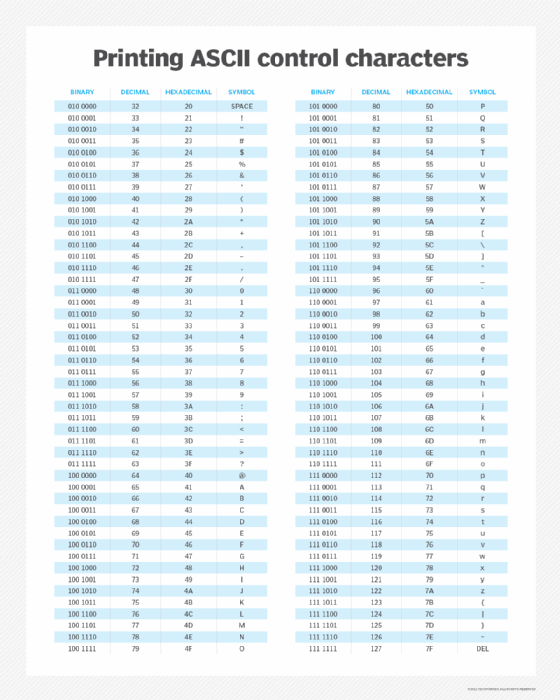
Other common examples of binary numbers converted to ASCII text code are the following:
| Binary number |
Decimal number |
ASCII code |
| 110000 |
48 |
0 |
| 1000001 |
65 |
A (uppercase) |
| 1111111 |
127 |
DEL key |
| 11011 |
27 |
ESC key |
Applications of binary
The binary number system is used in other areas, such as email communication, data compression systems and data encryption. Cryptographical systems use binary code to transform plaintext data into unreadable ciphertext. Compressing data into binary form reduces its size so it requires less storage space.
Binary information is also used in digital audio and video processing. Applications encode audio and video files as digital data in binary form. To enable playback, the data is decoded into analog form.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) applications also use binary data. These include language translation and image recognition apps.
Network admins should know how to convert binary to decimal and vice versa for IPv4 addressing, subnet masks, default gateways, and network IDs. Learn how to convert binary to decimal.
