What is carbon footprint?
Carbon footprint measures the total greenhouse gas emissions caused directly and indirectly by an individual, organization, product or activity. It's typically expressed in metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalent per year; CO2e is a standardized unit that combines the global warming potential of multiple greenhouse gases -- including carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxide -- into a single comparable metric.
Originally intended to measure all emissions contributing to global warming, the term carbon footprint is still commonly used as shorthand for all greenhouse gas emissions. Tracking a carbon footprint is one of the most accessible ways to understand and mitigate climate change impacts.
Why carbon footprints matter
Understanding and managing carbon footprints is critical to addressing human-caused climate change. The more greenhouse gases emitted, the more they trap heat in Earth's atmosphere, resulting in rising temperatures, more frequent extreme weather events and ecosystem disruption.
Reducing carbon footprints at the individual and organizational level is key to meeting global emission reduction targets outlined in agreements like the Paris Agreement and COP28 commitments. However, before individuals or businesses can hope to reduce their carbon footprint, it's key to understand how emissions are categorized.
Primary vs. secondary carbon footprints
A carbon footprint is composed of two parts, a primary and secondary footprint.
The primary footprint includes direct emissions from activities such as the following:
- Driving gas-powered vehicles.
- Heating a home with oil, natural gas or coal.
- Air travel.
- Electricity usage when derived from fossil fuels.
These emissions result directly from the combustion of fossil fuels.
The secondary footprint refers to indirect emissions from the following:
- Manufacturing and transporting products and food.
- Industrial supply chains.
- Use of digital services and cloud infrastructure.
- Waste and recycling processes.
This includes the full lifecycle emissions of goods and services consumed, from production to disposal.
How to reduce carbon footprints
Reducing carbon footprints has become a major focus in both personal and corporate sustainability initiatives. Key strategies include the following.
Switch to renewable energy
Powering homes or businesses with solar, wind or hydroelectric power can eliminate fossil fuel-based emissions from electricity use.
Choose low-emissions transportation
Use public transit, cycle, walk or switch to electric vehicles to reduce transport-related emissions.
Adopt sustainable consumption habits
Take note of personal and professional behaviors and, where possible, swap them for more sustainable alternatives. Below are a few examples:
- Buy local and seasonal food.
- Reduce meat and dairy consumption.
- Avoid single-use plastics.
- Support circular economy practices.
Implement green building practices
Energy-efficient construction, sustainable insulation, smart thermostats and low-carbon building materials help reduce the environmental effects of buildings.
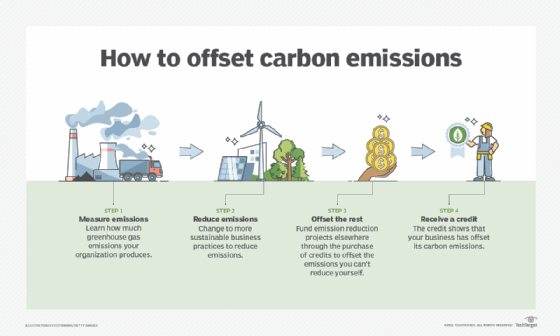
Purchase carbon offsets
Carbon offsets are credits used to compensate for emissions by funding environmental projects like reforestation, wind farms or methane capture. While not a long-term solution, they help organizations reduce net emissions when direct reductions are not possible.
Several countries worldwide have set targets for reductions in emissions, referred to as carbon reduction commitments, in international meetings with agreements like the Paris Agreement, the Copenhagen Accord and the Kyoto Protocol.
Global climate targets and carbon commitments
Numerous international frameworks aim to limit global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius above preindustrial levels, a goal set by the Paris Agreement. Key climate accords that define carbon reduction efforts include the following:
- Paris Agreement (2015). Signed by 196 countries to set legally binding climate goals.
- COP28 (2023). Called for phasing out unabated fossil fuels and tripling renewable energy capacity by 2030.
- Kyoto Protocol (1997). One of the first international efforts to establish emissions reduction targets.
- Net-zero pledges. Many countries and companies have committed to achieving net-zero carbon emissions by 2050.
Governments are also creating carbon pricing schemes, such as carbon taxes and emissions trading systems, to incentivize businesses to cut emissions.
New trends in carbon measurement
As our climate continues to change and evolve, so must our response to protect it. With that mindset, modern carbon tracking has been designed to include the following:
- AI-powered carbon calculators, or personalized apps that calculate and suggest reduction actions.
- Product-level carbon labels on packaging, which show carbon footprints to inform consumers.
- Scope 3 emissions tracking, as companies are increasingly required to report indirect emissions from suppliers, logistics and product use.
- Digital carbon twins, or real-time models that simulate an organization's carbon output across its entire operation.
These advances make it easier than ever for individuals and businesses to measure and reduce their environmental impacts in meaningful ways.
Businesses are essential in the fight against climate change. Explore ways businesses can reduce their carbon footprint. Also, learn about the main types of greenhouse gases, how evidence shows that telehealth cuts carbon emissions and about generative AI's sustainability problems.
