base station
What is a base station?
In telecommunications, a base station is a fixed transceiver that is the main communication point for one or more wireless mobile client devices.
A base station serves as a central connection point for a wireless device to communicate. It further connects the device to other networks or devices, usually through dedicated high bandwidth wire or fiber optic connections. Base stations are generally a transceiver, capable of sending and receiving wireless signals; otherwise, if they only transmitted signals out, they would be considered a transmitter or broadcast point. A base station will have one or more radio frequency (RF) antennas to transmit and receive RF signals to other devices.
Base stations are also central points that all clients connect to in a hub and spoke style network; it would not be a client among similar peers. Generally, if client devices wanted to communicate to each other, they would communicate both directly with the base station and do so by routing all traffic through it for transmission to another device.
Base stations in wireless data networks
Base stations in cellular telephone networks are more commonly referred to as cell towers. Each cellphone connects to the cell tower, which in turn connects it to the wired public switched telephone network (PSTN), the internet or to other cellphones within the cell. The size of the base station depends on the size of the area covered, the number of clients supported and the local geography.
Cell tower base stations can range from large towers that cover many miles to microcells in urban environments that only cover a few blocks. Telcos can install these base stations onto dedicated towers or attach them to existing structures. Many towers are camouflaged to blend in with their surroundings. For example, some can be painted and shaped to look like a large tree, while others may be inside a façade of a building's steeple or a rooftop water tower. Often a single cell tower will contain radios and equipment for several service providers.
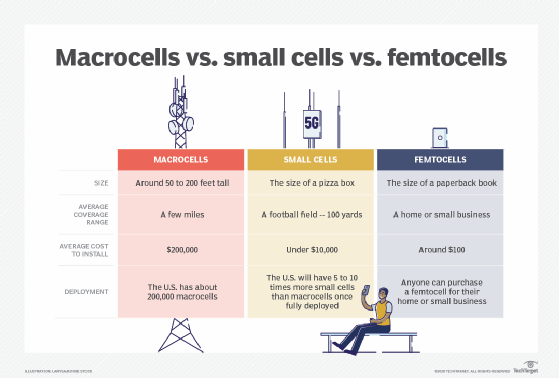
The number of cellular base stations will continue to increase to meet rising demand. More and more people use their cellphones for more data-heavy operations putting a strain on existing towers. 5G-NR high-speed cell technology often uses mmWave signals that do not cover as large an area as 4G/3G, so may require specialized base stations.
Satellite networks use base stations to connect a satellite to terrestrial networks. As the satellite moves relative to the earth, it may require more than a base station to connect to, however. For example, in home satellite internet, the client's personal dish transmits to the satellite, and the satellite then transmits to its base station on earth where it is hooked into the internet.
In Wi-Fi data networks, the client devices connect to a base station. These are generally referred to as wireless access points, access points or -- informally -- routers. The access point will then send the Wi-Fi radio transmission to a wired network.
Base stations in other uses
Two-way radio, also known as citizens band radio or ham radio, also use base stations. These are typically fixed stations that communicate with many mobile operators. A dispatcher, for example, may use a base station radio to communicate with workers in the field for emergency services, police, taxi or large work sites.
Many consumer systems also employ base stations to fill a role. A cordless home telephone has a base station to connect one or more handsets to PSTN wired telephone outlets and, perhaps, provide handset recharging. Most whole room virtual reality (VR) systems use one or more base stations to provide wireless data and fixed positions that the VR devices use to calculate its relative position in 3D space; this can be done with radio frequency or infrared signaling.
Some IoT devices use dedicated base stations to transmit data. Smart home hub automation systems may use proprietary wireless protocols to connect a base station to its sensors and controls. Some municipality public works systems use base stations to send and receive data from systems located throughout the area. A wireless sensor network will often connect many small sensors to a single base station.
