What is an asymmetric cyberattack?
An asymmetric cyberattack refers to cyberwarfare that inflicts a proportionally large amount of damage compared to the resources used by targeting the victim's most vulnerable security measure.
What does 'asymmetric' mean in asymmetric cyberattacks?
In asymmetric cyberattacks, the perpetrator has an unfair (or asymmetric) advantage over the victim that can be impossible to detect. Oftentimes, the aggressor cannot compete with the victim in terms of resources, strength or numbers, making this a popular option among small intelligence groups.
Despite this power imbalance, a smaller, less powerful and less capable attacker can cause serious damage by exploiting security weaknesses of the victim organization.
Why are asymmetric cyberattacks on the rise?
Asymmetric cyberattacks are becoming more common due to their low cost, readily available equipment and large potential damage. For a small investment, attackers can target larger organizations, exploit vulnerabilities in complex systems, and execute successful cyberattacks with a high potential payout. Readily available cybercrime equipment, such as ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS), makes it easy even for low-skilled individual hackers to execute successful attacks on selected targets.
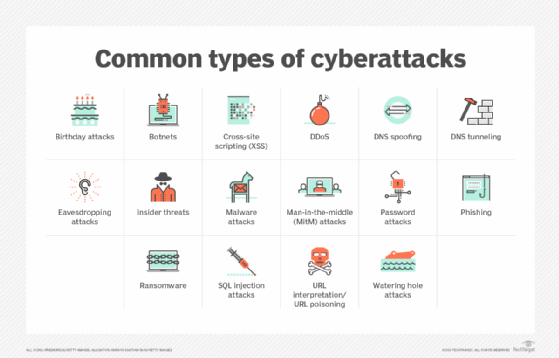
Types of asymmetric cyberattacks
Asymmetric cyberattacks occur frequently. One reason is that smaller attackers with few resources can successfully execute an attack against larger, more powerful victims. Another reason for the high frequency of asymmetric attacks is that adversaries have many types of attacks to choose from. Here are some examples:
- Phishing.
- Malware and ransomware.
- Social engineering.
- Denial of service (DoS) and distributed denial of service (DDoS).
- Man-in-the-middle (MitM).
- SQL injection.
Clever attackers can also explore zero-day vulnerabilities, i.e., newly discovered vulnerabilities in software (or hardware) to execute an attack.
Some threat actors also take advantage of insider threats. For example, they might identify an employee or third-party who has authorized access to the company's network or systems and then steal the credentials to gain unauthorized access to resources. Once accomplished, they can engage in illegal activities, such as spying, corporate espionage, systems sabotage or data theft. They can also maintain unauthorized access to the network for an extended period -- a type of cyberattack known as an advanced persistent threat (APT).
Asymmetric cyberattacks differ from symmetric cyberattacks. These attacks involve two parties of similar capabilities so there is little, if any, power imbalance between them. Cyberespionage between rival countries, state-sponsored cyber-terrorists targeting an enemy nation, and sophisticated cyber warfare campaigns between large organizations are all types of symmetric cyberattacks. These attacks tend to be rare.

Features of an asymmetric cyberattack
An asymmetric cyberattack has several unique features that differentiate it from its symmetric counterpart:
- Resource imbalance. Adversaries usually lack advanced technological and other resources to author and execute attacks, and asymmetric attacks require less planning and cost less compared to symmetric attacks. Nevertheless, asymmetric attacks frequently succeed because the attackers are able to exploit vulnerabilities in the victim organization.
- Tactics used. For example, the attacker might send a phishing email to induce fear in one or more victims, or they might use social engineering to threaten or fool a victim into sharing sensitive information (e.g., credentials) with the adversary. Attack perpetrators can also install malware or ransomware on one or more enterprise systems to force downtime or to demand a hefty ransom in return for unlocking the systems.
- Plan of attack. The nature of asymmetry makes the plan of attack unfair, uneven, and hard to track. This removes any advantages that the victim might have -- larger size, more resources, better security capabilities, etc. -- and allows the attacker to succeed.
- Thorough research of vulnerabilities. To execute a successful asymmetric attack and increase the odds of success, attackers research their victim's vulnerabilities. These might be anything from outdated programs and unpatched software to overlooked (or missing) security measures, misconfigurations, broken access controls, cryptographic failures or poor cyber hygiene among staff. The adversaries then exploit these weaknesses to cause significant damage to enterprise networks, systems, devices or data.
- High impact. Finally, asymmetric cyberattacks can have a high impact on the victim. Such attacks are employed to cause as much physical damage as possible. Some attacks also aim to cause psychological damage, including inflicting distress, causing shock and creating confusion.
Examples of asymmetric cyberattacks
In cybersecurity, an asymmetric attack might involve a perpetrator attacking security measures that have been put in place, such as the firewall or intrusion detection system, by capitalizing on the weakest link (such as software that is not updated with the latest security patch or the use of a low-strength password).
Many such attacks have occurred in recent years. Some high-profile attacks include the following:
- SolarWinds supply chain attack. In 2020, a group of cyber attackers launched a supply chain attack on SolarWinds' Orion IT monitoring and management software. By exploiting a vulnerability in the software, the hackers gained access to the networks of several organizations that used it, including large companies and local, state and federal agencies in the United States.
- Colonial Pipeline ransomware attack. In May 2021, the DarkSide ransomware gang leveraged a compromised VPN account to infiltrate the systems of Colonial Pipeline, a large and vital oil pipeline in the U.S. Once the attackers gained access to the network, they encrypted many of its systems, forcing the organization to shut down operations for several days. This caused widespread gasoline shortages in the southeastern U.S.
- Phishing attack on LinkedIn. In June 2021, a hacker going by the name "TomLiner" impersonated a well-known construction company to successfully execute a phishing attack on LinkedIn. TomLiner also delivered a credential harvesting payload to steal the credentials needed to access LinkedIn's file storage platform. This resulted in a data breach that exposed the personal and professional information of 700 million of its users, which the attacker put up for sale on a darknet forum.
- DDoS attack against a Google customer. In 2022, Google's DDoS Response Team blocked one of the largest DDoS attacks ever recorded. This attack, against a Google Cloud Armor customer, grew to 100,000 requests per second within just eight minutes. If not stopped by the Google team, the attack could have overwhelmed the organization's systems and made them unavailable to legitimate users, resulting in significant downtime and financial losses for the company.
How to protect against asymmetric cyberattacks
Companies, governments and networks should treat asymmetric cyberattacks as a serious threat that can cause massive damage in terms of financial losses, operational downtime, loss of customer trust and reputational damage. Organizations should be aware of their own vulnerabilities and create strategies to proactively address these potential weak points.
It's also critical to implement controls to prevent such attacks and measures to mitigate the affect of an attack should it occur. These controls and measures should include the following:
- Keep all software and hardware updated and patched.
- Ensure employees use strong passwords to access enterprise systems and data.
- Implement multifactor authentication (MFA).
- Deploy robust firewalls, antivirus and antimalware programs, and spam filter systems.
- Regularly run vulnerability scans to identify security weaknesses.
- Monitor shadow IT and implement tools to detect unauthorized and potentially dangerous tools used within the organization.
- Implement a comprehensive bring your own device (BYOD) policy, security standards and appropriate solutions like mobile device management (MDM) and data loss prevention (DLP)to reduce the security risks arising from employees' use of personal devices.
- Use only reliable, vulnerability-free open source software and software components.
- Encourage all developers to adopt secure coding practices.
- Regularly back up all business-critical data to minimize downtime and ensure fast recovery from attacks.
- Monitor the enterprise network to identify anomalous, suspicious, and potentially dangerous traffic.
- Implement robust access controls and adopt the principle of least privilege (POLP) to limit access, especially to sensitive or confidential systems and data.
- Implement a detailed incident response plan to respond quickly to in-progress attacks.
In addition to the above, addressing one of the weakest links in cybersecurity -- human beings -- is crucial by implementing cybersecurity training. This will involve employees in the overall cybersecurity effort and improve cyber-hygiene throughout the organization, ultimately translating into a more prepared and resilient organization.
With these evolving threats, it's important to stay on top of potential cyber threats. Learn more about cybersecurity trends and statistics to keep an eye on.
