self-driving car (autonomous car or driverless car)
What is a self-driving car?
A self-driving car -- sometimes called an autonomous car or driverless car -- is a vehicle that uses a combination of sensors, cameras, radar and artificial intelligence (AI) to travel between destinations without a human operator. To qualify as fully autonomous, a vehicle must be able to navigate without human intervention to a predetermined destination over roads that haven't been adapted for its use.
Self-driving cars have the potential to bring many changes to future roadways and transportation industries. They could potentially, for example, reduce traffic congestion; lower the number of accidents; and enable new self-driving, ride-hailing and trucking services.
Companies developing and testing autonomous cars include Audi, BMW, Ford, Google, General Motors, Tesla, Volkswagen and Volvo. Waymo, Google's parent company Alphabet Inc.'s self-driving car test project, involves a fleet of self-driving cars, including a Toyota Prius and an Audi TT, navigating hundreds of thousands of miles on streets and highways.
How self-driving cars work
AI technologies power self-driving car systems. Developers of self-driving cars use vast amounts of data from image recognition systems, along with machine learning and neural networks, to build systems that can drive autonomously.
Neural networks identify patterns in the data, which are fed to machine learning algorithms. That data comes from a collection of sensors, including radar, lidar -- light detection and ranging, a remote sensing method that measure ranges -- and cameras. These sensors collect data the neural network uses to learn to identify traffic lights, trees, curbs, pedestrians, street signs and other parts of a given driving environment.

The self-driving car builds a map of its environment to understand its relative surroundings and begins its path planning. It must determine the safest and fastest routes to its destination while following traffic rules and implementing obstacle avoidance. A concept called geofencing, which helps vehicles with self-driving features navigate within predefined boundaries, is also used.
Geofencing in cars refers to the use of a Global Positioning System (GPS) or other location-based technology to create virtual boundaries, or geofences, around specific geographic areas. These boundaries can trigger automated actions or alerts when a vehicle enters or exits the defined area. In automotive applications, geofencing is often used for fleet management, vehicle tracking and driver safety enhancement.
As an example, Waymo uses a mix of sensors, lidar and cameras, combining all the data those systems generate to identify everything around the vehicle and predict what those objects might do next. This happens in fractions of a second. Maturity is important for these systems; the more the system drives, the more data it can incorporate into its deep learning algorithms, helping it make more nuanced driving decisions.
The following outlines how Waymo vehicles work:
- The driver or passenger sets a destination. The car's software calculates a route.
- A rotating, roof-mounted lidar sensor monitors a 60-meter range around the car and creates a dynamic three-dimensional (3D) map of the car's current environment.
- A sensor on the left rear wheel monitors sideways movement to detect the car's position relative to the 3D map.
- Radar systems in the front and rear bumpers calculate distances to obstacles.
- AI software in the car is connected to all the sensors and collects input from Google Street View and video cameras inside the car.
- AI simulates human perceptual and decision-making processes using deep learning and controls actions in driver control systems, such as steering and brakes.
- The car's software consults Google Maps for advance notice of landmarks, traffic signs and lights.
- An override function is available to let a human take control of the vehicle.
Cars with self-driving features
The Waymo project is an example of a self-driving car that's almost entirely autonomous. It still requires a human driver to be present, but only to override the system when necessary. It isn't self-driving in the purest sense, but it can drive itself in ideal conditions and has a high level of autonomy.
Many cars today aren't fully autonomous due to several technological, regulatory and safety concerns. For example, while many people give credit to Tesla for pushing toward self-driving cars, and even though many Tesla cars have self-driving features, they still face challenges, including technological complexity, sensor limitations and safety issues.
Many of the cars available to consumers today have a lower level of autonomy but still have some self-driving features. Self-driving features that are available in many production cars include the following:
- Hands-free steering centers the car without the driver's hands on the wheel. However, the driver is still required to pay attention.
- Adaptive cruise control (ACC) automatically maintains a selectable distance between the driver's car and the car in front of them.
- Lane-centering steering intervenes when the driver crosses lane markings by automatically nudging the vehicle toward the opposite lane marking.
- Self-parking uses the car's sensors to automatically steer, accelerate and guide the car into a parking space with minimal or no driver input.
- Highway driving assist combines ACC and lane-centering assist while on a highway.
- Lane-change assist monitors a vehicle's surrounding traffic to help the driver safely change lanes. This feature either provides alerts or automatically steers the vehicle when safe.
- Lane departure warning (LDW) alerts the driver if the vehicle starts to change lanes without signaling.
- Summon is a feature in Tesla vehicles that can autonomously navigate out of a parking space and come to the driver's location.
- Evasive-steering assist automatically steers the vehicle to aid the driver in avoiding an imminent collision.
- Automatic emergency braking (AEB) detects imminent collisions and applies the brakes with the goal of preventing an accident.
Examples of car manufacturers that offer a mix of these autonomous technologies and driver assistance technologies include the following:
- Audi's Traffic Jam Assist feature helps drivers in heavy traffic by taking over steering, acceleration and braking.
- General Motors' Cadillac brand offers Super Cruise for hands-free driving on highways.
- Genesis learns the driver's preferences and implements autonomous driving that mirrors these mannerisms.
- Tesla's Autopilot feature provides drivers with LDW, lane-keep assist, ACC, park assist, Summon and advanced self-driving capabilities.
- Volkswagen IQ Drive with Travel Assist includes lane-centering and ACC.
- Volvo's Pilot Assist system provides semi-autonomous driving, lane-centering assist and ACC.
Levels of autonomy in self-driving cars
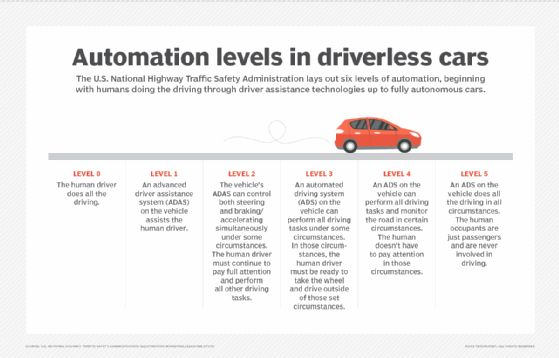
The Society of Automotive Engineers, commonly referred to as SAE, lays out the following six levels of driving automation as follows:
- Level 0: No driving automation. The driver performs all driving operations.
- Level 1: Driver assistance. This level enables driver assistance, where the vehicle can help with steering, accelerating and braking, but not simultaneously. The driver must also stay engaged.
- Level 2: Partial driving automation. This level includes partial automation, where two or more driving automated functions can work at once. The vehicle can control steering, accelerating and braking, but the driver must stay vigilant and be ready to regain control at any moment.
- Level 3: Conditional driving automation. The vehicle can drive itself in select scenarios. It can perform all driving tasks in scenarios like driving on stretches of specific highways. The driver is still required to take control when needed.
- Level 4: High driving automation. The vehicle can self-drive in certain scenarios without driver input. Driver input is optional in these scenarios.
- Level 5: Full driving automation. The vehicle can self-drive under all conditions without any driver input.
The U.S. National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) defines a similar level of driving automation.
Uses for autonomous vehicles
As of 2024, carmakers have reached Level 4. Manufacturers must clear a variety of technological milestones, and several important issues must be addressed before fully autonomous vehicles can be purchased and used on public roads in the U.S. Even though cars with Level 4 autonomy aren't available for public consumption, they're being used in other ways.
For example, Waymo partnered with Lyft to offer a fully autonomous commercial ride-sharing service named Waymo One. Riders can hail a self-driving car to bring them to their destination and provide feedback to Waymo. The cars still include a safety driver in case the ADS needs to be overridden. The service is available in the Phoenix metropolitan area; San Francisco; Los Angeles; and Austin, Texas.
Autonomous street-sweeping vehicles are also being produced in China's Hunan province, meeting the Level 4 requirements for independently navigating a familiar environment with limited novel situations.
Projections from manufacturers vary on when Level 4 and 5 vehicles will be widely available. A successful Level 5 car must be able to react to novel driving situations as well as or better than a human can. Likewise, roughly 30 U.S. states have passed legislation on self-driving vehicles. Laws vary in scope by state, but they tend to cover aspects such as testing, deployment, liability and regulation of autonomous vehicles.
The pros and cons of self-driving cars
Self-driving cars are a culmination of different technical complexities and achievements that continue to improve over time. They also come with many expected and unexpected benefits and challenges.
Benefits of autonomous cars
The top benefit touted by autonomous vehicle proponents is safety. A U.S. Department of Transportation and NHTSA statistical projection of traffic fatalities for 2022 estimated that 40,990 people died in motor vehicle traffic accidents that year -- of those fatalities, 13,524 were alcohol-related. Autonomous cars can remove risk factors such asas drunk or distracted driving from the equation. But self-driving cars are still vulnerable to other factors, such as mechanical issues, that cause crashes.
In theory, if the roads were mostly occupied by autonomous cars, traffic would flow smoothly and there would be less traffic congestion. In fully automated cars, the occupants could do productive activities while commuting to work. People who can't drive due to physical limitations could find new independence through autonomous vehicles and would have the opportunity to work in fields that require driving.
Autonomous trucks have been tested in the U.S. and Europe to let drivers use autopilot over long distances, freeing the driver to rest or complete tasks as well as improving driver safety and fuel efficiency. This initiative, called truck platooning, is powered by ACC, collision avoidance systems and vehicle-to-vehicle communications for cooperative ACC.
Disadvantages of self-driving cars
The downsides of self-driving technology could be that riding in a vehicle without a driver behind the steering wheel might be unnerving, at least at first. But as self-driving capabilities become commonplace, human drivers could become overly reliant on the autopilot technology and leave their safety in the hands of automation, even when they should act as backup drivers in case of software failures or mechanical issues.
With this being said, a Forbes survey found that self-driving vehicles are currently involved in twice as many accidents per mile when compared to other vehicles.
In one example from 2022, Tesla was criticized because of a video of a Tesla car crashing into a child test dummy during an auto-break test. In addition, there have been numerous reports of Tesla cars getting into crashes that involved full self-driving. One example happened in 2023, when a student stepping off a bus was hit by a Tesla Model Y that was in full self-driving mode. Although the student initially had life-threatening injuries, they were upgraded to good condition a few days after the crash.
Other challenges of self-driving cars also include the cost to produce and test these vehicles as well as the ethics involved in them being programmed to react a certain way in different situations.
Weather conditions can also be considered a challenge. The sensors on some vehicles that are used to collect environmental data might be obstructed by dirt or have their view blocked by heavy rain, snow or fog.
Self-driving car safety and challenges
Autonomous cars must learn to identify countless objects in the vehicle's path, from branches and litter to animals and people. Other challenges on the road include tunnels that interfere with the GPS, construction projects that cause lane changes or complex decisions, like where to stop to allow emergency vehicles to pass.
The systems need to make instantaneous decisions on when to slow down, swerve or continue normal acceleration. This is a continuing challenge for developers, and there are reports of self-driving cars hesitating and swerving unnecessarily when objects are detected in or near the roadways.
This problem was evident in a fatal accident in March 2018, which involved an autonomous car operated by Uber. The company reported that the vehicle's software identified a pedestrian but deemed it a false positive and failed to swerve to avoid hitting her. This crash caused Toyota to temporarily cease testing self-driving cars on public roads but, instead, continue evaluating them in its test facility. The Toyota Research Institute created a new test facility on a 60-acre site in Michigan to further develop automated vehicle technology.
With crashes also comes the question of liability, and lawmakers have yet to define who is liable when an autonomous car is involved in an accident. There are also serious concerns that the software used to operate autonomous vehicles can be hacked, and automotive companies are working to address cybersecurity risks.
In the U.S., carmakers are subject to Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards, which NHTSA issues and regulates.
In China, carmakers and regulators are adopting a different strategy to meet standards and make self-driving cars an everyday reality. The Chinese government is redesigning urban landscapes, policy and infrastructure to make the environment more friendly for self-driving cars. This includes writing rules about how humans move around and recruiting mobile network operators to take on a portion of the processing required to give self-driving vehicles the data they need to navigate. The autocratic nature of the Chinese government makes this possible, which bypasses the litigious democracy that tests are funneled through in the U.S.
History of self-driving cars
The path toward self-driving cars began with incremental automation features for safety and convenience before 2000 with cruise control and antilock brakes. After the turn of the millennium, advanced safety features, including electronic stability control, blind-spot detection and collision and lane shift warnings, became available in vehicles. Between 2010 and 2016, advanced driver assistance capabilities such as rearview video cameras, automatic emergency brakes and lane-centering assistance emerged, according to NHTSA.
Since 2016, self-driving cars have moved toward partial autonomy, with features that help drivers stay in their lane as well as ACC technology and the ability to self-park.
In September 2019, Tesla released its Smart Summon feature, which enabled Tesla vehicles to navigate parking lots and come to the owner's location without anyone inside the car. In November 2022, Tesla announced that its Full Self-Driving feature was in beta. Although now out of beta testing and still named Full Self-Driving, it isn't a true self-driving feature, as it's only a Level 2 autonomous system. It provides advanced driver assistance features but still requires the driver to always remain attentive.
Today, modern cars are being released with features that include ACC, AEB, LDW, self-parking, hands free-steering, lane-centering, lane change assist and highway driving assist. Fully automated vehicles aren't yet publicly available and might not be for many years. In the U.S., NHTSA provides federal guidance for introducing a new ADS onto public roads. As autonomous car technologies advance, so will the department's guidance.
In June 2011, Nevada became the first jurisdiction in the world to allow driverless cars to be tested on public roadways. California, Florida, Ohio and Washington, D.C., have followed in the years since. Roughly 30 U.S. states have now passed legislation on self-driving vehicles.
The history of driverless cars technically goes back much further than that, however. Leonardo da Vinci designed the first prototype around 1478. Da Vinci's "car" was designed as a self-propelled robot powered by springs, with programmable steering and the ability to run preset courses.
Self-driving cars are complex and contain many interconnected systems. Learn how AI assists in driving for autonomous vehicles.





