test-driven development (TDD)
What is test-driven development (TDD)?
Test-driven development (TDD), also called test-driven design, is a software programming method that interlaces unit testing, programming and refactoring on source code. The primary aims of TDD are to help teams accelerate development and deliver better-quality software.
Kent Beck, an American software engineer, developed TDD in the early 1990s as part of extreme programming, which he also developed. XP is a part of the Agile software development methodology that development teams worldwide have adopted with great results.
TDD applies Agile principles that are largely oriented to shortening the development cycle.
TDD is a feedback-driven, test-first development approach in which unit test cases are created even before the code is developed.
In TDD, the testing process drives the development process, which means developers only have to write new code -- or modify existing code -- if the unit tests fail. If the test fails, they rewrite the code to pass the test. This test-driven approach prevents test script duplication and helps teams create more optimized, resilient code and, ultimately, better-quality software.
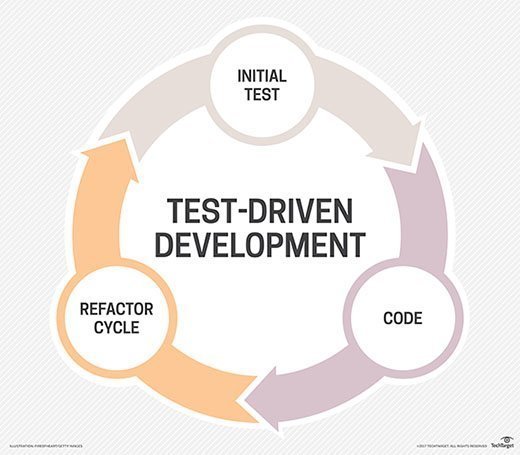
Steps in the TDD approach
TDD follows a systematic Agile approach that determines how development work occurs.
Before any new code is written, the programmer must first create a failing unit test. Then, the programmer -- or pair or mob -- creates just enough code to satisfy that requirement. Once the test passes, the programmer may clean up the code and refactor the design, making improvements without changing its behavior.
Here's how the TDD process goes:
- Write a list of test cases.
- Write a test for any new functionality, feature, or change that is to be added to the software.
- Make sure the test fails.
- Write the code until the test passes.
- Run the test cases again, and refactor the code to remove duplication and improve its structure.
- Deploy code.
- Repeat the process throughout development.
TDD vs. other development approaches
The most obvious difference between TDD and older development approaches is the order of development and testing. In TDD, tests are created before the code, while, in older methods, testing only happens after the code is developed. Having the tests known upfront improves first-time quality.
TDD focuses on programmer interactions at the unit level. There are other popular methods, such as acceptance test-driven development (ATDD) or behavior-driven development (BDD), which focus on tests customers can understand. These methods involve collaboration between the technical staff and customer to create concrete examples as tests before the code is created and then run the tests after the code is created to demonstrate that the code is implemented.
ATDD and BDD require developers, testers and the business side to collaborate to imagine and discuss the software and its implications before code is created. In contrast, TDD only requires development and testing teams to collaborate on creating test cases and updating code as development progresses.
TDD advantages
TDD can produce high-quality applications faster than is possible with older methods. This is because the tests provide constant feedback that development teams can immediately check and address to improve code quality.
Unlike traditional development approaches, TDD is an iterative approach that works in smaller, more manageable steps, enabling teams to keep testing the code and continuously improve quality of the code and, ultimately, the final output. They can add and test new functionalities as needed, even in the later stages of development. TDD also removes the need to recreate extensive test scripts. The tests are already created before development starts.
Proper implementation of TDD requires the developers and testers to accurately anticipate how the application and its features will work in the real world. If they can do this, TDD can help ensure that the application successfully meets its defined requirements and operates as expected.
TDD creates a test suite as a byproduct that can minimize human manual testing, while finding problems earlier, leading to quicker fixes. The methodical nature of TDD and its focus on testing small units of code at a time ensure much higher test coverage and first-time quality than classic phased code-test-fix-retest cycles.
Also, because tests start from the onset of the design cycle, TDD helps to identify errors and bugs early, which can simplify and accelerate debugging, while lowering its costs. TDD also simplifies code maintenance and helps to create a more flexible and resilient codebase.
Finally, teams looking to adopt TDD can choose from multiple unit testing frameworks, depending on their requirements and skill sets. For example, they can use PyUnit to test Python projects and csUnit for Microsoft .NET projects. Frameworks are also available for unit testing projects written in Java, Ruby and other programming languages.
Disadvantages of TDD
TDD may not be suitable for large or complex projects where it's difficult -- and, sometimes, impossible -- to test code in small steps before it can be integrated into the system.
TDD requires considerable skill to be successful, especially at the unit level. Many legacy systems are not created with unit testing in mind, making isolation of components to test impossible.
Many programmers lack the skills to isolate and create clean code. Everyone on the team needs to create and maintain the unit tests, or else they get out of date quickly. An organization looking at TDD needs to slow down a bit now to go faster later.
Finally, as with any method, TDD final results are only as good as the tests used, the thoroughness with which they have been done and the extent to which they mimic conditions likely to be encountered by users of the final product.
Learn about the fundamentals, and explore examples to see how test-driven development can benefit programmers.







