USART (universal synchronous/asynchronous receiver/transmitter)
What is a USART (universal synchronous/asynchronous receiver/transmitter)?
A USART (universal synchronous/asynchronous receiver/transmitter) is hardware that enables a device to communicate using serial protocols. It can function in a slower asynchronous mode, like a universal asynchronous receiver/transmitter (UART), or in a faster synchronous mode with a clock signal. USARTs are no longer common in consumer PCs but are still used in industrial equipment and embedded systems.
USART vs. UART
A UART device can use asynchronous communication protocols. A USART device can use both asynchronous and synchronous communication protocols. Therefore, a USART can do anything a UART can do and more. Because a USART requires more complex circuitry and more communication lines to fully implement, many devices may only implement a UART to save on cost, complexity or power usage.
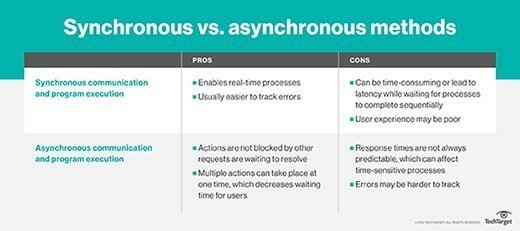
Asynchronous and synchronous serial communication
In serial communication, each bit of data is sent one at a time on a transmit wire. This is a serial communications interface. If the sender and the receiver don't agree on how the data is sent, such as the order and length of time of each bit, then the data becomes garbled, and they won't understand each other. Asynchronous and synchronous are two different ways to standardize how serial data is sent.
Asynchronous serial data
In asynchronous mode, only one data line is used to send data from the transmitter to the receiver. There is no shared synchronization signal from the sender to the receiver. So, the receiver has no way to know how fast or slow the data is coming. To circumvent this, both the sender and receiver must be manually configured beforehand to use the same data rate. A common shared baud rate is 9,600 bits per second.
Even sharing a common bit rate, it is possible for the devices to become slightly out of sync. Therefore, extra bits are added to each packet of data to ensure reliable transmission. A start and stop bit are almost always added to indicate each packet. Often, a parity bit is also added to indicate small errors. Adding these extra bits causes asynchronous communication to be less efficient.
The following are some example asynchronous serial protocols:
Synchronous serial data
In synchronous mode, a data and a clock line are used to send the data. The controller sends a clock signal, which synchronizes the controller and the peripheral at the same data rate. Because the clock signal keeps the devices in sync, the two devices don't need to be configured ahead of time to use the same bit rate.
Using a clock signal also removes the need to have extra start and stop bits. All the data can be sent continuously without pause. It also enables much faster bit rates as the sender doesn't need to worry about the receiver being able to keep up or get out of sync.
The following are some example synchronous protocols:
- Serial Peripheral Interface
- Inter-Integrated Circuit
- Controller Area Network
Current USART use
USARTs are no longer common for desktop computers, but they are still heavily used in industrial and embedded devices.
In the past, a USART was common in desktop PCs; it would control the serial port. The serial port would often be a DB9 connector on the rear of the computer. The serial port was used to connect to modems, mice and other peripherals. With the introduction of the much faster USB standard with autoconfiguration and plug and play, the serial port fell out of use. Most recent desktops no longer include a serial port.
A USART is still common in embedded and industrial systems, however. Many control systems still use serial communications to control equipment; programmable logic controllers; robotics; and heating, ventilation and air conditioning systems. A USART is also part of most microcontrollers to communicate with peripheral systems. Internet of things devices may have a USART to communicate with other devices.
See how CPU, GPU and DPU differ from one another, check out best practices for data center network optimization, explore the many components of modern storage infrastructure management and learn the differences between synchronous vs. asynchronous communications.
