What is open source and how does it work?
The term open source refers to any program whose source code is made available for use or modification as users or other developers see fit.
Unlike proprietary software, open source software is computer software that is developed as a public, open collaboration and made freely available to the public.
The following are several frequently asked questions (FAQs) about open source software.
Who uses open source software?
Software programmers and application developers are the primary users of open source software. Depending on the software selected, developers can use the open source code, programming language and operating system to create new applications and other resources (e.g., web pages) without the need to obtain proprietary software (typically called closed source software) and their proprietary licenses. While open source software licenses must be approved, the flexibility of open source software ensures that apps can be created for a nominal investment and tailored to an organization's needs.
What is the history of open source software?
During the early years of software development, programmers would often share software in order to learn from one another and grow the field of computer programming.
This spurred the creation of the Free Software Foundation (FSF) and included David Knuth's TeX typesetting program in 1979 and Richard Stallman's GNU operating system in 1983. In fact, the early web browser Netscape was a free software with source code that would later go on to help develop open source projects like Mozilla Firefox, a web browser that is still commonly used today.
As the free software movement progressed, the FSF was replaced by the Open Source Initiative (OSI) -- a group of software developers that creates software intended to be freely shared, improved and redistributed by others.
The open source movement has not been without its detractors. For example, Microsoft Windows executive Jim Allchin stated in 2001 that the OSI was an "intellectual property destroyer."
Today, however, Microsoft and many others have joined the free and open source community in various ways. This has created a major shift in how open source software is viewed.
Some other open source project contributors, funders and nonprofits include the Linux Foundation, the WordPress Foundation, Creative Commons, the Android Open Source Project, Free Software Foundation, Open Source Software Institute, and the Mozilla Foundation.
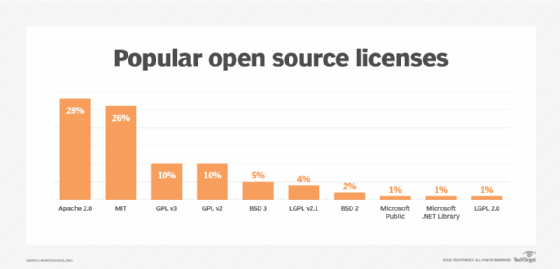
What are some examples of open source software licenses?
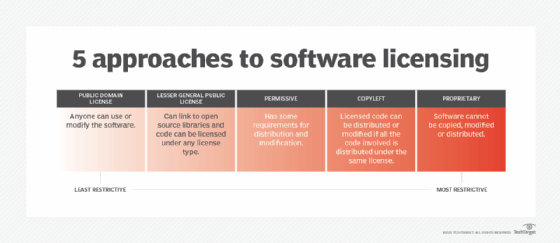
To summarize, the open source definition designates that:
- An open source software license is free of charge and redistribution is allowed to anyone without any restriction.
- The source code must be made available so that the receiving party will be able to improve or modify it.
- The license can require improved versions of the software to carry a different name or version from the original software.
- The software might be ported to a new operating system.
The image below lists some notable and widely used open source software licensing agreements that have adopted the definition of open source in recent years:
- The Apache web server license.
- The Berkeley Software Distribution license.
- The GNU General Public License.
- The Massachusetts Institute of Technology License.
- The Mozilla Public License.
- The Microsoft .NET Framework.
- Microsoft Visual Studio Code.
How is open source used in software development?
As mentioned previously, open source has played a large role in the software development community. In fact, a generation of open source tools has been developed and it is used today by developers specifically to help them improve and troubleshoot issues with open source code during the early days of a software product's development.
Some examples include the following:
- Eclipse.
- GitHub.
- Launchpad.
- NetBeans.
- SourceForge.
What are some other open source products?
Open source technology is not limited to software development tools. Following are examples of other popular open source software types tools and business applications:
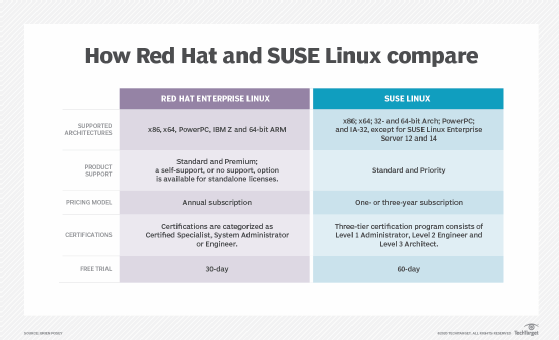
- Red Hat Software. An open source software platform, and IBM derivative, Red Hat provides a variety of enterprise-level productivity applications.
- LibreOffice. An open source office productivity suite, LibreOffice is similar to Microsoft Office programs.
- GNU Image Manipulation Program (GIMP). A GNU open source image manipulation tool with similar components to Adobe Photoshop.
- VLC Media Player. An open source audio and video file player.
What are the pros and cons of open source software?
While open source licenses have made software generally more affordable and contributed immensely to the growth of software development, its widespread use is considered by many to be negative.
This criticism often is focused on the lack of regulation that can open the door to numerous legal issues.
Furthermore, determining what should be open source and what should be closed source software remains a difficult and hotly debated topic.
In trying to settle the debate, the open source community has taken to implementing classification schemes -- typically, dependent upon copyleft provisions in order to determine appropriate use cases for the open source software development model.

In 2008, a U.S. federal appeals court determined that OSS licenses must have legally binding requirements for any use of copyrighted material.
Should end users violate these open standards, they will lose their license and, therefore, be in violation of the copyright infringement standard, similar to if they used a proprietary license without authorization.
The impact of AI on the future of open source
The long-term prospects of open source software are good; the impact of artificial intelligence (AI) on the concept improves its value. Availability of open source AI systems brings the performance of AI to a broader audience.
When using open source AI in the course of developing a new software ecosystem, AI can streamline development and foster innovation, while supporting the open source community and enabling economic growth.
Examine the future of AI and open source software and importance and limitations of open source AI models. Learn about the advantages of open source for business applications. Explore open source databases to consider and open source PaaS options developers should know.