What is web application (web apps) and its benefits?
A web application (web app) is an application program that is stored on a remote server and delivered over the internet through a browser interface. Web services are web apps by definition and many, although not all, websites contain web apps.
Developers design web applications for a wide variety of uses and users, from an organization to an individual for numerous reasons. Commonly used web applications can include webmail, online calculators, social networking or e-commerce shops. While users can only access some web apps by a specific browser, most are available no matter the browser.
Unlike traditional desktop applications that are installed on a computer, web apps can be used on any device with a web browser, including smartphones, tablets and desktops.
What is the difference between web applications and websites?
There can be confusion among users between a web app and a website since both are accessed through web browsers and require an internet connection. However, they serve different purposes. Websites are primarily for information dissemination, whereas web applications are designed for user interaction and functionality.
A web application enables users to interact with the content and perform specific tasks. It often includes functionalities such as data processing, user authentication and real-time updates. Examples include online banking systems, social media platforms and e-commerce sites.
On the other hand, a website is a collection of interconnected web pages that provide users with information and content. Websites are primarily static, meaning the content does not change frequently and is mainly for viewing and reading. Examples include blogs, news sites and informational pages, such as a restaurant's menu or hours of operation.
How web applications work
Web applications do not need to be downloaded since they are accessed through a network and work in a client-server model. Users can access a web application through a web browser, such as Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox or Safari.
For a web app to operate, it needs a web server, application server and database. Web servers manage the requests that come from a client, while the application server performs the requested task. A database stores any necessary information.
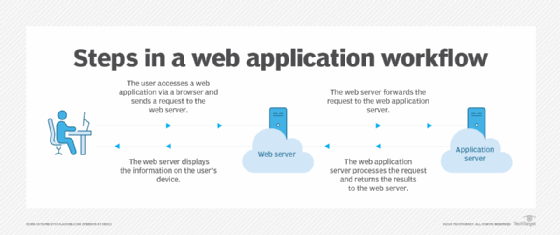
Here are typical steps that are involved in the workings of a web application:
- The user opens a web application through a browser or app on their mobile device, sending a request to the web server over the internet. This involves the request potentially passing through various data security measures, such as firewalls and load balancers.
- The web server forwards the request, such as querying a database, to the web application server. The web application server processes the task and generates the results.
- The web application server sends the results back to the web server.
- The web server delivers the information to the user's device, displaying it on their screen.
Web applications typically have short development cycles and small development teams. Developers write most web apps in JavaScript, HTML5 or CSS. Client-side programming typically utilizes these languages, which help build an application's front end. Server-side programming creates the scripts a web app will use. Languages such as Python, Java and Ruby are commonly used in server-side scripts or programming.
Examples of web applications
A wide variety of web applications exist, each designed to meet specific needs. Here are some examples from various categories:
- Webmail. Webmail apps are used by both personal and enterprise users to access their emails and often include other communication tools such as video meetings and instant messaging tools. Gmail by Google is an example of a webmail application.
- E-commerce. Amazon.com is an example of an e-commerce web application that enables users to browse, search and pay for products online. Etsy is another example of an e-commerce platform where users can sell and buy vintage and handmade goods.
- Online banking. Personal and business users utilize online banking web apps to access their accounts and other financial products. PayPal is an example of a web app as it's an online payment system for transactions and money transfers. Another example is Venmo, which is a mobile app that enables users to send and receive payments, split bills and make purchases.
- Workplace collaboration. Web apps for workplace collaboration enable team members to access shared calendars, documents, business instant messaging services and other enterprise tools. Examples include Microsoft Teams, Zoom, Slack and Google Drive.
- Social media. Meta, TikTok and X (formerly Twitter) are examples of social media web applications.
- Content management systems. Content management systems (CMS) are an example of a web application. Common CMS examples include WordPress, Drupal and Joomla.
- Project management tools. Project management applications, such as Trello and Asana, help teams organize tasks, track progress and collaborate on projects effectively.
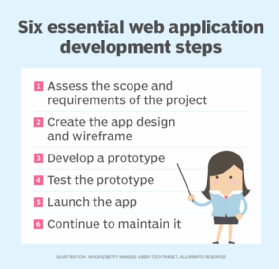
What are the benefits of web applications?
Web applications have many benefits. Some common benefits include the following:
- Compatibility with multiple platforms. Multiple users can access the same version of a web application from various browsers and across different devices, such as desktops, mobile phones and laptops.
- Low maintenance. Users of a web app don't need to install the app and, therefore, don't need to maintain it. Web apps receive automatic updates which ensure they're always up to date and less prone to security breaches.
- Scalability. Web applications can easily scale to accommodate growing user bases or increased data loads. This flexibility enables businesses to expand their services without significant infrastructure changes.
- Enhanced security. Many web applications incorporate advanced security measures, such as encryption and secure user authentication to protect sensitive data.
- Improved collaboration. Many web applications support real-time collaboration. This enables multiple users to work on the same project simultaneously and can be very useful for teams that are geographically dispersed.
- Cost-effective development. Web application development can be more cost-effective compared to traditional desktop applications as they often require less initial investment and can be easier to maintain and update. For example, a single version can operate seamlessly across all modern browsers and devices, removing the need to produce multiple iterations for different browser platforms.
What are the cons of web applications?
While web applications offer many benefits, they also come with certain drawbacks including the following:
- Dependence on internet connectivity. Web applications require a stable internet connection to function effectively. For example, if the internet is slow or unavailable, users can experience disruptions or not be able to access the application altogether.
- Performance limitations. Due to their reliance on web browsers and internet speed, web apps can have slower performance compared to other native applications. This can affect user experience, especially for resource-intensive tasks.
- Security issues. Although web applications can enforce strong security measures, they are still vulnerable to various online threats, such as hacking and data breaches. Sensitive information transmitted over the internet can be at risk if not properly secured.
- User experience. While many web applications are designed to be user-friendly, they don't always provide the same experience as native apps, especially when it comes to responsiveness and user interface design.
- Limited functionality. Some web applications don't offer the same level of functionality as native applications, particularly when it comes to accessing device-specific features, such as GPS, camera or offline capabilities. This can limit their usability in certain contexts.
What is a progressive web app (PWA)?
A progressive web app (PWA) is a type of application that is built using standard web technologies such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, but provides a user experience similar to that of a native mobile app. PWAs are designed to work on any device and browser, making them highly accessible and versatile.
While web apps typically lack native functionalities such as push notifications and offline access, PWAs provide these features. However, the drawback of PWAs is that they're only compatible with Google Chrome which excludes Apple iOS users and might not work for all business types.
Web app vs. native app vs. hybrid app
The choice between web, native and hybrid apps depends on various factors, including budget, target audience and specific use cases of an organization.
Within the mobile computing sector, web apps are sometimes contrasted with native apps, which are applications developers build specifically for a particular platform or device and install on that device typically from an app store. Native apps can commonly make use of device-specific hardware, such as a GPS or camera on a mobile native app.
With web apps, user interactions are restricted to what web browsers support. For example, while they might provide feature-rich designs, they cannot access device functions. In contrast, native mobile apps enable direct interaction with a device's internal hardware and operating systems.
Programs that combine the two approaches are sometimes referred to as hybrid applications. Hybrid apps work similarly to web apps but install to the device as a native app would. Hybrid apps can also take advantage of device-specific resources by using internal application programming interface (APIs). Downloaded native apps can sometimes operate offline; however, hybrid apps don't have this functionality. A hybrid app will typically share similar navigation elements to a web app since they are primarily based on web apps.
Explore popular languages and discover their key features. Learn how to choose the right language to enhance your application programming skills and career potential.







