resolution
What is resolution?
Resolution is a measurement of the number of pixels -- picture elements or individual points of color -- that can be contained on a display screen or in a camera sensor. In practical terms, resolution describes the sharpness, or clarity, of an image or picture. It is expressed in terms of the number of pixels that can be displayed both horizontally and vertically.
Resolution is an important factor to measure the visual quality of digital images, photos and videos. A higher resolution signifies the picture contains more pixels, which means it can display more visual information. As a result, a high-resolution picture is sharper and clearer than a low-resolution one.
Resolution is also used to assess the visual quality of various hardware devices:
- computer monitors,
- digital signage,
- TVs,
- mobile devices and
- printers.
Monitor size is another factor in image quality. An image displayed on a smaller monitor will appear sharper compared to the identical image on larger monitors with the same resolution. This happens because the pixels are spread over a larger number of inches, leading to a loss of clarity and sharpness. A smaller screen will have a higher number of pixels per inch (PPI) than a larger screen, so its image will be sharper and more vivid. Due to this phenomenon, larger screens need higher resolutions to preserve image quality.
Resolution expressed: Displays, printers and audio
In most displays and digital images, resolution is expressed as PPI, which refers to the number of pixels that can be displayed over one inch of the screen or display. A high PPI means there are more pixels in every inch, which results in a higher resolution and a crisper image. If the image has a low PPI, it results in a blurry, blocky or pixelated image that's difficult to see and interpret.
For printers, resolution is usually expressed as dots per inch (DPI), which refers to the number of dots produced in the printer's output. The smaller and finer the dots, the higher the DPI and the sharper the printout.
Consumer laser printers or inkjet printers have a much lower DPI than professional-grade printers. That's why the former aren't suitable for printing certain media, such as photographs, where high-quality output is required.
The term resolution is also used in digital audio. It refers to the number of bits or bit depth in the audio sample or digital recording. As with PPI and DPI, a higher bit depth correlates directly with the quality of the output.
Types of resolution
There are two types of resolution:
- Image resolution. Image resolution refers to the density of pixels in an image, expressed as PPI. This shouldn't be confused with image dimension, which is expressed as a measurement of the number of rows and columns of pixels an image contains, such as 640x480.
- Screen resolution. Display resolution or screen resolution expresses how many pixels are present in a display or entire screen. A given display will have a maximum resolution that depends on its physical ability to focus light. For example, a 15-inch 640x480 monitor will display approximately 50 dots per inch. A smaller display would have more PPI.
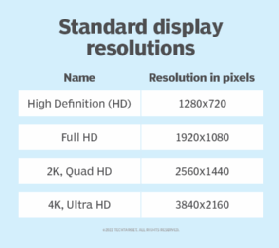
In general, screen resolution is the number of pixels a screen can show horizontally and vertically. So, a screen with a resolution of 1920x1080 -- 1080p or full HD -- can display 1,920 pixels horizontally and 1,080 pixels vertically.
In addition to its maximum resolution, a display can support several lower resolutions. For instance, a 1280x1023 display can also support 1024x768, 800x600 and 640x480 resolutions.
While applying the maximum resolution to a larger monitor may result in a sharper display, it doesn't necessarily translate to the same quality when used on a smaller screen. Icons and texts may appear too small on screens configured with a greater resolution than they are meant to accommodate. On the other hand, if the screen resolution is too low, it usually results in poor image quality.
Screen size vs. resolution
The terms screen resolution and screen size are sometimes used interchangeably. However, they are not the same. Screen resolution refers to the number of pixels and density, while screen size refers to the screen's physical dimensions. The latter is usually measured diagonally in inches, from one corner of the screen to the other.
Two displays with the same resolution can have different physical dimensions, which is why pixel density expressed in PPI is an important factor. The clarity of an image is affected by the screen size and not having enough pixels to go around.
Similarly, two monitors with the same screen size can have different resolutions. The screen with a higher number of pixels and greater PPI will have a better resolution than the same size screen with a lower number of pixels.
Image quality is also affected if two screens have the same resolution but different sizes. The smaller display of the same resolution will have more PPI, and show a clearer, more detailed image than the bigger display.
