JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group)
What is JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group)?
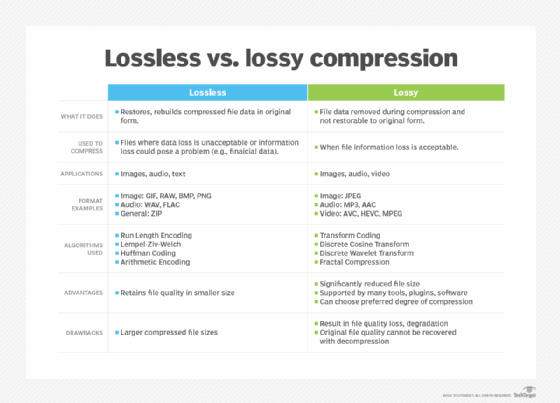
JPEG (pronounced JAY-peg) is a graphic image file compressed with lossy compression using the standard developed by the ISO/IEC Joint Photographic Experts Group. JPEG is one of the most popular image formats on the internet and is supported by most web browsers and image editing software.
How does a JPEG work?
JPEG images are compressed using a technique called discrete cosine transform (DCT). DCT is a mathematical algorithm that breaks down an image into a series of cosine functions. These functions are then compressed using a variety of techniques, such as quantization and Huffman coding.
The amount of compression that can be applied to a JPEG image depends on the quality setting. The higher the quality setting, the less compression is applied, and the larger the file size. The lower the quality setting, the more compression is applied, and the smaller the file size.
What are the benefits of using a JPEG?
There are many benefits to using JPEG, including the following:
- Small file size. JPEG images are typically much smaller than uncompressed images, which make them ideal for storing and transmitting images over the internet.
- Wide support. JPEG is supported by most web browsers and image editing software.
- Good quality. JPEG images can be of good quality, even with a high degree of compression.
What are the drawbacks of using a JPEG?
There are a few drawbacks to using JPEG, including the following:
- Lossy compression. Some data is lost during the compression process, which can lead to a loss of quality in the image.
- Not suitable for all images. JPEG is not suitable for all images. For example, it is not a good choice for images with sharp edges or fine details.

Some popular lossless compression-based image formats include PNG, GIF, RAW and BMP.
