What is ISO 27001?
ISO 27001, formally known as ISO/IEC 27001:2022, is an information security standard jointly created by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). It provides a risk-based framework and guidelines for establishing, implementing and managing an information security management system (ISMS).
According to its documentation, ISO 27001:2022 was developed to "provide a model for establishing, implementing, operating, monitoring, reviewing, maintaining and improving an information security management system." Once information security risks have been identified, the standard, plus its companion ISO/IEC 27002:2013 -- Code of practice for information security controls, provides the foundation for developing a resilient and compliant cybersecurity environment.
The specification includes details for documentation, management responsibility, internal audits, continual improvement, and corrective and preventive action. The standard requires cooperation among all sections of an organization. It also recommends the application of a risk management process as part of building the ISMS.
The goal of ISO 27001 is to help organizations protect their critical information assets and comply with applicable legal and regulatory requirements.
Organizations should apply the controls specified in ISO 27001 appropriately, in support of their specific risks. Third-party accredited certification is recommended for ISO 27001 conformance but not required as individual controls depend on the unique risks of each business.
Introduction to ISO 27001
ISO 27001 is technology-neutral and uses a top-down, risk-based approach. The specification defines a set of security controls that are divided into 14 sections, each containing specific requirements.
ISO 27001 also includes a set of control objectives and activities to help organizations reduce the risk of data breaches and other security incidents.
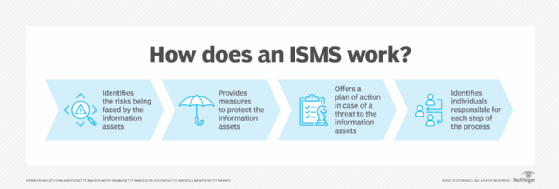
Organizations might use ISO 27001 as part of their overall information security strategy, or they can choose to be certified by an ISO-accredited certification body. ISO 27001 certification shows an organization's commitment to protecting its critical data assets and complying with applicable laws and regulations. Figure 1 depicts the elements of an ISMS.
The 14 phases of ISO 27001
ISO 27001 is the most widely adopted international information security standard and is used by organizations worldwide. By following ISO 27001, organizations can be confident their ISMSes are up to date and comply with best practices.
ISO 27001 provides a comprehensive framework that helps organizations develop and maintain a secure ISMS. It is divided into 14 phases:
- Information Security Policy.
- Organization of Information Security.
- Risk Assessment and Treatment.
- Asset Management.
- Access Control.
- Cryptography.
- Physical Security.
- Operations Security.
- Communications Security.
- System Acquisition, Development and Maintenance.
- Supplier Relationships.
- Compliance with Legal Requirements and Industry Standards.
- Information Quality Management.
- Risk Monitoring and Review.
Best practices for preparing for ISO 27001 certification
ISO 27001 is a powerful tool for organizations to use when creating a secure ISMS, but remember that it's a framework, not an inflexible set of rules. Many organizations strive for ISO 27001 compliance to demonstrate their commitment to a secure IT environment to their customers and prospects. However, compliance is not mandatory, as is the case with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
ISO 27001 and ISO 27002 must be studied, adapted and applied in the context of each organization's circumstances. ISO 27001 provides best practices and guidance, but it's up to each organization to develop its own ISO 27001-compliant information security system. ISO 27002 must be used along with ISO 27001 as it provides specific guidance on how to implement the controls defined in ISO 27001.
Organizations should find an ISO-accredited certification body to assess their ISO 27001 compliance and provide training on topics such as risk assessment, access control, cryptography, physical security, communications security and more. Organizations should also ensure they have sufficient resources to plan and implement ISO 27001-compliant processes and controls.
To facilitate the information gathering and documentation process associated with preparing for ISO certification, organizations can employ templates, consulting firms and/or software. Among the companies offering ISO 27001 compliance software tools are Drata, A-LIGN, Vanta, and Secureframe.
Getting prepared for ISO 27001 certification
Organizations can ensure they are properly prepared for ISO 27001 certification, positioned to protect their critical data assets, and compliant with applicable laws and regulations. This requires a specific set of actions:
- Step 1. Build an ISO 27001-compliant ISMS.
- Step 2. Identify risks and develop risk treatment strategies.
- Step 3. Implement ISO 27001-compliant processes and controls.
- Step 4. Have an ISO-accredited certification body assess compliance.
- Step 5. Monitor your ISO 27001 compliance regularly.
The ISO 27001 accreditation process is rigorous and can be expensive and time-consuming. Securing the services of an accreditation firm is important if an organization wishes to be officially certified. Included in the process are certification audits conducted by trained lead auditors, performance evaluations, documentation reviews, and demonstration of compliance with information security lifecycles.
By following ISO 27001 and ISO 27002, organizations can identify potential vulnerabilities, reduce the risk of data breaches and other security threats, provide data protection of their critical information technology assets, comply with applicable legal and regulatory requirements, and ensure business continuity following a cyberattack.
Other ISO standards in the 27000 family
The 27000 family of standards includes several topics directly supporting ISO 27001 and ISO 27002, along with other complementary security issues:
- ISO/IEC 27003 -- Planning and implementing an ISMS.
- ISO/IEC 27004 -- Monitoring and measuring cybersecurity and ISMS performance.
- ISO/IEC 27005 -- Implementing ISMS risk management activities.
- ISO/IEC 27006 -- Guidelines for organizations providing certification and auditing of a completed ISMS.
- ISO/IEC 27007 -- Conducting an ISMS audit.
- ISO/IEC 27008 -- Assessing the implementation and operation of security controls.
- ISO/IEC 27009 -- Guidelines for aligning ISO 27001 requirements to specific market segments and different technologies.
- ISO/IEC 27010 -- Guidance on implementing information security techniques for information-sharing groups in various market sectors.
Additional 27XXX standards include:
- ISO/IEC 27031 -- Provides guidance on IT disaster recovery as applicable to business continuity.
- ISO/IEC 27032 -- Guidelines for Internet security.
- ISO/IEC 27033 -- Guidance on network security.
- ISO/IEC 27034 -- Guidance on application security.
- ISO/IEC 27035 -- Guidance on information security incident management.
- ISO/IEC 27036 -- Guidance on managing risks relating to acquiring products and services from IT suppliers.
- ISO/IEC 27037 -- Guidelines for handling digital evidence.
Important information security standards
Many standards, regulations and frameworks were developed that may be considered in addition to or in lieu of ISO 27001. Here is a brief list of examples:
NIST. The National Institute for Standards and Technology has developed several important cybersecurity standards and frameworks. Among these are SP 800-53, the principal Federal government cybersecurity standard, and the Framework for Improving Critical Infrastructure Cybersecurity, also known as the NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF). Both can also be used in the private sector.
GDPR. The General Data Protection Regulation, released by the European Union (EU) in 2016, governs the protection of personal information processed in an EU member country, or companies doing business with EU member organizations.
COBIT. Developed by ISACA (Information Systems Audit and Control Association), Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies is a framework for IT management and governance.
FISMA. The Federal Information Security Modernization Act provides a security framework for protecting federal government data and systems. It can also be used in the private sector.
Pros and cons of ISO 27001 certification
Organizations of virtually any size and type can aim for ISO 27001 certification. It confirms that the organization is committed to providing a secure IT environment that protects company data. It also ensures that the organization has deployed sufficient controls and solutions to address all aspects of cybersecurity management and comply with relevant standards. Having a secure IT infrastructure and ISMS enhances business continuity and can reduce costs by preventing or mitigating cyberattacks.
Among the negatives are the complexities associated with compliance, the potential costs associated with securing accreditation, and possible cultural issues (e.g., employee resistance to cybersecurity activities) from implementing an ISMS. While these are not trivial considerations, nor are the risks the organization might face without having an ISMS or cybersecurity program.
Learn about the different types of cybersecurity controls and how to place them, and see how organizations can make educating their employees on cybersecurity risks interesting. Explore compliance and its related security concerns and common risk management failures and how to avoid them.